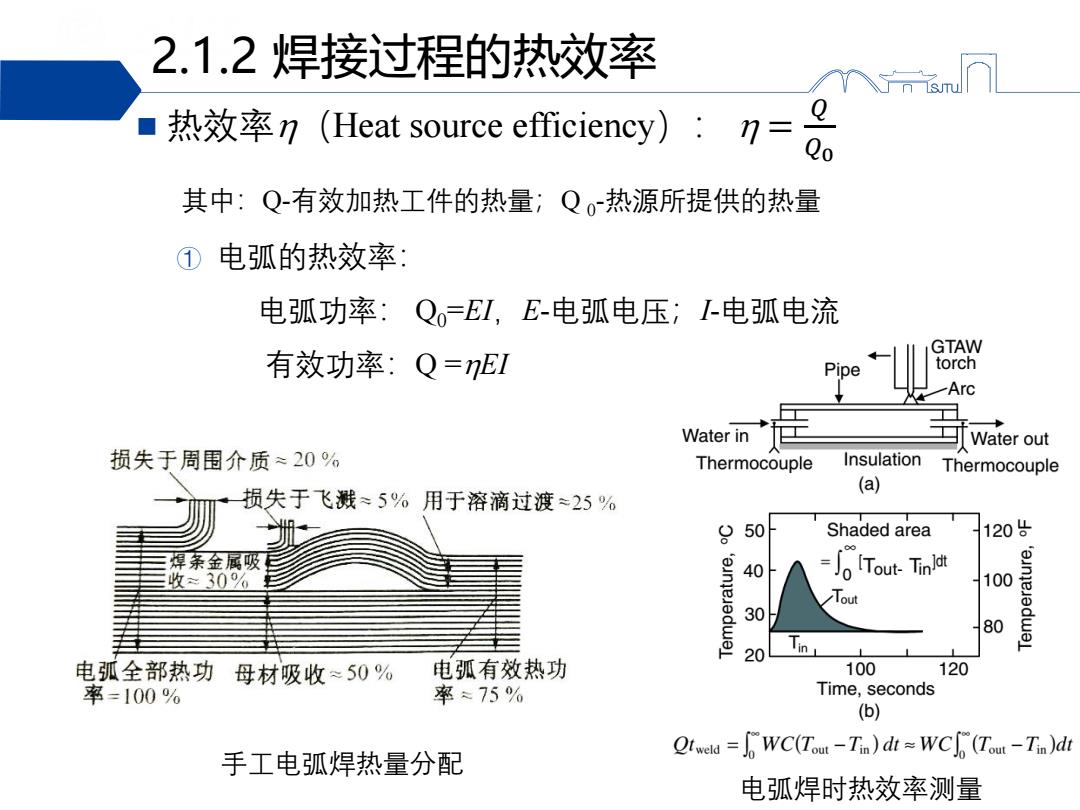
2.1.2焊接过程的热效率 个sm 热效率n(Heat source efficiency):7= Q Qo 其中:Q-有效加热工件的热量;Q。-热源所提供的热量 ①电弧的热效率: 电弧功率:Q=E1,E-电弧电压;I电弧电流 GTAW 有效功率:Q=nE1 Pipe torch Arc Water in Water out 损失于周围介质≈20% Thermocouple Insulation Thermocouple 损失于飞溅≈5%用于溶滴过渡25% (a) 9 50 Shaded area 120÷ 焊条金属吸 收30% 40 Tout-Tin 100 'eunje Tout 30 80 20 in 电弧全部热功 母材吸收≈50% 电弧有效热功 100 120 率=100% 率75% Time,seconds (b) Qiea=DWC(Tout-Tn)d≈WC(Tut-Tn)dh 手工电弧焊热量分配 电弧焊时热效率测量
2.1.2 焊接过程的热效率 热效率(Heat source efficiency): = 𝑄 𝑄0 其中:Q-有效加热工件的热量;Q 0 -热源所提供的热量 ① 电弧的热效率: 电弧功率: Q0=EI,E-电弧电压;I-电弧电流 有效功率:Q =EI 电弧焊时热效率测量 手工电弧焊热量分配

2.1.2焊接过程的热效率 (cont'd 不同焊接方法的电弧热效率? 焊接 厚皮焊条手 自动埋 电渣 电子束及 钨极缸弧焊 熔化氯弧焊 碳弧焊 方法 工电弧焊 弧焊 焊 激光束 交流 直流 钢 铝 0.5≈ 0.77≈ 0.77≈ 0.68- 0.78 0.66- 0.70~ n 0.83 >0.9 0.65 0.87 0.90 0.85 0.85 0.69 0.85 Increasing 电子束的热 damage to 热损失少 workpiece 激光的热效 激光的吸收 gas welding 1.0 0.8 arc welding 0.6 入 0.4 indu!jeeH Increasing penetration, 0.2 welding speed, weld quality, LBW PAW G high energy equipment cost beam welding Heat source efficiencie Power density of heat source Current.A
2.1.2 焊接过程的热效率(cont’d) ② 电子束的热效率:能量集中, 热损失少 ③ 激光的热效率:取决于工件对 激光的吸收程度 Heat source efficiencies in several welding processes
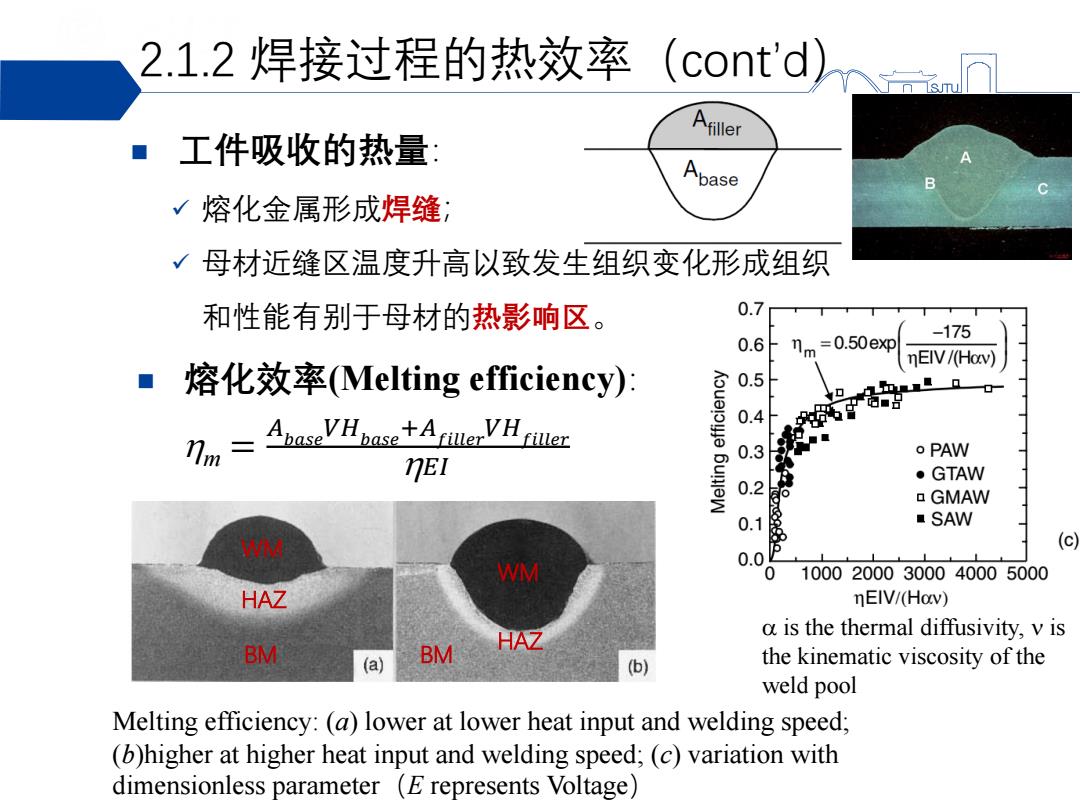
2.1.2焊接过程的热效率(cont'd) sm 工件吸收的热量: √熔化金属形成焊缝; √母材近缝区温度升高以致发生组织变化形成组织 和性能有别于母材的热影响区。 0.7 TIm=0.50exp -175 0.6 mEIV/(Hav) ■熔化效率(Melting efficiency): 0.5 IsAeV He 0.4 E话日0 0.3 o PAW 7E1 ·GTAW 0.2 aGMAW 0.1 SAW (c) 0.0 WM 10002000300040005000 HAZ mEIV/(Hov) a is the thermal diffusivity,v is BM HAZ (a) BM (b) the kinematic viscosity of the weld pool Melting efficiency:(a)lower at lower heat input and welding speed; (b)higher at higher heat input and welding speed;(c)variation with dimensionless parameter (E represents Voltage)
工件吸收的热量: 熔化金属形成焊缝; 母材近缝区温度升高以致发生组织变化形成组织 和性能有别于母材的热影响区。 2.1.2 焊接过程的热效率(cont’d) 熔化效率(Melting efficiency): m = 𝐴𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒𝑉𝐻𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒+𝐴𝑓𝑖𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟𝑉𝐻𝑓𝑖𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑟 𝐸𝐼 Melting efficiency: (a) lower at lower heat input and welding speed; (b)higher at higher heat input and welding speed; (c) variation with dimensionless parameter(E represents Voltage) is the thermal diffusivity, is the kinematic viscosity of the weld pool HAZ HAZ WM WM BM BM
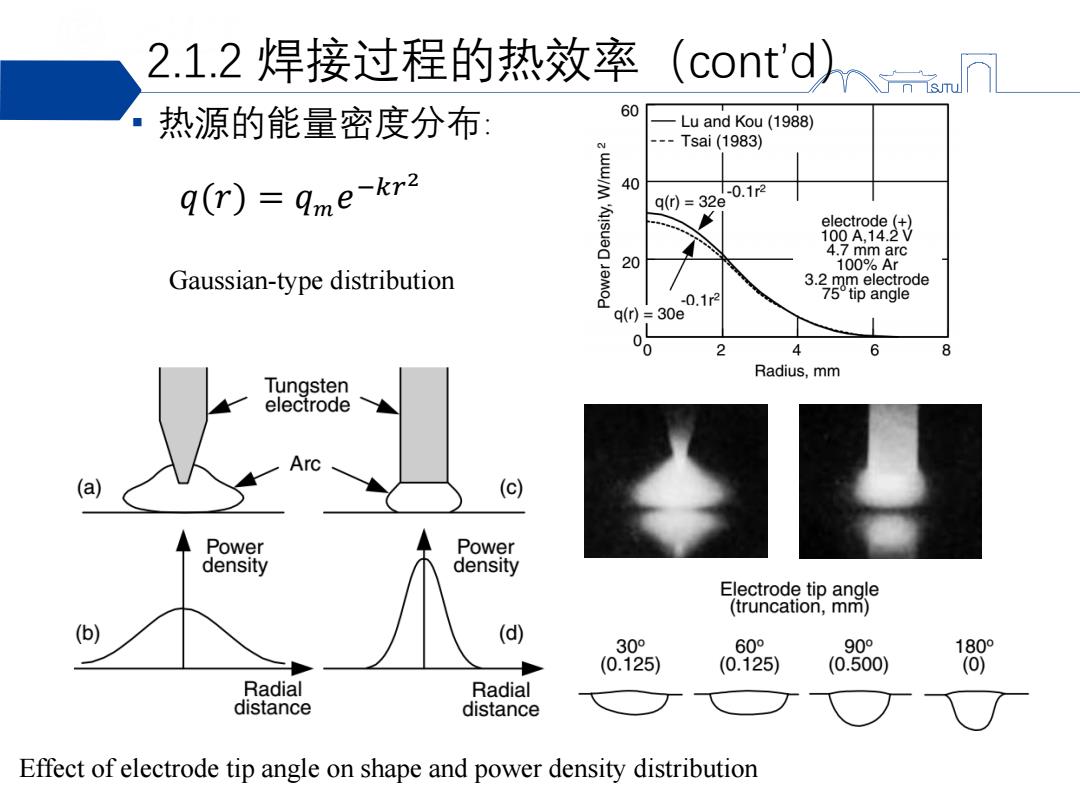
2.1.2焊接过程的热效率 (cont'd 热源的能量密度分布: 60 Lu and Kou(1988) ce Tsai(1983) q(r)=9me-kr2 40 0.1r2 q0)=32e electrode (+ 100A,14.2V 4.7 mm arc 20 100%Ar Gaussian-type distribution 3.2 mm electrode 0.1r2 75°tip angle q(r)=30 00 6 8 Radius,mm Tungsten electrode Arc a) (c) Power Power density density Electrode tip angle (truncation,mm) (b) (d) 30° 60° 90° 180° (0.125) (0.125) (0.500) (O) Radial Radial distance distance Effect of electrode tip angle on shape and power density distribution
2.1.2 焊接过程的热效率(cont’d) ▪ 热源的能量密度分布: Effect of electrode tip angle on shape and power density distribution 𝑞(𝑟) = 𝑞𝑚𝑒 −𝑘𝑟 2 Gaussian-type distribution

2.1.3焊接温度场 ·热量的传递基本方式: √传导、对流、辐射 ·熔化焊接过程中热传递方式 √大多数热源:以对流、辐射为主来传递热量 √金属内部:以热传导为主传递热能 ·电弧焊为例: √电弧以对流、辐射传递热量给工件、焊条(焊丝) √工件内部、焊条中热的传播则以热传导为主
2.1.3 焊接温度场 ▪ 热量的传递基本方式: 传导、对流、辐射 ▪ 熔化焊接过程中热传递方式 大多数热源:以对流、辐射 为主来传递热量 金属内部:以热传导 为主传递热能 ▪ 电弧焊为例: 电弧以对流、辐射传递热量给工件、焊条(焊丝) 工件内部、焊条中热的传播则以热传导为主