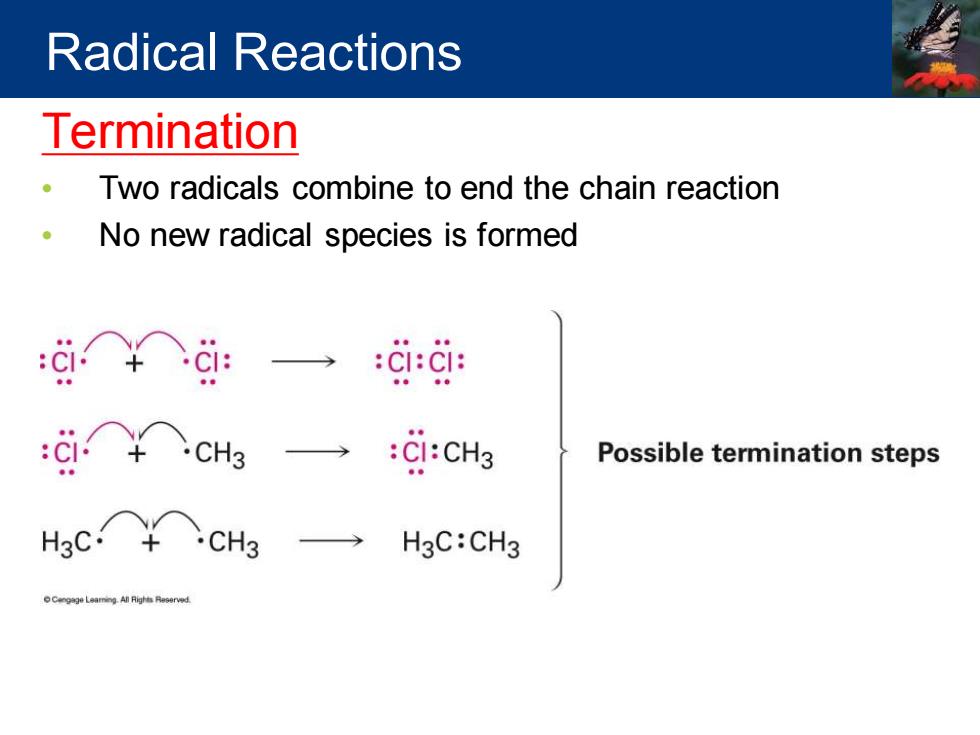
Radical Reactions Termination Two radicals combine to end the chain reaction No new radical species is formed :ci○+ci: CI:CI: → :CI:CH3 Possible termination steps Hec○+cH → H3C:CH3
Termination • Two radicals combine to end the chain reaction • No new radical species is formed Radical Reactions
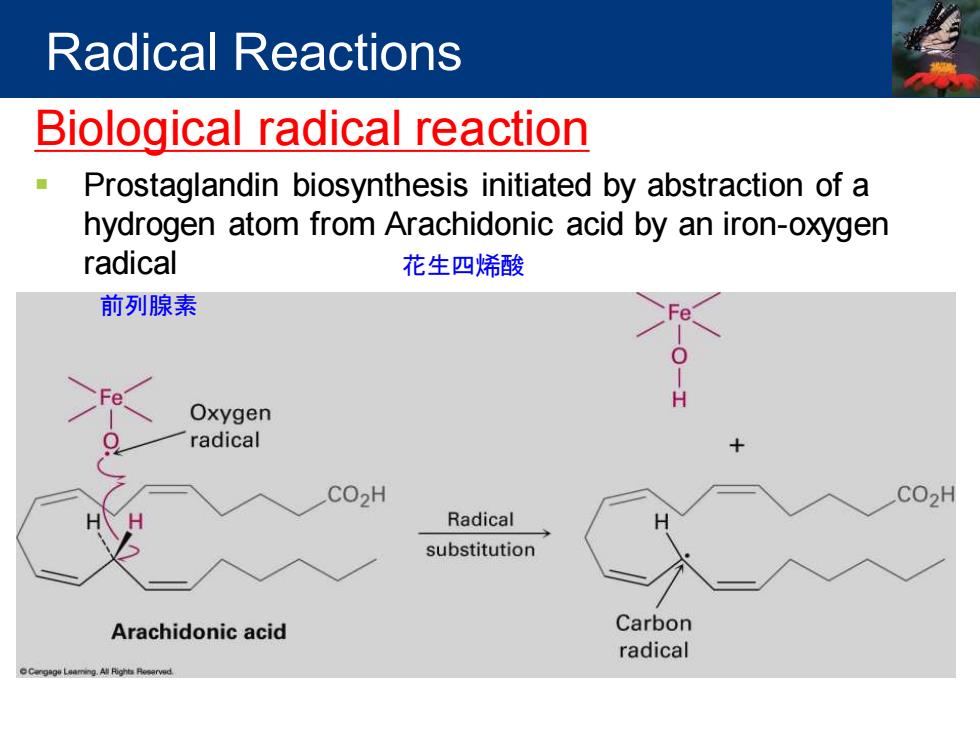
Radical Reactions Biological radical reaction ◆ Prostaglandin biosynthesis initiated by abstraction of a hydrogen atom from Arachidonic acid by an iron-oxygen radical 花生四烯酸 前列腺素 Oxygen radical CO2H CO2H Radical substitution Arachidonic acid Carbon radical
Biological radical reaction ▪ Prostaglandin biosynthesis initiated by abstraction of a hydrogen atom from Arachidonic acid by an iron-oxygen radical Radical Reactions 花生四烯酸 前列腺素
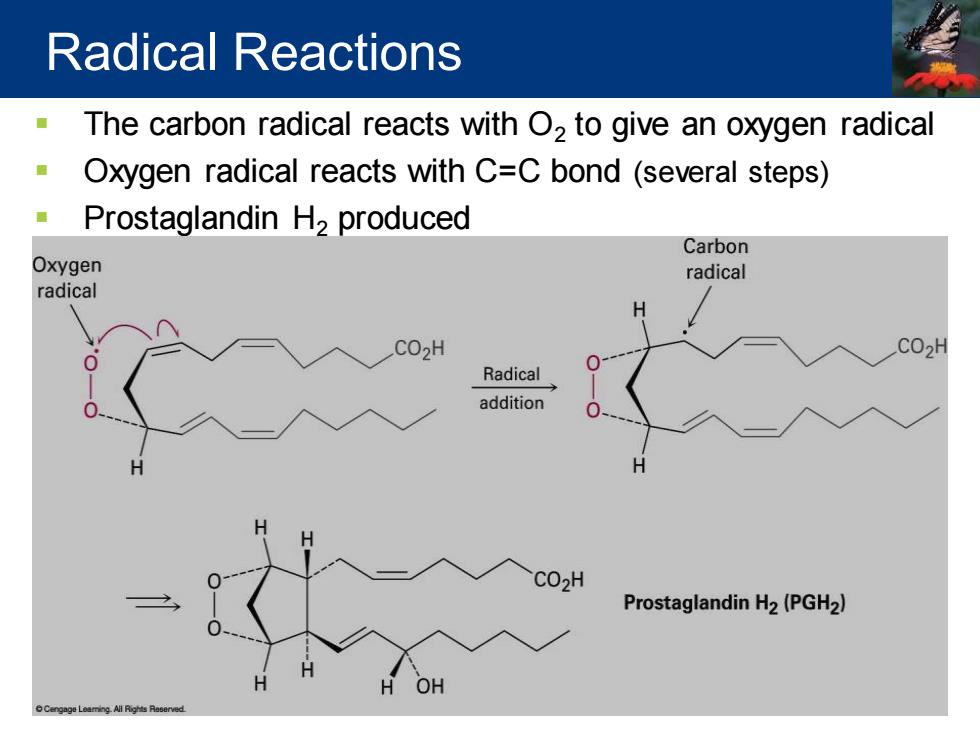
Radical Reactions The carbon radical reacts with O2 to give an oxygen radical Oxygen radical reacts with C=C bond (several steps) Prostaglandin H2 produced Carbon Oxygen radical radical H CO2H CO2H Radical addition CO2H Prostaglandin H2(PGH2) OH
▪ The carbon radical reacts with O2 to give an oxygen radical ▪ Oxygen radical reacts with C=C bond (several steps) ▪ Prostaglandin H2 produced Radical Reactions
6-4 Polar Reactions Polar reactions Occur because of electrical attraction between positively polarized and negatively polarized centers on functional groups in molecules Bond polarity 。 Most organic compounds are electrically neutral,they have no net charge Certain bonds within a molecule are polar Consequence of an unsymmetrical electron distribution in a bond Due to the difference in electronegativity of the bonded atoms
Polar reactions • Occur because of electrical attraction between positively polarized and negatively polarized centers on functional groups in molecules Bond polarity • Most organic compounds are electrically neutral, they have no net charge • Certain bonds within a molecule are polar • Consequence of an unsymmetrical electron distribution in a bond • Due to the difference in electronegativity of the bonded atoms. 6-4 Polar Reactions