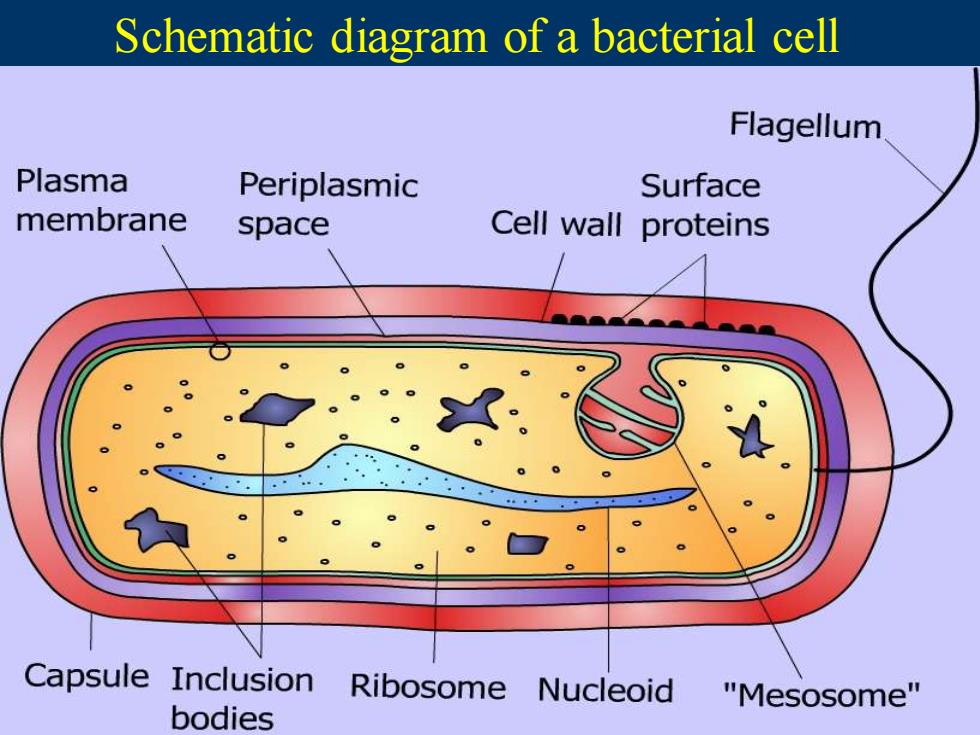
Schematic diagram of a bacterial cell Flagellum Plasma Periplasmic Surface membrane space Cell wall proteins Capsule Inclusion Ribosome Nucleoid "Mesosome" bodies
Schematic diagram of a bacterial cell
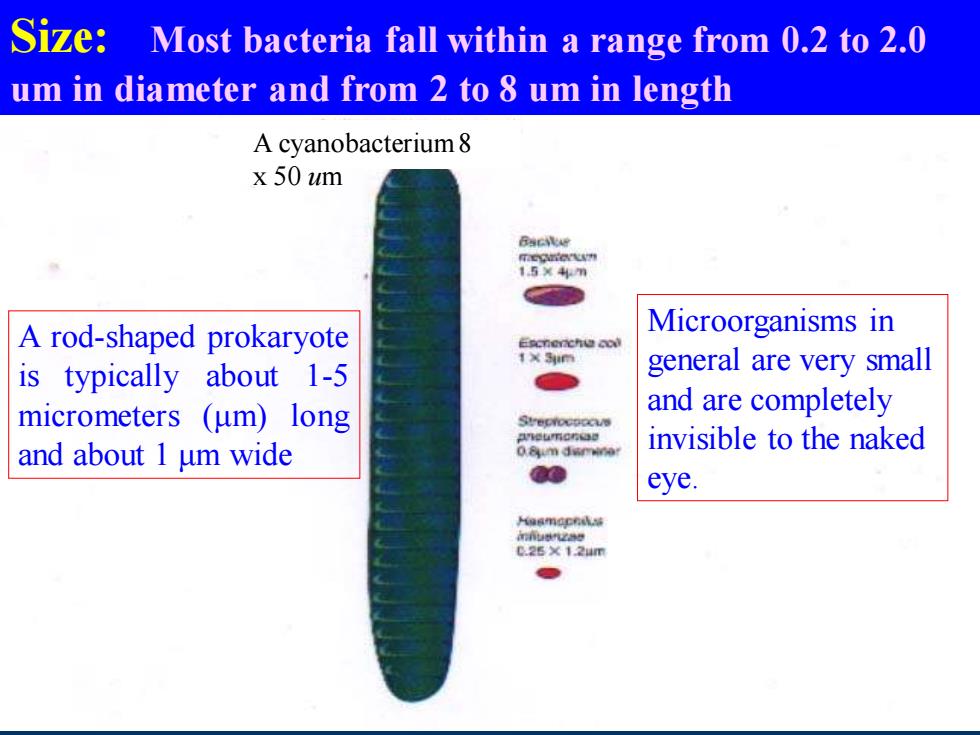
Size:Most bacteria fall within a range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and from 2 to 8 um in length A cyanobacterium8 x 50 um BscNe 1544m A rod-shaped prokaryote Microorganisms in Escnerchu cod 1×利m is typically about 1-5 general are very small micrometers (um)long and are completely eu有C量 and about 1 um wide 0.8um dumin invisible to the naked eye. 每餐m工有城 0.26×124m
Size: Most bacteria fall within a range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and from 2 to 8 um in length A rod-shaped prokaryote is typically about 1-5 micrometers (μm) long and about 1 μm wide Microorganisms in general are very small and are completely invisible to the naked eye. A cyanobacterium 8 x 50 um
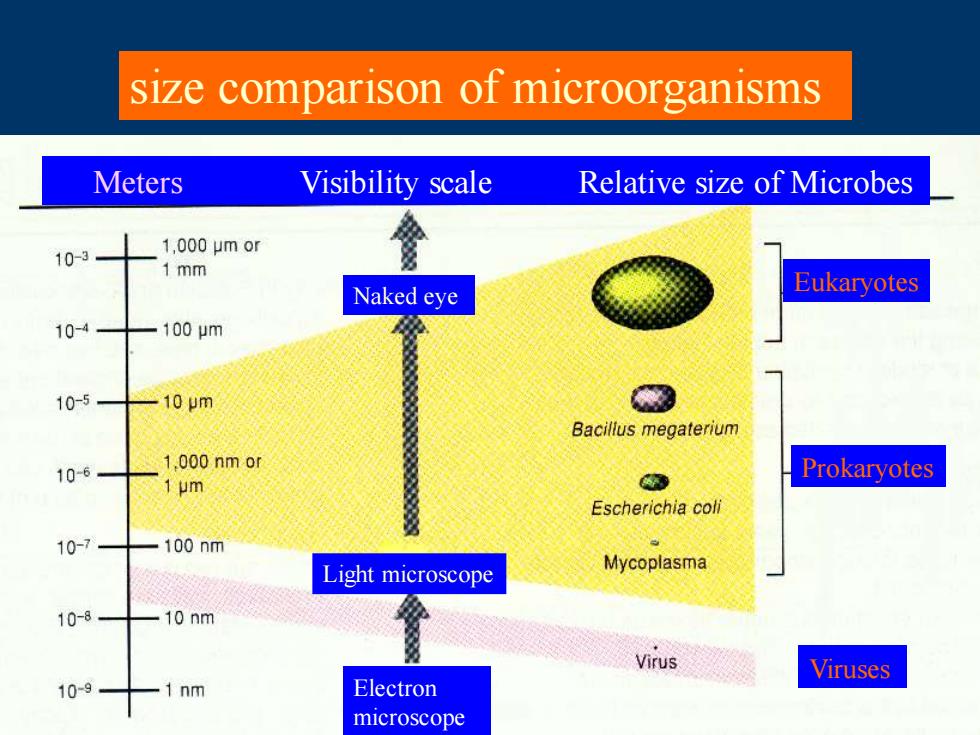
size comparison of microorganisms Meters Visibility scale Relative size of Microbes 10-3 1,000μmor 1 mm Naked eye Eukaryotes 10-4 100m 10-5 10m Bacillus megaterium 10-6 1.000 nm or Prokaryotes 1 um Escherichia coli 10-7 100nm Light microscope Mycoplasma 10-8 10 nm Virus Viruses 10-9 1nm Electron microscope
size comparison of microorganisms Meters Visibility scale Relative size of Microbes Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Viruses Naked eye Light microscope Electron microscope
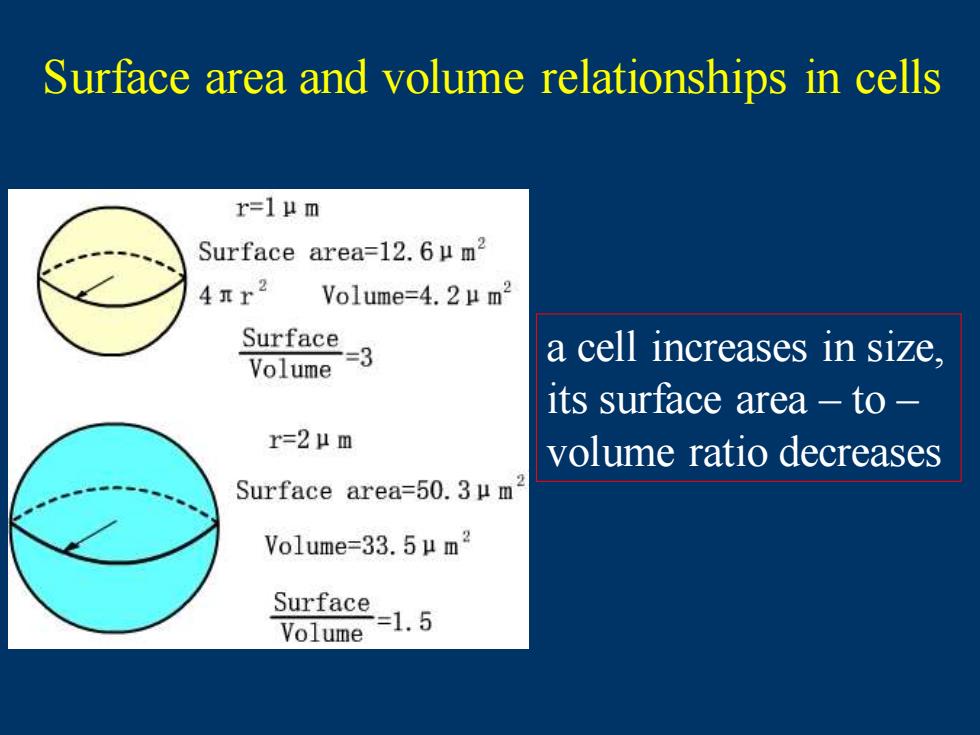
Surface area and volume relationships in cells r=1μm Surface area=l2.6μm2 4nr2 Volume=4.2μm2 Surface Volume 另 a cell increases in size, its surface area to r=2μm volume ratio decreases Surface area=50.3μm Volume=-33.5μm2 Surface=1.5 Volume
a cell increases in size, its surface area – to – volume ratio decreases Surface area and volume relationships in cells
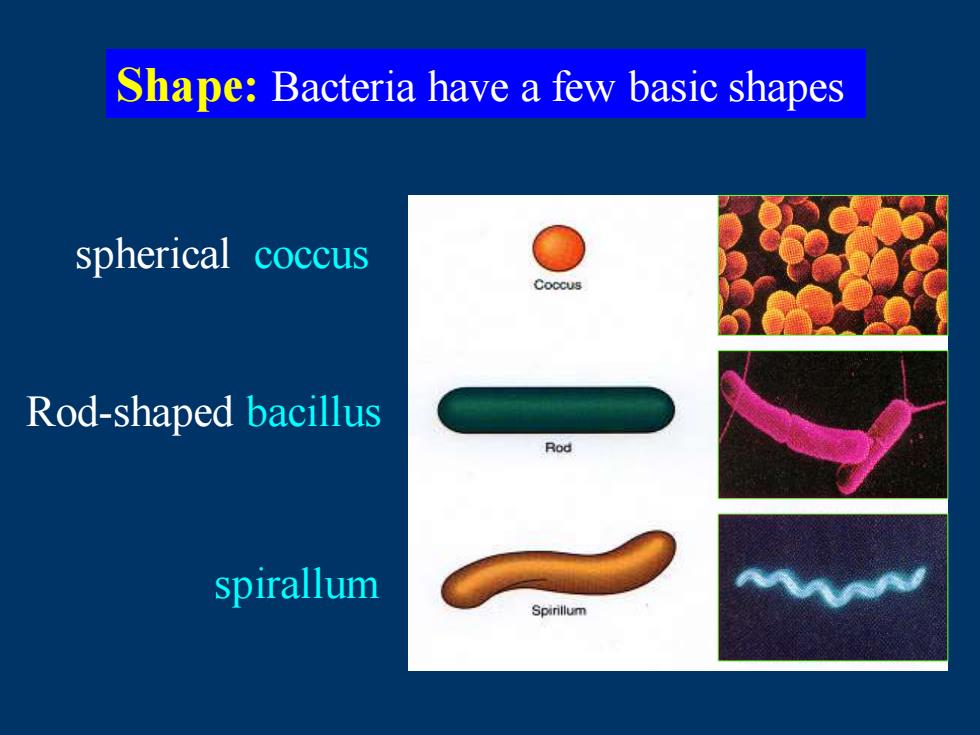
Shape:Bacteria have a few basic shapes spherical coccus Coccus Rod-shaped bacillus Ro spirallum
spirallum Shape: Bacteria have a few basic shapes spherical coccus Rod-shaped bacillus