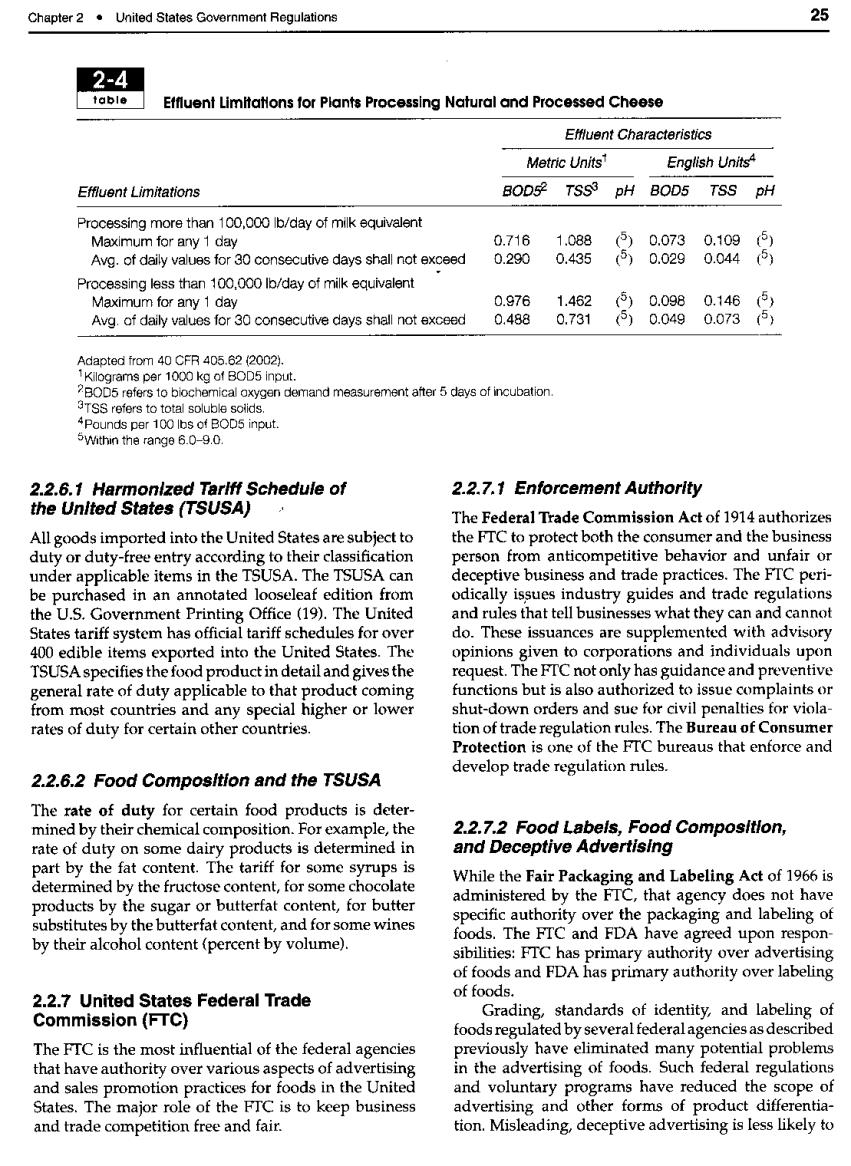
Chapter 2.United States Governmont Regulations 25 2-4 b1 Effluent Limitatons for Plants Processing Natural and Processed Cheese Effluent Characteristics Metric Units' English Units Effiluent Limitations BOD5 TSS3 pH BOD5 TSS pH sing m ethan 10.0 lb/day of mik equivalent 071 Avg.of e for 30 concutive days shall not exceed 8298888阳8 Processing less than100 b/day of milk equivalen 0.976 Avg.of daily 6f630c0n9ecumecayssndnoaced 2.2 6.1 Harmonlzed Tarlff Schedule of 2.2.7.1 Enforcement Authority the Unlted States (TSUSA) The Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914 authorizes All goods imported into the United States are subject to the FTC to protect both the consumer and the business duty or duty-free entry according to their classification person from anticompetitive behavior and unfair or under applicable items in the TSUSA.The TSUSA can deceptive business and trade practices. The FIC per be purchased in an annotated looselea editio n from trade regulations the U.S.Government Pri Unite canno nces are supplem te od i p T ida ctions but is also authe r or low to issue laints or nd any ecial higher shut-down orders and sue for civil nenalties for viola rates of duty for certain other countries. tion of trade regulation rules.The Bureau of Consumer Protection is one of the FTC bureaus that enforce and develop trade regulation rules. 2.2.6.2 Food Composltion and the TSUSA The rate of duty for certain food products is deter mined by their chemical composition.For exa nle the 2.2.7.2 Food Labels,Food Composltlon, rate of duty on some dairy products is determined in and Deceptive Advertising part by the fat content.The tariff for some syrups is determined by the fructose content,for some chocolate While the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act of 1966 is dministered by the FTC products by the sugar or butterfat content,for butter The verth eP3agndg that agency doe substitutes by the butterfat content,and for some wines FTC and FDA ha by their alcohol content (percent by volume) bilit agreed upon respon ority ove 2.2.7 United States Federal Trade of foods Commission (FTC) standards of identity.and labeling o foods regulated by several federal agencies as described The fTC is the most influential of the federal agencies previously have eliminated many otential problems that have authority over various as cts of advertising in the advertising of foods.Such federal regulations and sales promotion practices for foods in the United and voluntary programs have reduced the scope of States.The major role of the FTC is to keep business advertising and other forms of product differentia and trade competition free and fair. tion.Misleading,deceptive advertising is less likely to

26 he an issue and is more easily controlled.For Pasleurized Milk Ordinance standards to Grade A Pasteurized Milk and Milk butter have standards of identity that set minimum 2-5 Bulk-Shipped Heat-Treated ingredient standards.If these standards are not met, table Milk Proc the food must be given a different generic designa on (e.g.,salad dr ing instead of m or be "imitation. Cooled to7C(45F)or less and maintained thereat m ma qu Bacterial limits 20.000 per ml a nd s s in which the FICinter renes,data from a chemical analysis shipments,shall not exceed 100 per ml become central evidence for all parties involved. Phosphatase2 the Scharer Drugs3 No positive results on drug residue detection methods :ND Noieoom20 The safety and muality of milk and dair applic at-treed mik products Inited State responsibility of both federal (FDA and USDA)and state agencies.The FDA has regulatory authority over the dairy industry interstate commerce, The standards for Grade A pasteurized milk and while the USDA involvement wi the dairy industry is milk products and bulk-shipped heat-treated milk voluntary and service oriented Each sta e has Its ow products under the PMO are given in Table 2-5 ns for m try within tha state The PMO specifies that"all sampling procedures and ve sever al types requ tory exa ce with lic Health Ass 9 n of of 2.3.1 FDA Responsibilities Methods of Analysis of the The FDA has responsibility under the FD&C Act,the ndtheaiootoficalAna lytical Chemists.(Insert edition number current at time Public Health Service Act,and the Import Milk Act to of adoption.)"(20-22). rs that the United tate The FDA monitors state programs for compliance ry pre spect rs.To facilitat f b with the PMO and and Grade B milk in intersta the Int ce 1 lations to take re edial action when conditions This that could ieonardize the safety and wholesomeness o intained hy the milk and dair products being handled.As described Milk Shipments,which is a voluntary organization in section 2.2.1 the FDA also promulgates standards that includes representatives from each state,the FDA of identity and label ity,and fill-of-container the USDA,and the dairy industry.In this program,the producers of Grade A milk are requ nt kand dairy pro o pass be ra ng s and nd mad authorities and milk hu rs to ensun with the National Conference on Interstate Milk the safety of milk shipp ped from Shipments,which is comprise of all 50 states. dairy indus 2.3.2 USDA Responsibilities velope for state ilk.Th aspects Under authorityof 046 the ai of the USDA off A。ADae edMi red or pro Ordinance (PMO)(20),which all states have adopted ed dairy (CER 58)insnectiono as minimum requirements. a dairy manufacturing plant shows that good sanitation

Chapter 2.United States Government Regulations 27 24 REGULATIONS AND 2 ndards for ades of Nonfat Dry RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SHELLFISH Shellfish include fresh or frozen oysters,clams,and Laboratory Tests2 mussels.They may transmit intestinal diseases such as typhoid fever or act as carriers of natural or chem- Bac ecount pe ndard 10.000 75,000 ical toxins. Ifs makes it very importar 2 be obtai dfrom unpolluted waters and h proce tary manne 15 U.S.High Hear 2.4.1 State and Federal Shellfish acidity (lactic acid). Sanitation Programs The growing,handling,and processing of shellfish dards/NOM 02-02-01 must com ogra (NSS is L pra are meet the rement 26).The ed interstate nd grading se ice (24),the lant ver.the Public Health Service Act authorizes ndofproducroduc the FDA to make recommendations and to cooperate with state and local authorities to ensure the safety such as nonfat dry milk is graded based on flavor, and wholesomeness of shellfish.Under e28Ppeaene4ndaioilhboao7a7r ment, certain other countries are in are As with t the gh the health eu hacter ant ns in shellfish. Any con ire change aminated location is superv ised or patrolled so that ons.The USDA,under an arrangement with the shellfish cannot be harvested from the area.State FDA.assists states in establishing safety and inspectors check harvesting boats and shucking plants ity regulations for manufacturing-grade milk.Muc before issuing approval certificates, as described previously for the FDA with Gr milk,the USDA has d approv plant on each packag state ad shippe aspect re es and Its Production and Process 2.4.2 Natural and Environmental cnade hv eme Toxic Substances in Shellfish A major concern is the ability of shellfish to con- regulations. centrate lioactive material,in 2.3.3 State Responsibilities the N om their en NS Be iously individualstates h nhic tech and heavy metals an ntially identi uantitated by atomic the pMO and the IsDA Recomme nded absorption spectroscopy (e.g.,AOAC Method 977.15) ectively.The department of health Another safety problem with regard to shellfish is the or 'agriculture in each state normally is respon- control of natural toxins,which is a separatei sible for enforcing these regulations. The states sanitat on.The naturally occu also establish their own standards of identity and corga labeling and this of harvesting requirements

28 Partl General Information 25 VOLUNTARY FEDERAL RECOMMENDATIONS AFFECTING FOOD COMPOSITION at Purchase Specifications for 35 2.5.2 National Conference on Welghts and Measures:State Food are purcha sedby fed Packaglng Regulatlons e ome e.g.,s and other teran hospital e that the weighing scale for a food t a package of fl fications or descripti the label.While this a 0 products are used by federal agencies in procure. ment of foods,to ensure the safety and quality of the city or county offices responsible for weights and n n sures need to police any unfair practices.Leadership inf Such specifications or descriptions n that requires assu in this area is provided by the National Conference These speci ures (NCWM),which was estab following: y th of Standards and au c cificat scriptio The nCwM has no regulator but it de n(PPD many technical,legal and ee 4 USDA Specifications in the field of weights and measures administration 5.Commodity Specifications and technology.The NCWM is a membership orga 6.Military Spccifications. niz on com se tat local tory officers otne USDA Specifications are used by the USDA to p of manufacture etd meat products for programs such as school lunches th CID for canned tuna (27)specifies The NIST Handbook 133,Checking the Net Contents me thod of a of Packaged Goods (36),gives model state packaging nd lab ing regula ns that have been a dopted by a majority Handbook specifies that the und heof producs 29) eSpecifica tion for lean finely textured beefspecifies minimums for the individual p nd th protein content,protein efficiency ratio,and essential quantity not too "unreasonably larg Variations are amino acid co nt (29 permitted within the bounds of GMPs and are due to s fo ari s po oy the and (the oud ). oil in the sta,ric m0 must meet specifications for the following. age con ons by the dete mined by American Oil Chemists'Society (AOCS)test methods:free fatty acid value,peroxide value,linolenic ,03c e ar matter,todine value, and INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS AND (see C apter t生for some of the fications indica With th dwid contents of nonfat dry milk,the me ishne need compete the cheese and butter,the milkfat content and pH of butter allowed food in aware th and the moisture and fat contents of pasteurized pro- ired and allowed label information d sta cess A la cheese(32) dards for foods and food ingredients differ between e Personne oupport Cente of the countries.For example,colorings and preservatives Agency, epartm ense allowed in foods differ widely betwee countries. in the purchase of ana no labeling is not universally requi xample develop foods for,and market foods in.a global

西 mmonaiignimsegananhOganatoisR one must seek such information from Codex has strengthened its comm ent to onst杠ong sct nce,ra specific regions and countries. s The ndard od quality h has beer n a high priority in world trade to min 2.6.1 Codex Allmentarius imize "nontariff"trade barriers.International trade of food and raw agricultural products has increased is Lat orned with nourishment") due to reduced economic trade restrictons and tarim bished in 1962 by two United Nations organi- impos d,but food stand he pas zations,the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) d som and the World Health Organization (WHO),to develop d h m international standards and he untry when the stan ety pracnce s do m to nr ect pr ural prd oducts in a country from in the C nded to the co mpetition of imports than to protect the health of 1 sure fa Decisions at the 1994 Ur a nd f the Gen foods (38) The Codex Alimentarius is published in 13 vol 11 safety a grod The Un rra that are members of Codex.The United States rec- import/export ins on sta lad n ognizes treaty obligations related to Codex that have dity ban odes ides and arisen from GATT As a result,repr aves of in foods and one on methods of anal FDA.USDA,and EPA (the th ysis and san oling (Table 2-7).Codex has efforts to eral par validate and harmonize methods of food sa ty ana In the ysis among countries and regions,to help maintain the is increased participation of A overnmental organizations (e.g Grocery Man the ufacturers of America,GMA)in the Codex process, e safcty of perishable foods with many food companies working through thes and is dete how HACCP will be implemented organizations. 2-7 2.6.2 ISO Standards Content of the Codex(38) In addition to food standards and policies estab- Volume Subject al Organiz tion for has the U00 Generalraauremrtstoodhy ma nel nt and quality perfo ds ie to esidue oduct integrity,and sat- sfy cus 3 s in foods ry use bach to quality management.Companies can elect to become registered only in the relevant the ISO standard Some manufacturer 067 3 ust 1S0 es).and derived products vant toto auditable HAcCP standard This stan 8901 product dard will define the requirements for a food safety management system and will be based on the seven Mik and m principles as defined by Codex Alimer ntarius Com Methods of analysis and sampling mission (J.G.Surak,Clemson University,persona communication