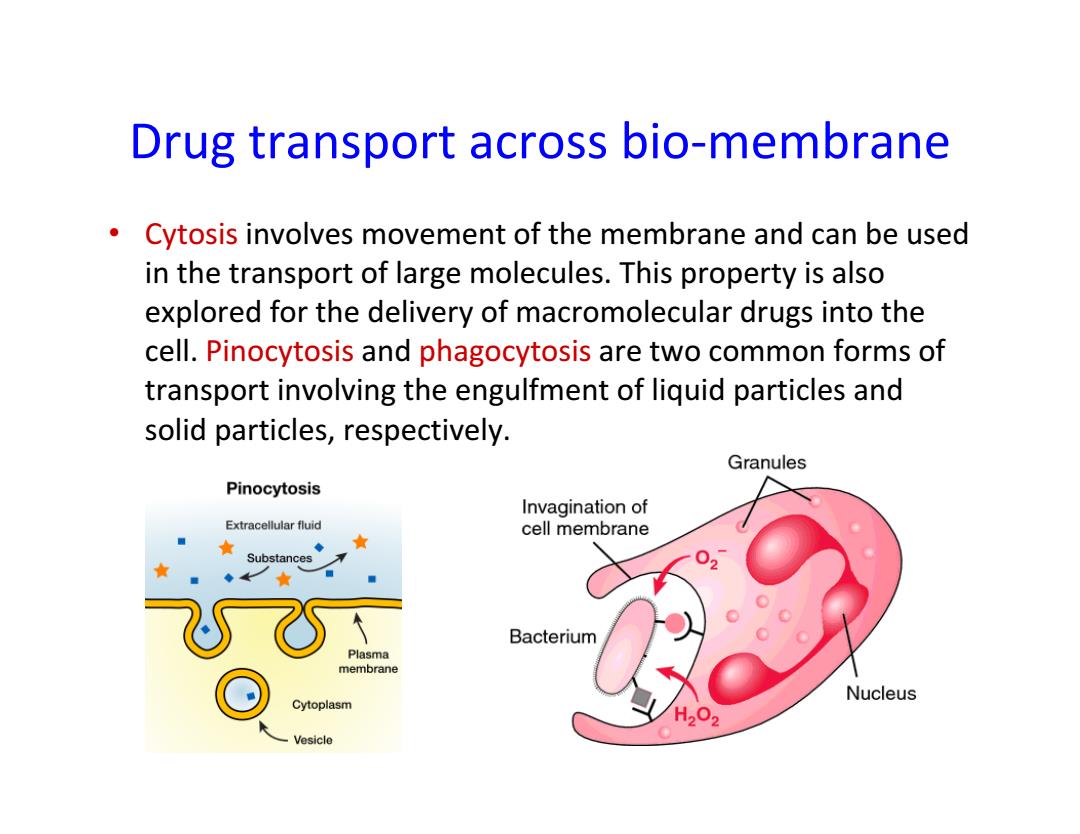
Drug transport across bio-membrane Cytosis involves movement of the membrane and can be used in the transport of large molecules.This property is also explored for the delivery of macromolecular drugs into the cell.Pinocytosis and phagocytosis are two common forms of transport involving the engulfment of liquid particles and solid particles,respectively. Granules Pinocytosis Invagination of Extracellular fluid cell membrane Substances Bacterium Plasma membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm H202 Vesicle
Drug transport across bio‐membrane • Cytosis involves movement of the membrane and can be used in the transport of large molecules. This property is also explored for the delivery of macromolecular drugs into the cell. Pinocytosis and phagocytosis are two common forms of transport involving the engulfment of liquid particles and solid particles, respectively

Absorption:how pH affects it Effect of pH on absorption of weak acids and bases: Many drugs are weak acids(HA)or weak bases(BH+).For a weak acid,when pH pK(pK,or pKa:equilibrium constant of a drug),the protonated form(non-ionized form)predominates.Raising the pH will make a weak acid to donate hydrogen ion and become unprotonated (ionized): HA台H++A A drug passes through biological membrane more easily when it is uncharged (that is,non-ionized),because an uncharged drug is more lipid-soluble.lonized molecules have difficult to pass through biological membrane,a phenomenon termed "ion trapping". When pH pK,there are equal amount of weak acid in the ionized and non-ionized form (Figure).Reducing pH will make more of the weak acid in non-ionized form
Absorption: how pH affects it