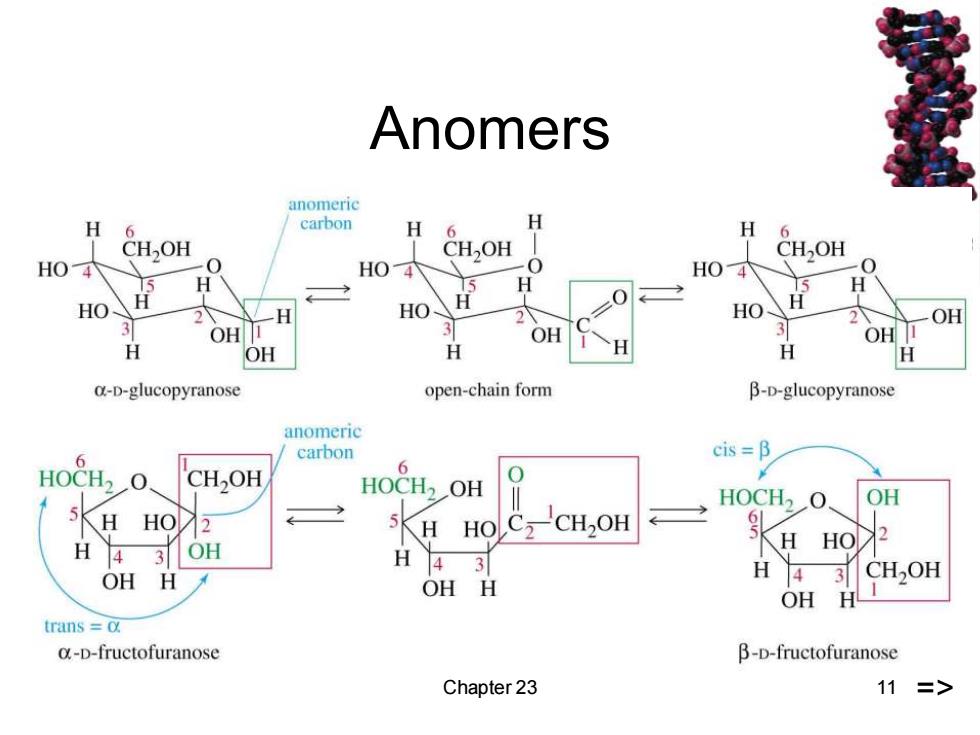
Anomers anomeric H 6 carbon H H 6 H OH OH CH2OH HO4 -0 HO4 -0 HO H H H HO HO HO 2 OH OH OH 3 OH I H OH H H a-D-glucopyranose open-chain form B-D-glucopyranose anomeric cis =B 6 carbon HOCH2O 6 CH,OH HOCH2OH HOCH2O. OH HO → 5 H HOC2CH2OH H OH H H4 3 OH H 43 CH,OH OH H OH H trans =o. o-D-fructofuranose β-D--fructofuranose Chapter 23 11 =>
Chapter 23 11 Anomers =>
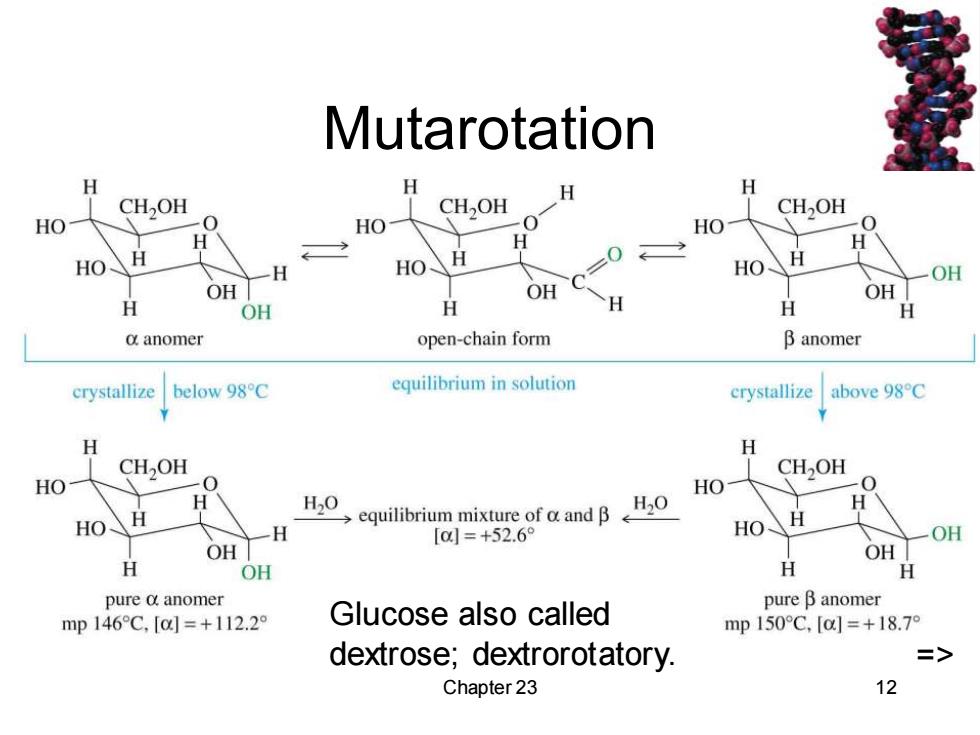
Mutarotation H 令 CH2OH CH,OH H CH2OH HO 0 HO- HO H H HO H H HO H HO H OH OH OH OH H OH H H H H d anomer open-chain form B anomer crystallize below 98C equilibrium in solution crystallize above 98C H H CH2OH CH2OH HO -0 HO -0 H20 H >equilibrium mixture of a and B H20 HO H [0=+52.6° HO OH OH OH H OH H H pure d anomer mp146C,[a=+112.2° Glucose also called pure B anomer mp150C,[a]=+18.7° dextrose;dextrorotatory. => Chapter 23 12
Chapter 23 12 Mutarotation => Glucose also called dextrose; dextrorotatory

Epimerization In base,H on C2 may be removed to form enolate ion.Reprotonation may change the stereochemistry of C2. Abstraction of the a proton Reprotonation H、 H H =0 HO: HCOH :C一OH OH HO-C✉H HO- -H OH HO- H HO- H H一 0-H HO- H +-OH H OH H OH OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH D-glucose enolate D-mannose Chapter 23 13
Chapter 23 13 Epimerization In base, H on C2 may be removed to form enolate ion. Reprotonation may change the stereochemistry of C2. =>

Enediol Rearrangement In base,the position of the C=O can shift. Chemists use acidic or neutral solutions of sugars to preserve their identity. Step I:Remove Step 2: Step 3: Step 4:Reprotonate on CI the a proton Reprotonate Deprotonate onO the O on C2 H H H OH OH +OH +H,O TOH H20 H-C- OH +-OH H-C-OH OH 一OH C=0 HO H HO H HO- 一H →HO H HO 一H H OH H -OH H OH H OH H OH H一OH H OH H一OH H OH H -OH CH,OH CHOH CH,OH CH2OH CH2OH D-glucose enolate enediol enolate D-fructose => Chapter 23 14
Chapter 23 14 Enediol Rearrangement In base, the position of the C=O can shift. Chemists use acidic or neutral solutions of sugars to preserve their identity. =>

Reduction of Simple Sugars C=O of aldoses or ketoses can be reduced to C-OH by NaBH4 or H2/Ni. Name the sugar alcohol by adding -itol to the root name of the sugar. Reduction of D-glucose produces D-glucitol,commonly called D-sorbitol. Reduction of D-fructose produces a mixture of D-glucitol and D-mannitol. => Chapter 23 15
Chapter 23 15 Reduction of Simple Sugars • C=O of aldoses or ketoses can be reduced to C-OH by NaBH4 or H2 /Ni. • Name the sugar alcohol by adding -itol to the root name of the sugar. • Reduction of D-glucose produces D-glucitol, commonly called D-sorbitol. • Reduction of D-fructose produces a mixture of D-glucitol and D-mannitol. =>