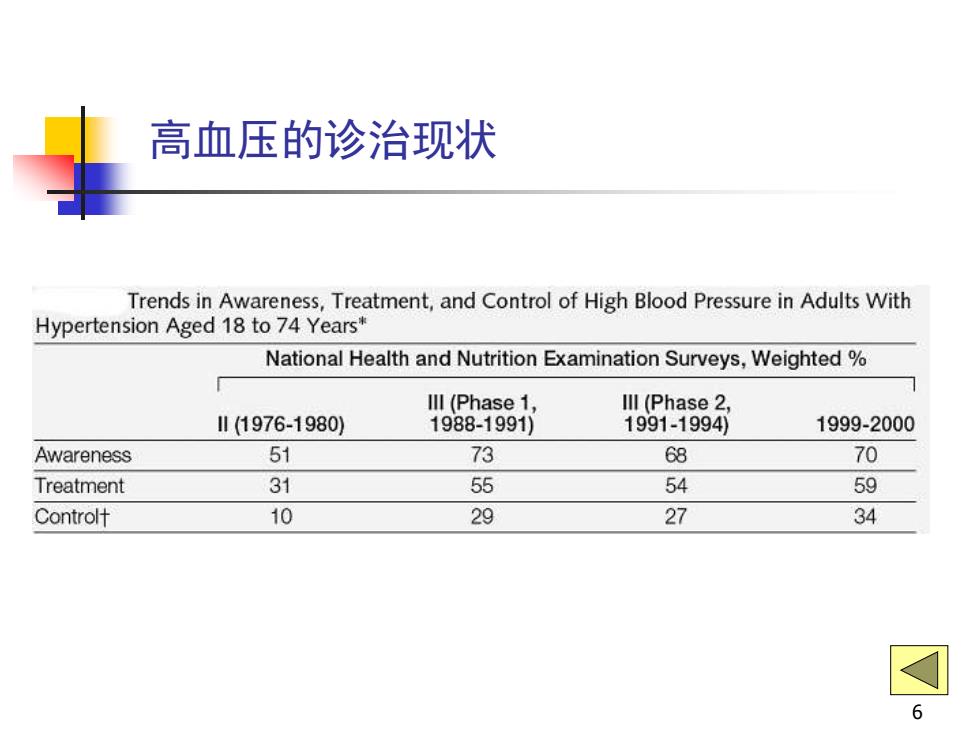
高血压的诊治现状 Trends in Awareness,Treatment,and Control of High Blood Pressure in Adults With Hypertension Aged 18 to 74 Years* National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys,Weighted Ill (Phase 1, Ill (Phase 2, I1(1976-1980) 1988-1991) 1991-1994) 1999-2000 Awareness 51 73 68 70 Treatment 31 55 54 59 Controlt 10 29 27 34 可 6
6 高血压的诊治现状
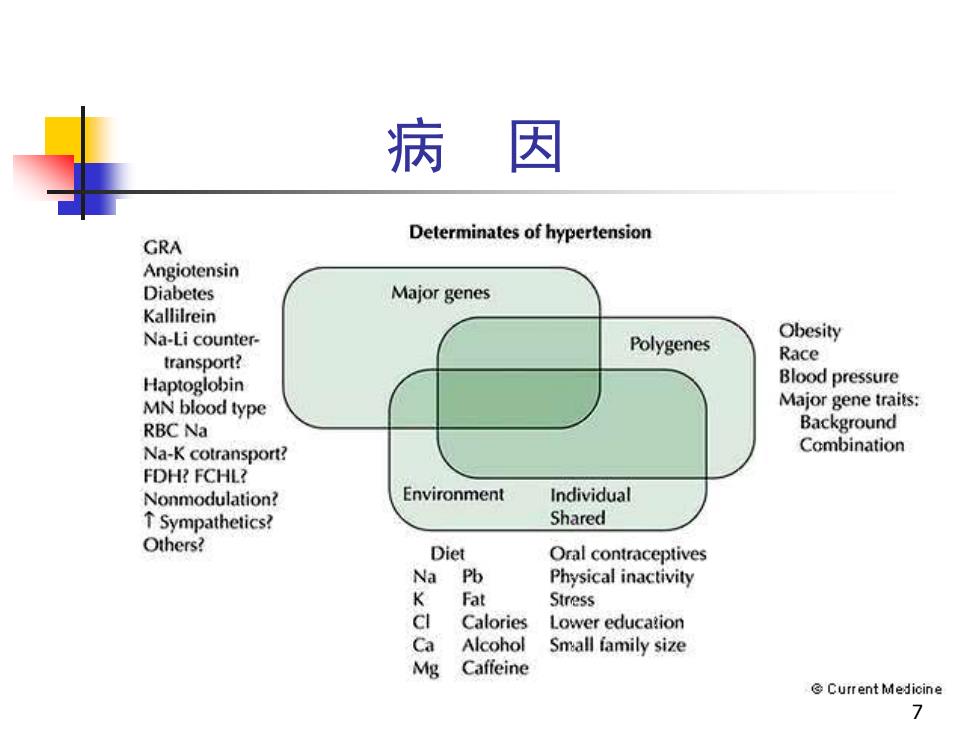
病因 Determinates of hypertension GRA Angiotensin Diabetes Major genes Kallilrein Na-Li counter- Polygenes Obesity transport? Race Haptoglobin Blood pressure MN blood type Major gene traits: RBC Na Background Na-K cotransport? Combination FDH?FCHL? Nonmodulation? Environment Individual ↑Sympathetics! Shared Others? Diet Oral contraceptives Na Pb Physical inactivity K Fat Stress CI Calories Lower education Ca Alcohol Small family size Mg Caffeine Current Medicine
7 病 因
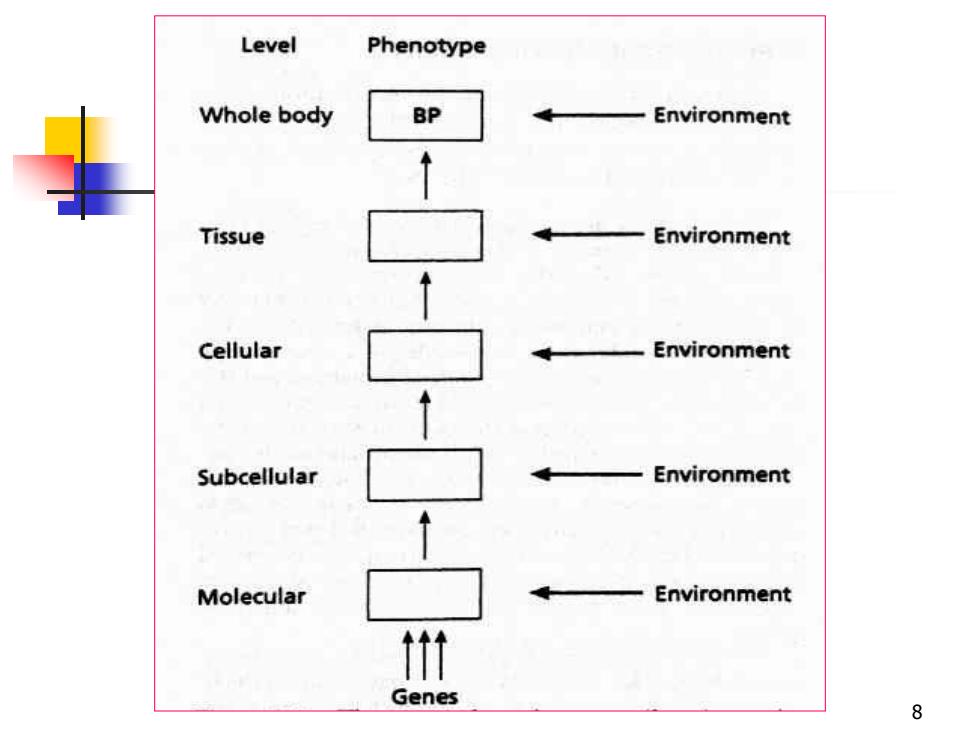
Level Phenotype Whole body BP Environment Tissue Environment Cellular Environment Subcellular Environment Molecular Environment t Genes 8
8
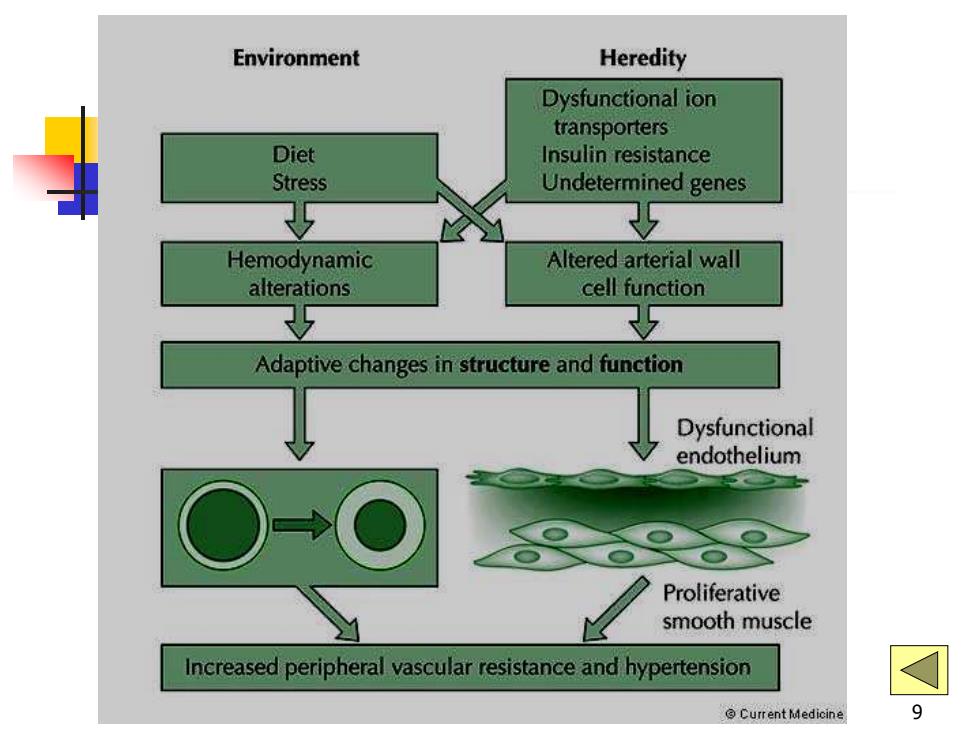
Environment Heredity Dysfunctional ion transporters Diet Insulin resistance Stress Undetermined genes 5 9 Hemodynamic Altered arterial wall alterations cell function 亚 5 Adaptive changes in structure and function Dysfunctional endothelium Proliferative smooth muscle Increased peripheral vascular resistance and hypertension Current Medicine 9
9

发病机制 交感神经系统活性亢进:神经中枢功能改变,交感神经系 统活性亢进,儿茶酚胺浓度升高,阻力小动脉收缩增强 肾性水钠潴留:各种病因引起的肾性水钠潴留,组织过渡 灌注,全身阻力小动脉收缩 肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS)激活:血管紧张 素Ⅱ为主要效应物质,作用于AT1受体,使小动脉收缩, 并刺激醛固酮和去甲肾上腺素分泌 ■细胞膜离子转运异常 10
10 发病机制 ◼ 交感神经系统活性亢进:神经中枢功能改变,交感神经系 统活性亢进,儿茶酚胺浓度升高,阻力小动脉收缩增强 ◼ 肾性水钠潴留:各种病因引起的肾性水钠潴留,组织过渡 灌注,全身阻力小动脉收缩 ◼ 肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS)激活:血管紧张 素II为主要效应物质,作用于AT1受体,使小动脉收缩, 并刺激醛固酮和去甲肾上腺素分泌 ◼ 细胞膜离子转运异常