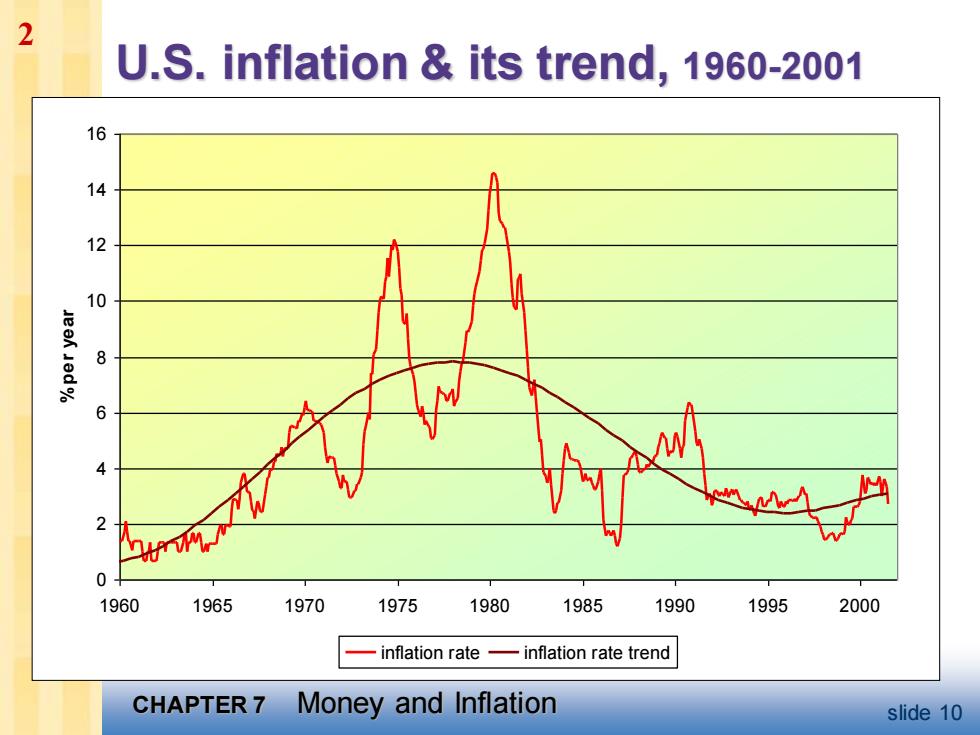
2 U.S.inflation its trend,1960-2001 16 14 12 8 0 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 inflation rate-inflation rate trend CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 10
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 10 U.S. inflation & its trend, 1960-2001 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 % per year inflation rate inflation rate trend 2

2 The connection between money and prices -Inflation rate the percentage increase in the average level of prices. price amount of money required to buy a good. ■ Because prices are defined in terms of money,we need to consider the nature of money,the supply of money,and how it is controlled. CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 11
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 11 The connection between money and prices ▪ Inflation rate = the percentage increase in the average level of prices. ▪ price = amount of money required to buy a good. ▪ Because prices are defined in terms of money, we need to consider the nature of money, the supply of money, and how it is controlled. 2

2 The Quantity Theory of Money A simple theory linking the inflation rate to the growth rate of the money supply. Begins with a concept called "velocity". CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 12
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 12 The Quantity Theory of Money ▪ A simple theory linking the inflation rate to the growth rate of the money supply. ▪ Begins with a concept called “velocity”. 2
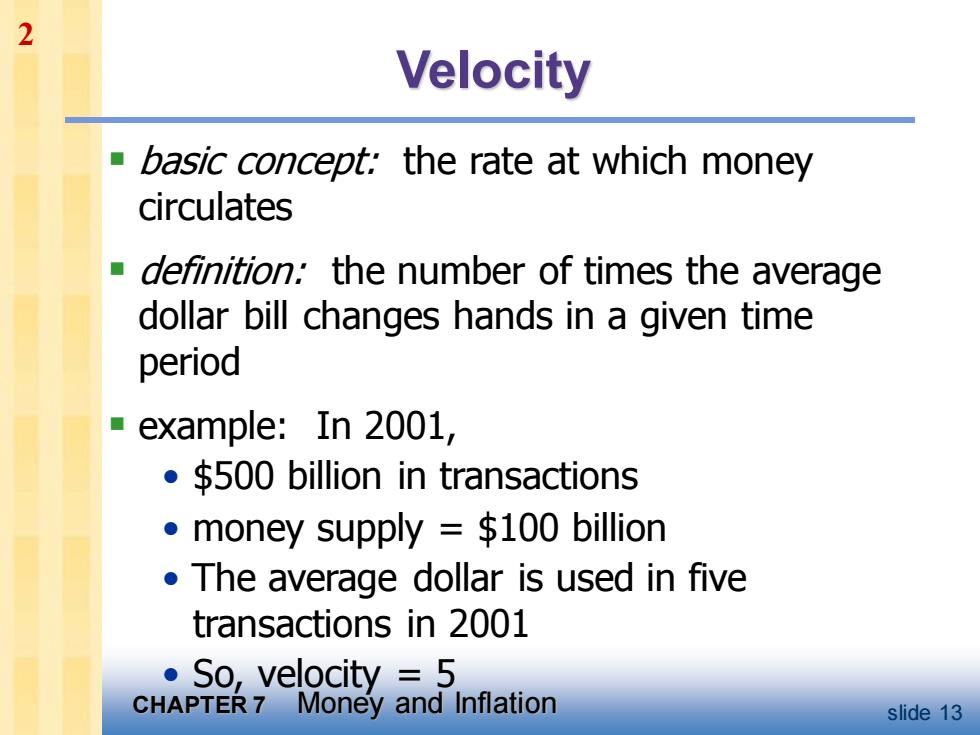
2 Velocity ■ basic concept:the rate at which money circulates definition:the number of times the average dollar bill changes hands in a given time period example:In 2001, .$500 billion in transactions money supply $100 billion The average dollar is used in five transactions in 2001 ·So,velocity=5 CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 13
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 13 Velocity ▪ basic concept: the rate at which money circulates ▪ definition: the number of times the average dollar bill changes hands in a given time period ▪ example: In 2001, • $500 billion in transactions • money supply = $100 billion • The average dollar is used in five transactions in 2001 • So, velocity = 5 2
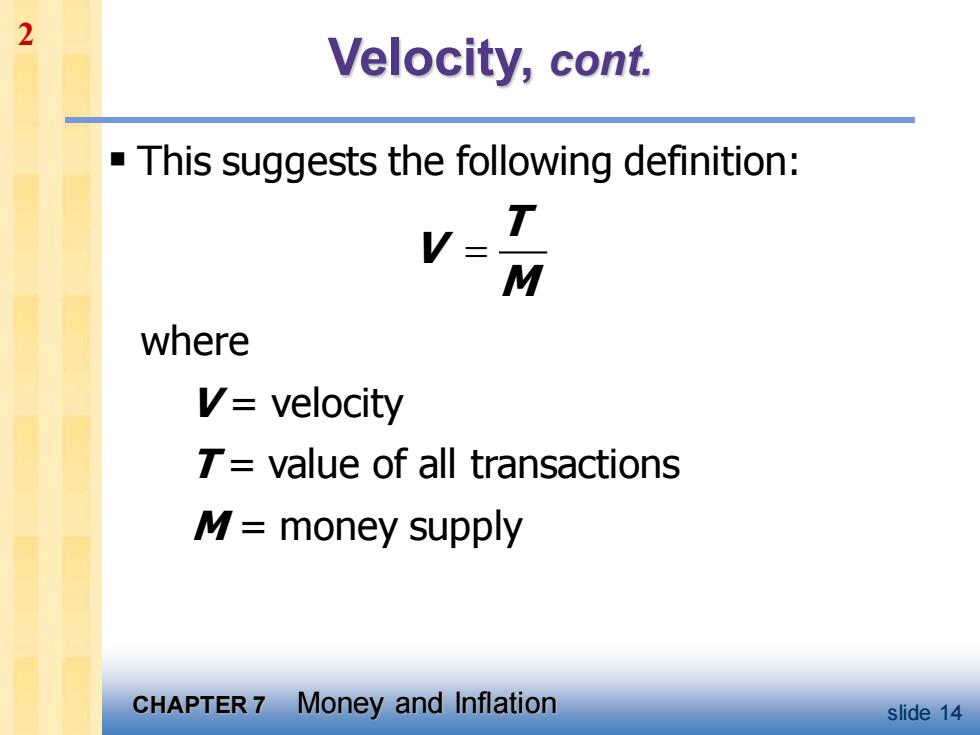
2 Velocity,cont. -This suggests the following definition: V= T M where V=velocity value of all transactions M=money supply CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 14
CHAPTER 7 Money and Inflation slide 14 Velocity, cont. ▪ This suggests the following definition: = T V M where V = velocity T = value of all transactions M = money supply 2