
R Organic Chemistry,5th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr
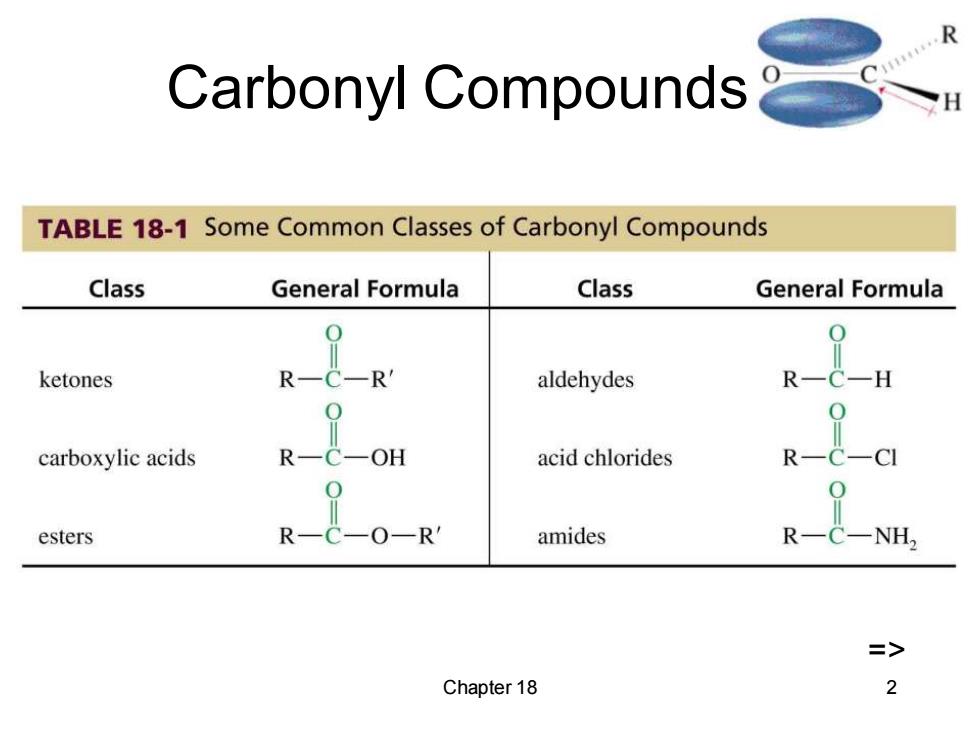
Carbonyl Compounds TABLE 18-1 Some Common Classes of Carbonyl Compounds Class General Formula Class General Formula ketones R aldehydes R-C-H carboxylic acids R -OH acid chlorides R esters O-R amides R => Chapter 18 2
Chapter 18 2 Carbonyl Compounds =>
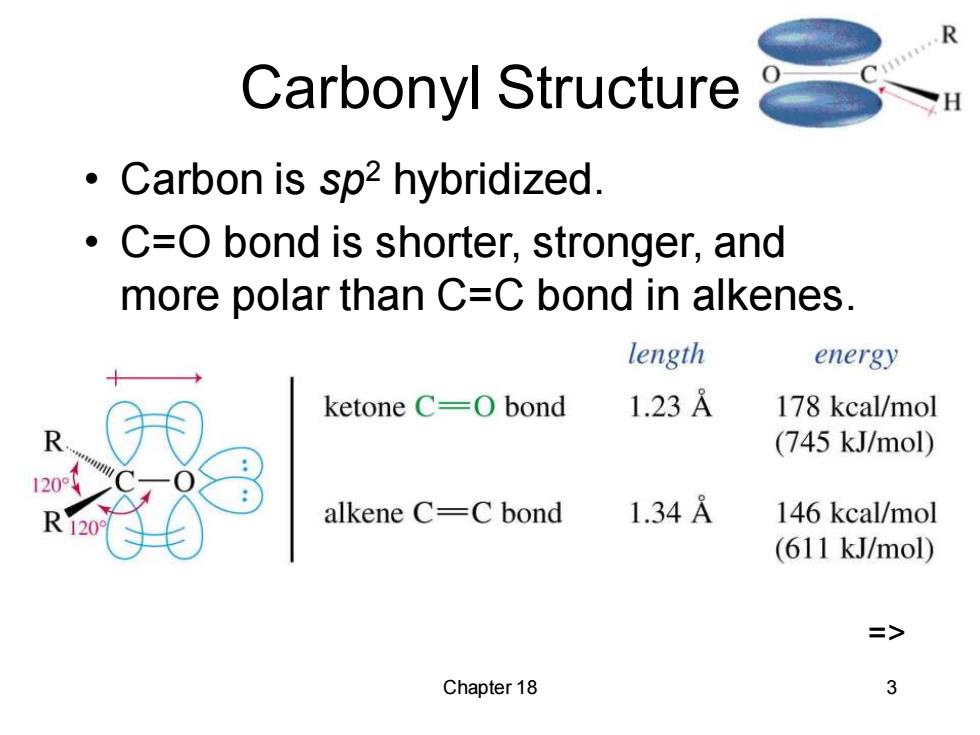
Carbonyl Structure ● Carbon is sp2 hybridized. C=O bond is shorter,stronger,and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. length energy ketone C=0 bond 1.23A 178 kcal/mol (745 kJ/mol) alkene C=C bond 1.34A 146 kcal/mol (611 kJ/mol) => Chapter 18 3
Chapter 18 3 Carbonyl Structure • Carbon is sp2 hybridized. • C=O bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than C=C bond in alkenes. =>

IUPAC Names for Ketones Replace -e with -one.Indicate the position of the carbonyl with a number. Number the chain so that carbonyl carbon has the lowest number. For cyclic ketones the carbonyl carbon is assigned the number 1. => Chapter 18
Chapter 18 4 IUPAC Names for Ketones • Replace -e with -one. Indicate the position of the carbonyl with a number. • Number the chain so that carbonyl carbon has the lowest number. • For cyclic ketones the carbonyl carbon is assigned the number 1. =>
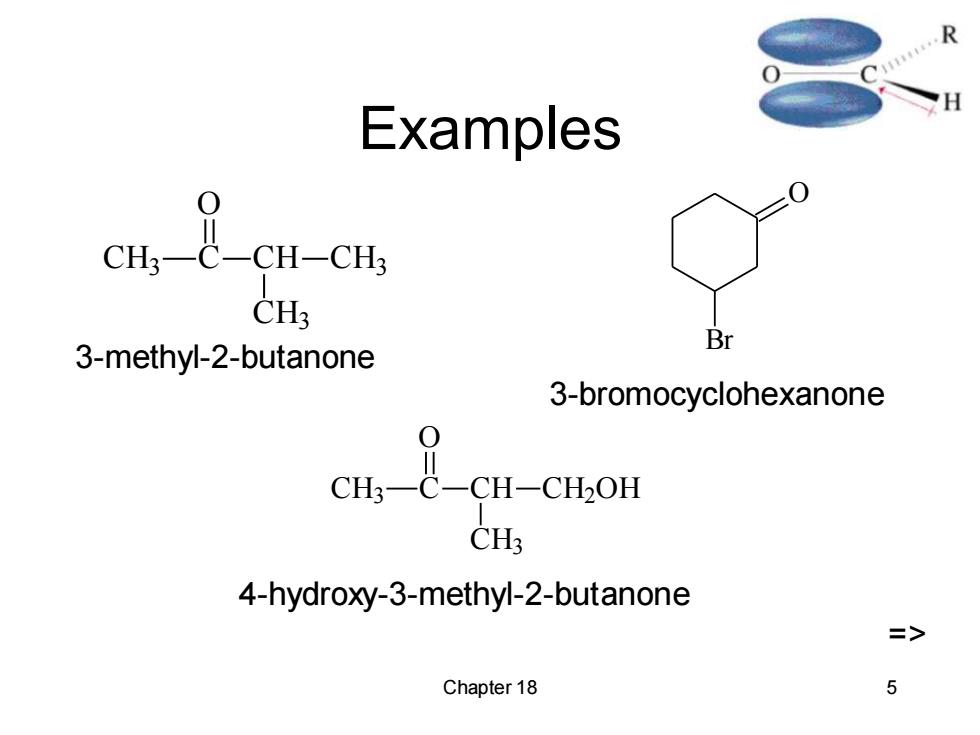
Examples CH-CH CH3 3-methyl-2-butanone Br 3-bromocyclohexanone CH C-CH-CBOL CH3 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butanone => Chapter 18 5
Chapter 18 5 Examples CH3 C O CH CH3 CH3 O Br CH3 C O CH CH3 CH2OH 3-methyl-2-butanone 3-bromocyclohexanone 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butanone =>