2.Signal Molecules and Receptors 2.1 Signal molecules: Lipid-soluble hormones; Water-soluble hormones; nitric oxide (NO)and carbon monoxide(CO) as cellular messengers. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
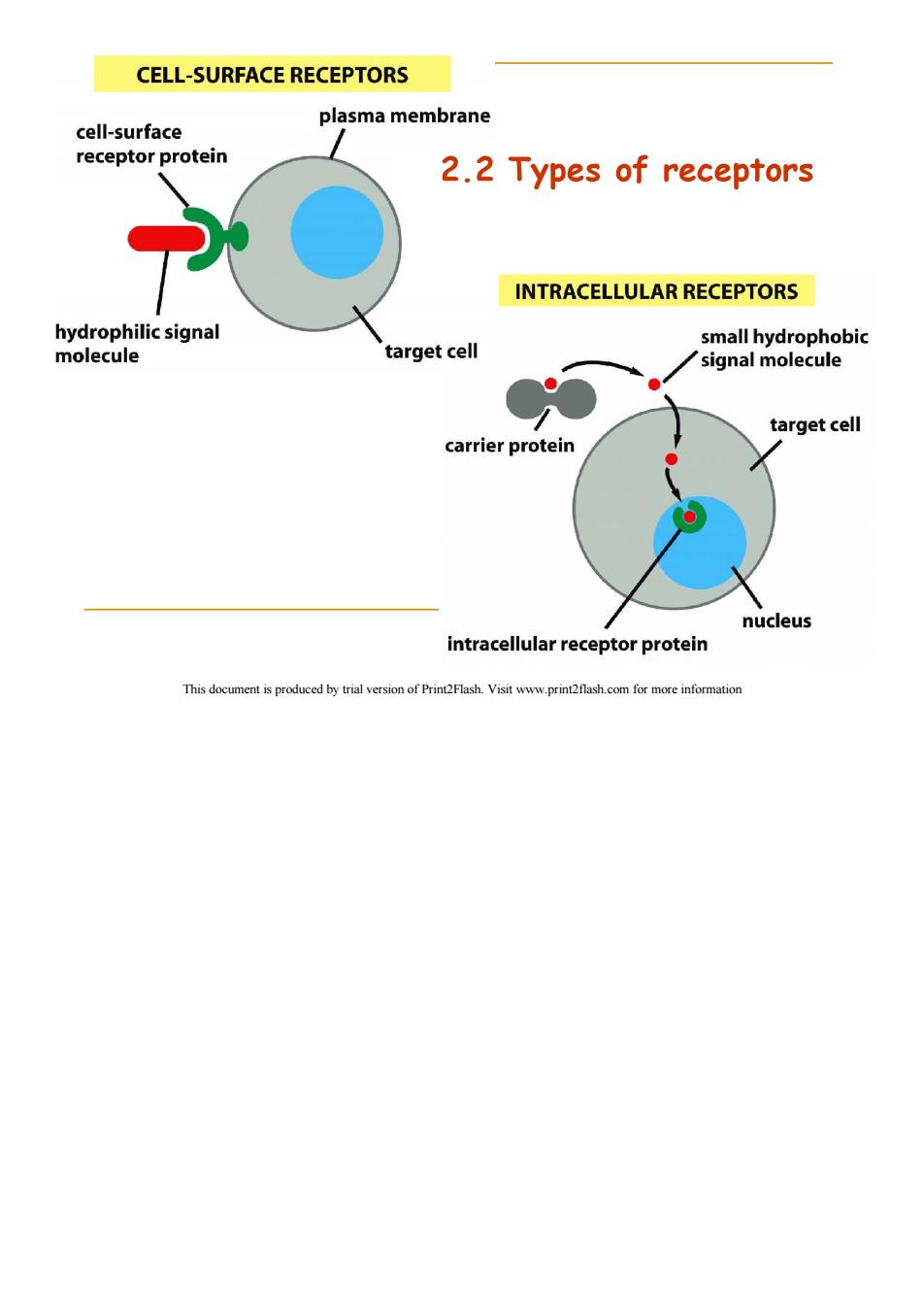
CELL-SURFACE RECEPTORS plasma membrane cell-surface receptor protein 2.2 Types of receptors INTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS hydrophilic signal small hydrophobic molecule target cell signal molecule target cell carrier protein nucleus intracellular receptor protein This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Cell surface receptors include three classes:glycoproteins (A)ION-CHANNEL-LINKED RECEPTOR IB)G-PROTEIN-LINKED RECEPTOR G prote activated enzyme or enzyme or ion channel IC)ENZYME-LINKED RECEPTOR inactive active catalytic catalytie dom湾in domin This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
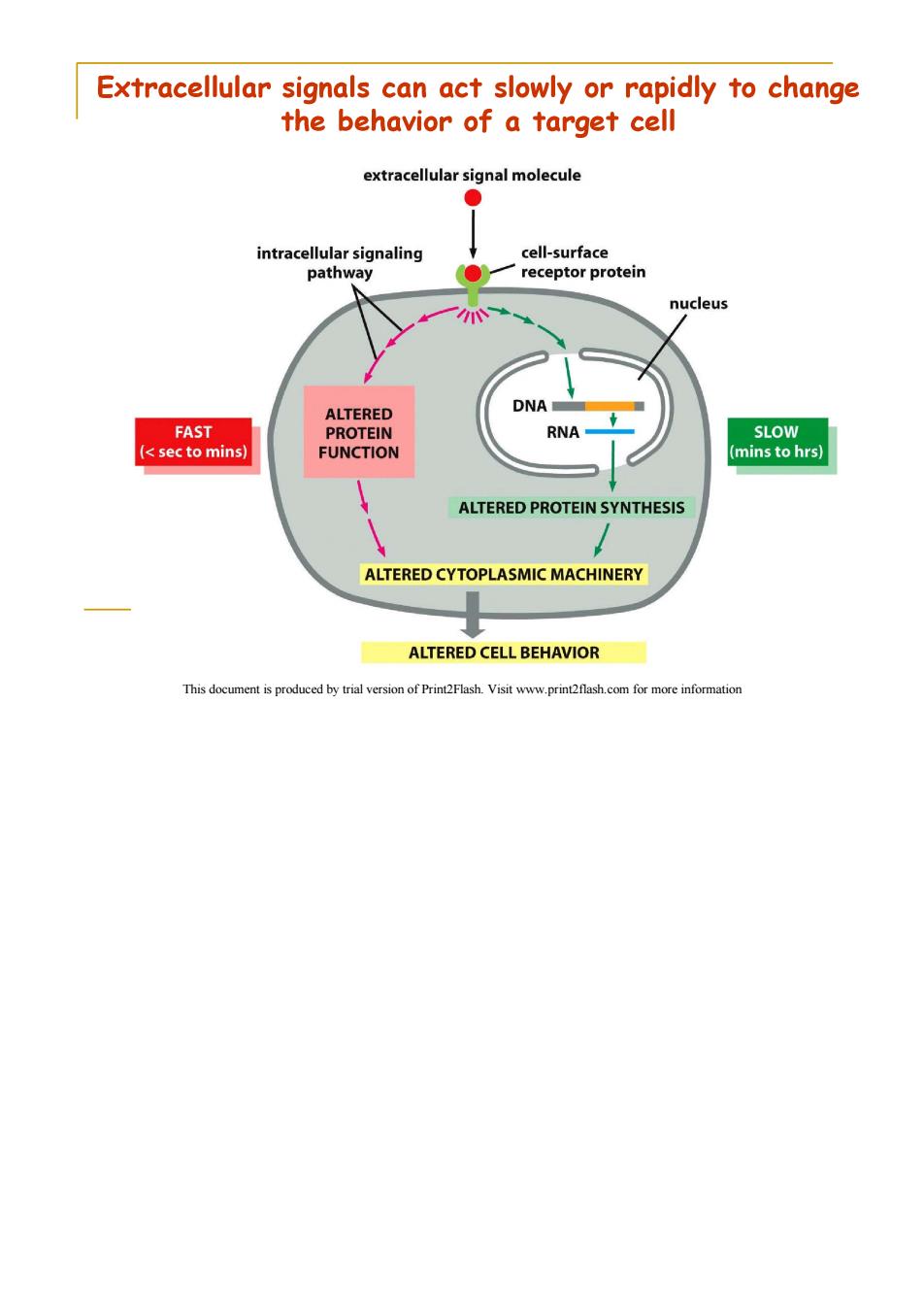
Extracellular signals can act slowly or rapidly to change the behavior of a target cell extracellular signal molecule intracellular signaling cell-surface pathway receptor protein nucleus ALTERED DNA FAST PROTEIN RNA SLOW (sec to mins) FUNCTION (mins to hrs) ALTERED PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ALTERED CYTOPLASMIC MACHINERY ALTERED CELL BEHAVIOR This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

2.3 Second messengers and molecular switch Second messengers: The first second messenger molecular-cAMP. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1971. cAMP,cGMP,Ca2+,DAG,IP3 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information