
凯氏带 具厚次生 壁的木质部 细胞途径 韧皮部 (戈质体和 避过藏) 皮 根形 表良 内斑层 中柱 质外体递径 觀任带 图1-6根部吸水的途径
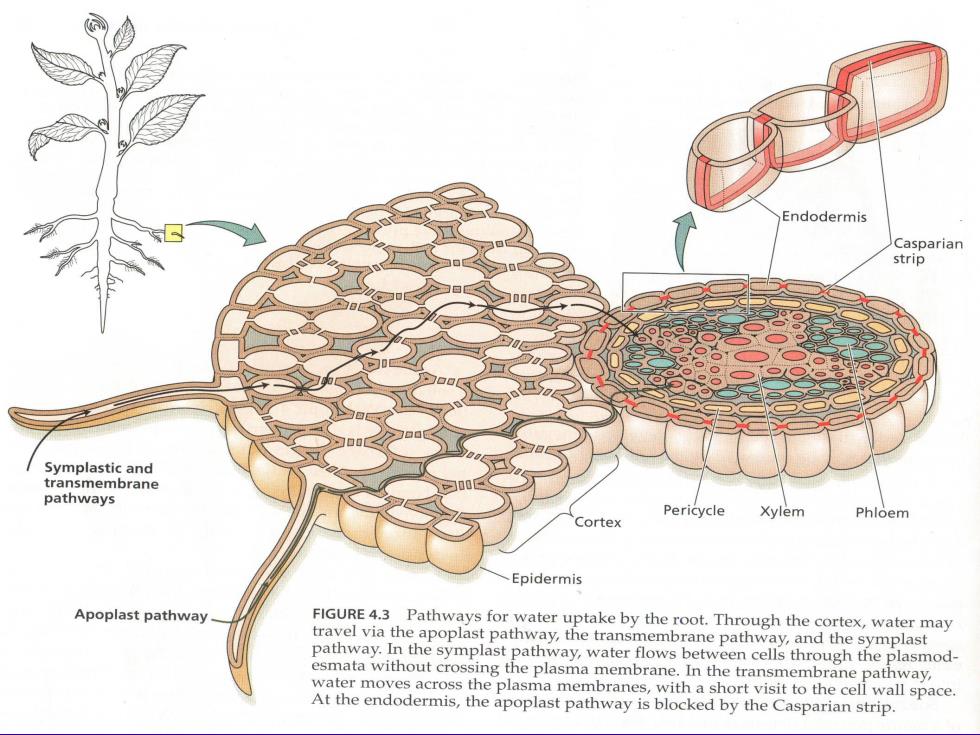
Endodermis Casparian strip Symplastic and transmembrane pathways Pericycle Xylem Cortex Phloem Epidermis Apoplast pathway FIGURE 4.3 Pathways for water uptake by the root.Through the cortex,water may travel via the apoplast pathway,the transmembrane pathway,and the symplast pathway.In the symplast pathway,water flows between cells through the plasmod esmata without crossing the plasma membrane.In the transmembrane pathway, water moves across the plasma membranes,with a short visit to the cell wall space. At the endodermis,the apoplast pathway is blocked by the Casparian strip

三、根系吸水的机理 根据吸水的动力植物根系吸水的方式有两种: 主动吸水 被动吸水 主要方式
三、根系吸水的机理 根据吸水的动力植物根系吸水的方式有两种: 主动吸水 被动吸水 主要方式

(一)根压与主动吸水 1.根压 主动吸水是由于根系本身生理活动引起的水分吸收, 一般认为主动吸水的动力是根压。 根压(root pressure)——由于植物根系生理活 动产生的促使水分从根部上升的压力
(一)根压与主动吸水 1.根压 主动吸水是由于根系本身生理活动引起的水分吸收, 一般认为主动吸水的动力是根压。 根压(root pressure)——由于植物根系生理活 动产生的促使水分从根部上升的压力

伤流 吐水 证实根压存在的两种现象: 如果从植物的茎基部靠近地 面的部位切断,不久可看到 有液滴从伤口流出。这种从 受伤或折断的植物组织中溢 出液体的现象,叫做伤流 (bleeding)。流出的汁液是 伤流液(bleeding sap)
伤流 吐水 证实根压存在的两种现象: 如果从植物的茎基部靠近地 面的部位切断,不久可看到 有液滴从伤口流出。这种从 受伤或折断的植物组织中溢 出液体的现象,叫做伤流 (bleeding)。流出的汁液是 伤流液(bleeding sap)