
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 Part 1: Equilibrium 10. Equilibrium electrochemistry
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 Part 1: Equilibrium 10. Equilibrium electrochemistry

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 2 This chapter is concerned with the description of the thermodynamic properties of reactions that take place in electrochemical cells. There are two major topics. One is for the definition and tabulation of standard potentials; the other is for the use of these standard potentials to predict the equilibrium constants of chemical reactions. 10. Equilibrium electrochemistry
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 2 This chapter is concerned with the description of the thermodynamic properties of reactions that take place in electrochemical cells. There are two major topics. One is for the definition and tabulation of standard potentials; the other is for the use of these standard potentials to predict the equilibrium constants of chemical reactions. 10. Equilibrium electrochemistry

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 3 The thermodynamic properties of ions in solution 10.1 Thermodynamic functions of formation 10.2 Ion activities Electrochemical cells 10.3 Half-reactions and electrodes 10.4 Varieties of cells 10.5 Standard potentials Applications of standard potentials 10.6 The electrochemical series 10.7 Solubility constants 10.8 The measurement of pH and pK 10.9 Thermodynamic functions from cell potential measurements 10. Equilibrium electrochemistry
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 3 The thermodynamic properties of ions in solution 10.1 Thermodynamic functions of formation 10.2 Ion activities Electrochemical cells 10.3 Half-reactions and electrodes 10.4 Varieties of cells 10.5 Standard potentials Applications of standard potentials 10.6 The electrochemical series 10.7 Solubility constants 10.8 The measurement of pH and pK 10.9 Thermodynamic functions from cell potential measurements 10. Equilibrium electrochemistry

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 4 10.1 Thermodynamic functions of formation 1) Standard functions of formation of ions The standard enthalpy and Gibbs energy of a reaction involving ions in solution are expressed in terms of standard enthalpies and Gibbs energies of formation, which can be used in exactly the same way as those for neutral compounds. The values of and refer to the formation of solutions of ions from the reference states of the parent elements. However, solutions of cations cannot be prepared without their accompanying anions. Δf o Δf G o H
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 4 10.1 Thermodynamic functions of formation 1) Standard functions of formation of ions The standard enthalpy and Gibbs energy of a reaction involving ions in solution are expressed in terms of standard enthalpies and Gibbs energies of formation, which can be used in exactly the same way as those for neutral compounds. The values of and refer to the formation of solutions of ions from the reference states of the parent elements. However, solutions of cations cannot be prepared without their accompanying anions. Δf o Δf G o H
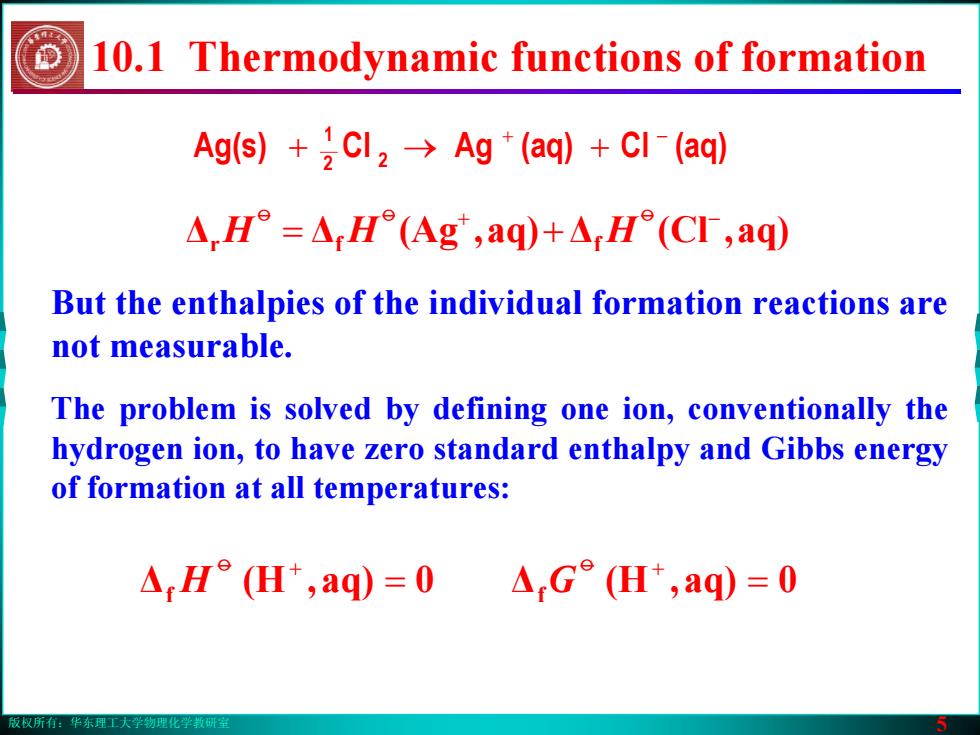
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 5 But the enthalpies of the individual formation reactions are not measurable. ΔΔ aq),(Ag Δ aq),(Cl r f f + − = + oo o HH H Ag(s) (aq)Cl(aq)AgCl 2 2 1 + − →+ + The problem is solved by defining one ion, conventionally the hydrogen ion, to have zero standard enthalpy and Gibbs energy of formation at all temperatures: 10.1 Thermodynamic functions of formation Δ 0aq),(H f = o + Δf = 0aq),(H G o + H
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 5 But the enthalpies of the individual formation reactions are not measurable. ΔΔ aq),(Ag Δ aq),(Cl r f f + − = + oo o HH H Ag(s) (aq)Cl(aq)AgCl 2 2 1 + − →+ + The problem is solved by defining one ion, conventionally the hydrogen ion, to have zero standard enthalpy and Gibbs energy of formation at all temperatures: 10.1 Thermodynamic functions of formation Δ 0aq),(H f = o + Δf = 0aq),(H G o + H