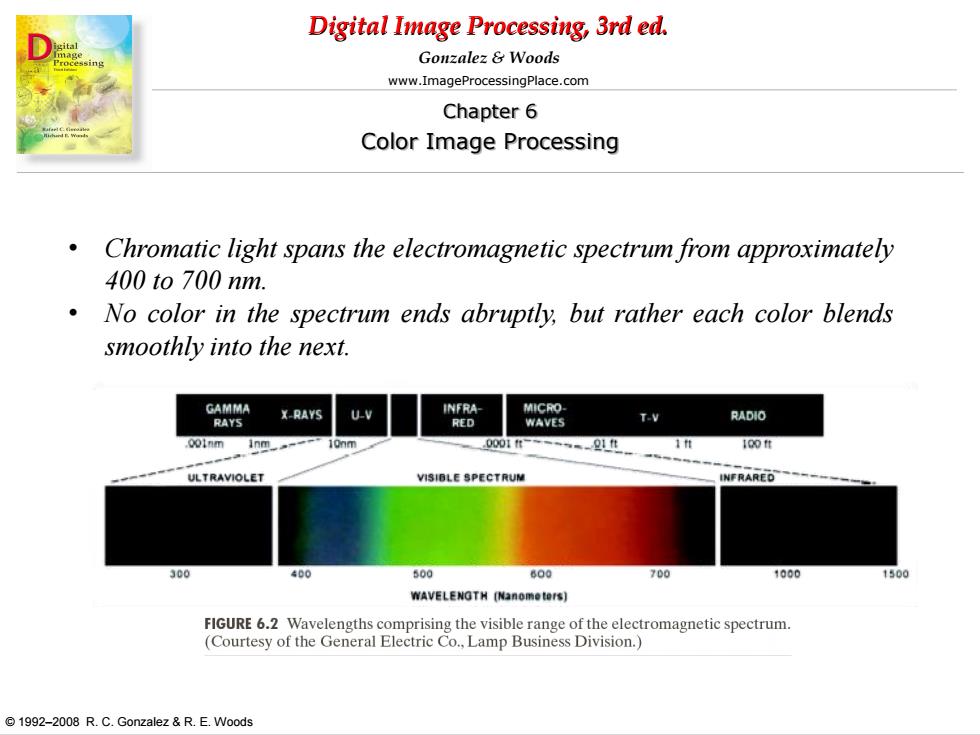
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez&Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Chromatic light spans the electromagnetic spectrum from approximately 400to700nm. 。 No color in the spectrum ends abruptly,but rather each color blends smoothly into the next. X-RAYS INFRA MICRO- T.V RADIO RED WAVES 001nm 0001t 100性 ULTRAVIOLET VISIBLE SPECTRUM NFRARED 300 400 500 600 700 1000 1500 WAVELENGTH [Nanometers) FIGURE 6.2 Wavelengths comprising the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. (Courtesy of the General Electric Co.,Lamp Business Division.) 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez &R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Chromatic light spans the electromagnetic spectrum from approximately 400 to 700 nm. • No color in the spectrum ends abruptly, but rather each color blends smoothly into the next

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Basic quantities to describe the quality of light source: Radiance:Total amount of energy that flows from the light source (in W). Luminance:A measure of the amount ofenergy an observer perceives from the light source (in Im) Brightness:A subjective descriptor that embodies the achromatic notion of intensity and is practical impossible to measure. 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Basic quantities to describe the quality of light source: Radiance: Total amount of energy that flows from the light source (in W). Luminance: A measure of the amount of energy an observer perceives from the light source (in lm) Brightness: A subjective descriptor that embodies the achromatic notion of intensity and is practical impossible to measure
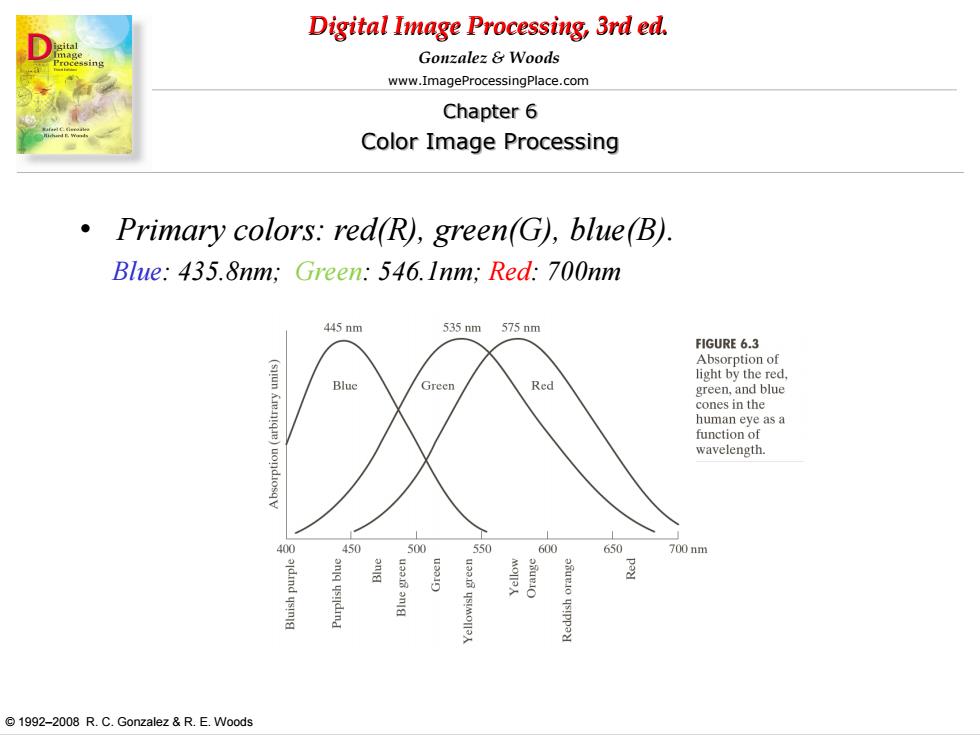
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez&Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Primary colors:red(R),green(G),blue(B) Blue:435.8nm;Green:546.Inm;Red:700nm 445nm 535nm 575nm FIGURE 6.3 Absorption of light by the red. Blue Green Red green,and blue cones in the human eye as a function of wavelength. 400 450 500 550 600 650 700nm 盖 ys!ppa 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez &R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Primary colors: red(R), green(G), blue(B). Blue: 435.8nm; Green: 546.1nm; Red: 700nm
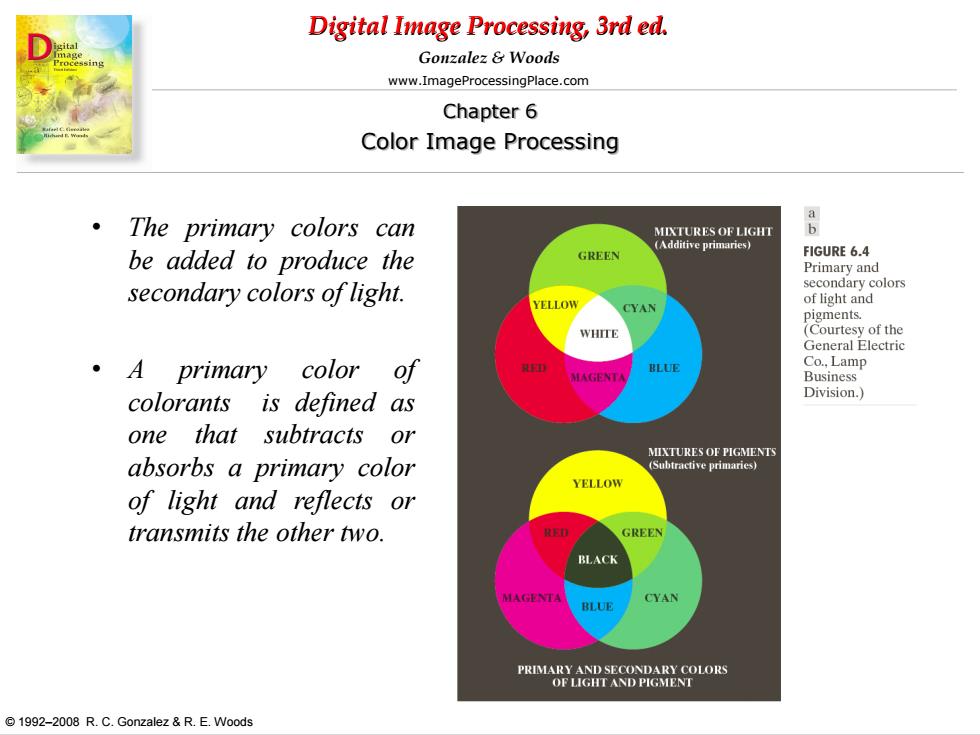
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing The primary colors can a MIXTURES OF LIGHT be added to produce the GREEN FIGURE 6.4 Primary and secondary colors of light. secondary colors YELLOW of light and CYAN pigments. (Courtesy of the General Electric ·A primary color of Co..Lamp MAGENTA Business colorants is defined as Division.) one that subtracts or MIXTURES OF PIGMENTS absorbs a primary color (Subtractive primaries) YELLOW of light and reflects or transmits the other two. GREEN BLACK CYAN BLUE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY COLORS OF LIGHT AND PIGMENT 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • The primary colors can be added to produce the secondary colors of light. • A primary color of colorants is defined as one that subtracts or absorbs a primary color of light and reflects or transmits the other two