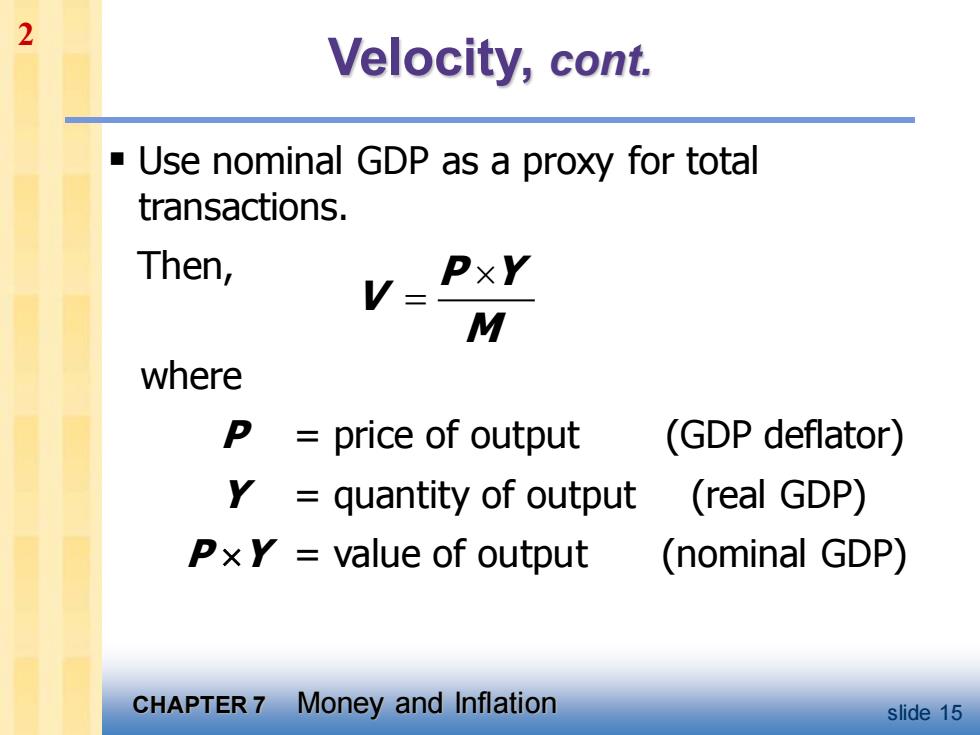
2 Velocity,cont. Use nominal GDP as a proxy for total transactions. Then, V= PxY M where P price of output (GDP deflator) quantity of output (real GDP) PxY value of output (nominal GDP) CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 15
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 15 Velocity, cont. ▪ Use nominal GDP as a proxy for total transactions. Then, P Y V M = where P = price of output (GDP deflator) Y = quantity of output (real GDP) P Y = value of output (nominal GDP) 2
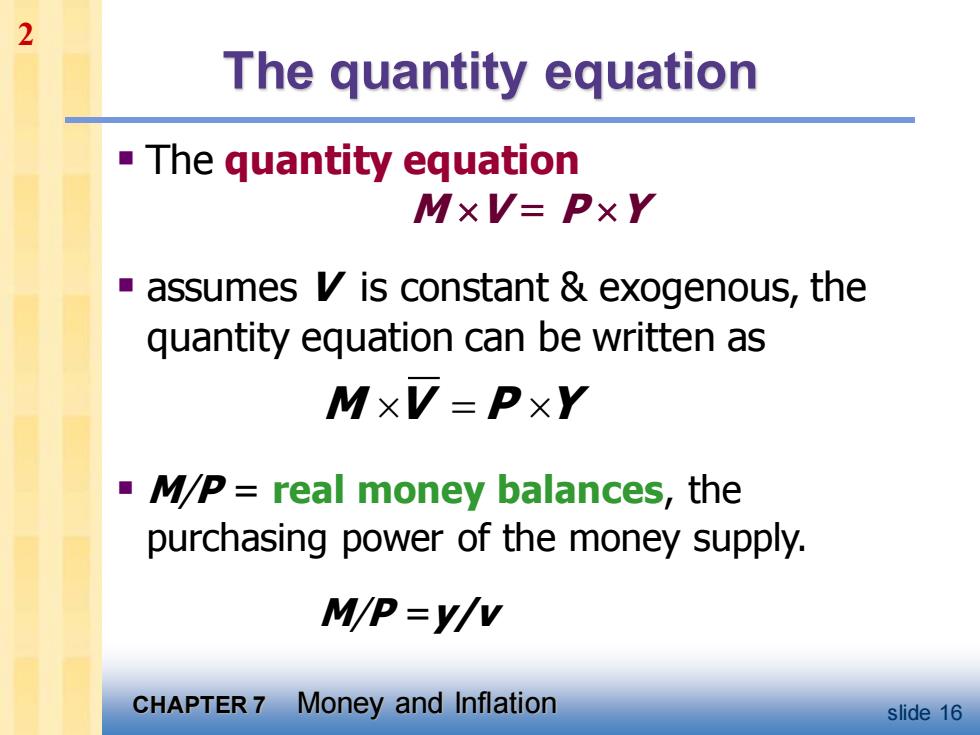
2 The quantity equation The quantity equation MxV=PxY -assumes V is constant exogenous,the quantity equation can be written as MxV=PXY MP=real money balances,the purchasing power of the money supply. M/P=y/v CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 16
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 16 The quantity equation ▪ The quantity equation M V = P Y ▪ assumes V is constant & exogenous, the quantity equation can be written as ▪ M/P = real money balances, the purchasing power of the money supply. M/P =y/v M V P Y = 2
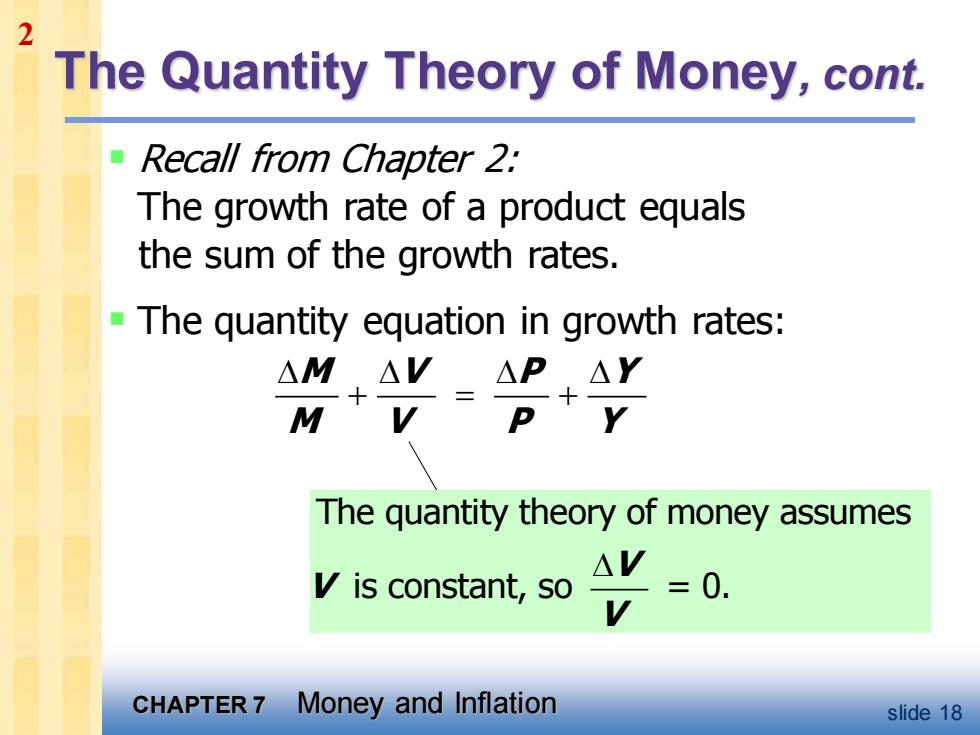
2 The Quantity Theory of Money,cont. Recall from Chapter 2: The growth rate of a product equals the sum of the growth rates. The quantity equation in growth rates: △M,AV△P,△Y M D The quantity theory of money assumes is constant,so △V =0. CHAPTER7 Money and Inflation slide 18
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 18 The Quantity Theory of Money, cont. ▪ Recall from Chapter 2: The growth rate of a product equals the sum of the growth rates. ▪ The quantity equation in growth rates: M V P Y M V P Y + = + The quantity theory of money assumes is constant, so = 0. V V V 2

2 The Quantity Theory of Money,cont. The result from the △M △Y preceding slide was: M P Let n (Greek letter "pi") △P π denote the inflation rate: Solve this result △M △Y forπto get π M CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 19
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 19 The Quantity Theory of Money, cont. Let (Greek letter “pi”) denote the inflation rate: M P Y M P Y = + P P = = − M Y M Y The result from the preceding slide was: Solve this result for to get 2
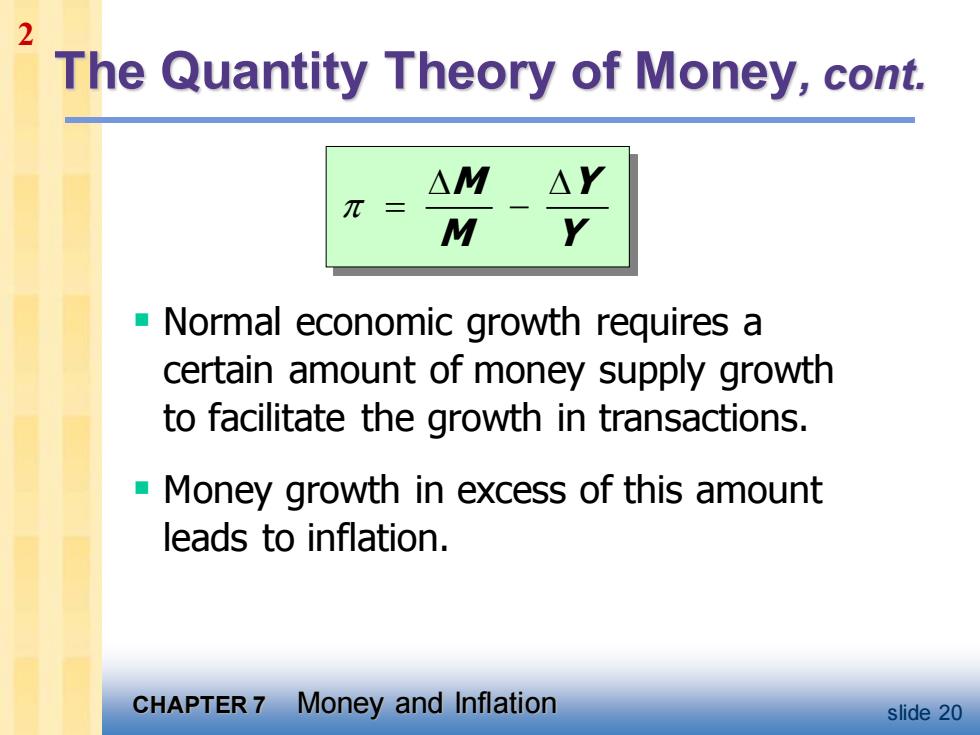
2 The Quantity Theory of Money,cont. △M △Y π M -Normal economic growth requires a certain amount of money supply growth to facilitate the growth in transactions. Money growth in excess of this amount leads to inflation. CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 20
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 20 The Quantity Theory of Money, cont. ▪ Normal economic growth requires a certain amount of money supply growth to facilitate the growth in transactions. ▪ Money growth in excess of this amount leads to inflation. = − M Y M Y 2