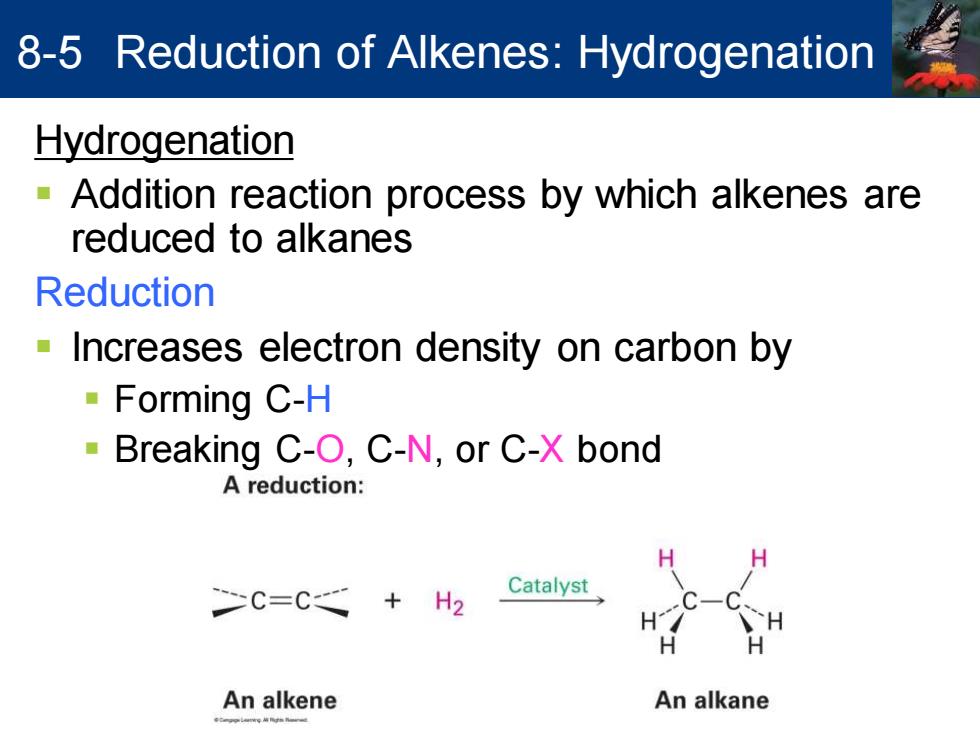
8-5 Reduction of Alkenes:Hydrogenation Hydrogenation -Addition reaction process by which alkenes are reduced to alkanes Reduction Increases electron density on carbon by Forming C-H -Breaking C-O,C-N,or C-X bond A reduction: C=C Catalyst +H2 An alkene An alkane
Hydrogenation ▪ Addition reaction process by which alkenes are reduced to alkanes Reduction ▪ Increases electron density on carbon by ▪ Forming C-H ▪ Breaking C-O, C-N, or C-X bond 8-5 Reduction of Alkenes: Hydrogenation

Reduction of Alkenes:Hydrogenation Catalytic hydrogenation A heterogeneous process that takes place on the surface of insoluble catalyst particles Common catalysts for alkene hydrogenation: Platinum-PtO2(Adams'Catalyst) Palladium-very fine powder supported on inert material such as charcoal(Pd/C) Occurs with syn stereochemistry Both hydrogens add to the double bond from the same side CH3 CH3 .H H2,PtO2 CH3CO2H CH3 solvent H CH3 1,2-Dimethyl- cis-1,2-Dimethyl- cyclohexene cyclohexane (82%)
Catalytic hydrogenation ▪ A heterogeneous process that takes place on the surface of insoluble catalyst particles ▪ Common catalysts for alkene hydrogenation: ▪ Platinum – PtO2 (Adams’ Catalyst) ▪ Palladium – very fine powder supported on inert material such as charcoal (Pd/C) ▪ Occurs with syn stereochemistry ▪ Both hydrogens add to the double bond from the same side Reduction of Alkenes: Hydrogenation

Reduction of Alkenes:Hydrogenation Mechanism of catalytic Metal hydrogenation catalyst Molecular hydrogen adsorbs to the catalyst surface and dissociates into 010- hydrogen atoms. H2 bound to catalyst The alkene adsorbs to the catalyst surface.using its bond to complex to the metal atoms. H2 and alkene bound A hydrogen atom is transferred from to catalyst the metal to one of the alkene carbon atoms.forming a partially reduced intermediate with a C-H bond and carbon-metalbond. Partially A second hydrogen is transferred from reduced the metal to the second carbon,giving intermediate the alkane product and regenerating the catalyst Because both hydrogen are transferred to the same face of the alkene,the reduction has syn stereochemistry. Alkane plus regenerated catalyst
Mechanism of catalytic hydrogenation Reduction of Alkenes: Hydrogenation
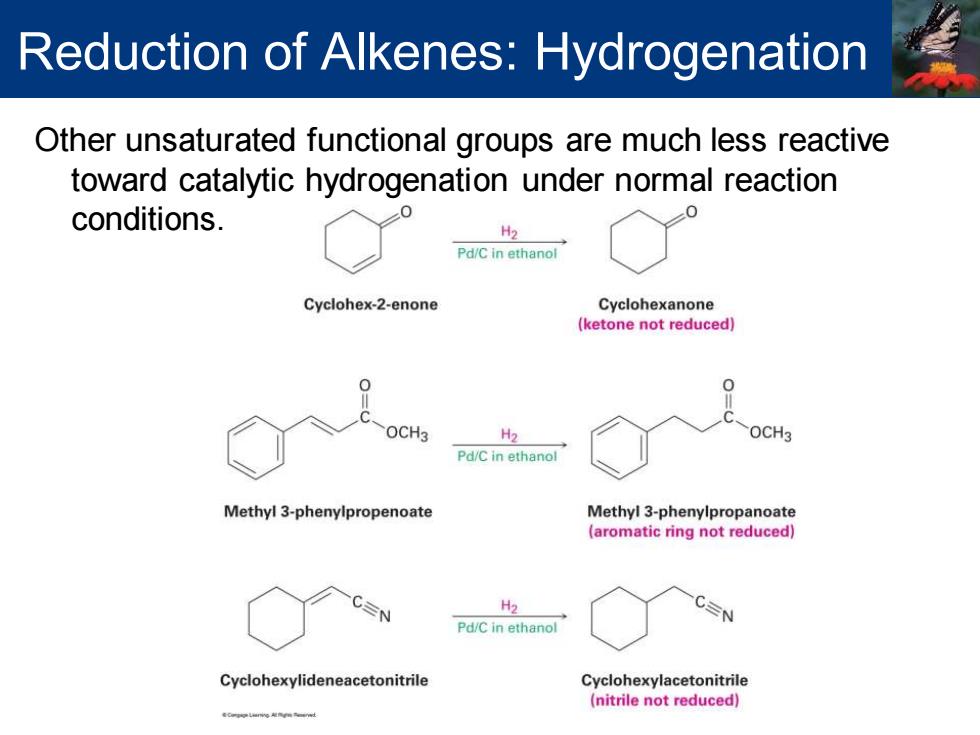
Reduction of Alkenes:Hydrogenation Other unsaturated functional groups are much less reactive toward catalytic hydrogenation under normal reaction conditions. H2 Pd/C in ethanol Cyclohex-2-enone Cyclohexanone (ketone not reduced) OCH3 H2 OCH3 Pd/C in ethanol Methyl 3-phenylpropenoate Methyl 3-phenylpropanoate (aromatic ring not reduced) H2 Pd/C in ethanol Cyclohexylideneacetonitrile Cyclohexylacetonitrile (nitrile not reduced)
Other unsaturated functional groups are much less reactive toward catalytic hydrogenation under normal reaction conditions. Reduction of Alkenes: Hydrogenation

Reduction of Alkenes:Hydrogenation Hydrogenation a Unsaturated vegetable oils reduced to produce saturated fats used in margarine and cooking products Vegetable oils Triesters of glycerol,HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH,with three long-chain carboxylic acids called fatty acids Fatty acids Polyunsaturated carboxylic acids containing long hydrocarbon chains Double bonds have cis stereochemistry
Hydrogenation ▪ Unsaturated vegetable oils reduced to produce saturated fats used in margarine and cooking products ▪ Vegetable oils ▪ Triesters of glycerol, HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH, with three long-chain carboxylic acids called fatty acids ▪ Fatty acids ▪ Polyunsaturated carboxylic acids containing long hydrocarbon chains ▪ Double bonds have cis stereochemistry Reduction of Alkenes: Hydrogenation