
Observing the dendrites and SEl BATTERIES Atomic structure of sensitive battery materials and interfaces revealed by cryo-electron microscopy Yuzhang Li,*Yanbin Li,1*Allen Pei,Kai Yan,Yongming Sun,1 Chun-Lan Wu,1 Lydia-Marie Joubert,2 Richard Chin,Ai Leen Koh,Yi Yu,*John Perrino,2 Benjamin Butz,15 Steven Chu,6.7 Yi Cuils Yi CUI Li et al.,Science 358,506-510(2017) Whereas standard transmission electron microscopy studies are unable to preserve the native state of chemically reactive and beam-sensitive battery materials after operation,such materials remain pristine at cryogenic conditions.It is then possible to atomically resolve individual lithium metal atoms and their interface with the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI).We observe that dendrites in carbonate-based electrolytes grow along the <111>(preferred).<110>,or <211>directions as faceted,single-crystalline nanowires.These growth directions can change at kinks with no observable crystallographic defect.Furthermore,we reveal distinct SEl nanostructures formed in different electrolytes. 6
6 Observing the dendrites and SEI Yi CUI
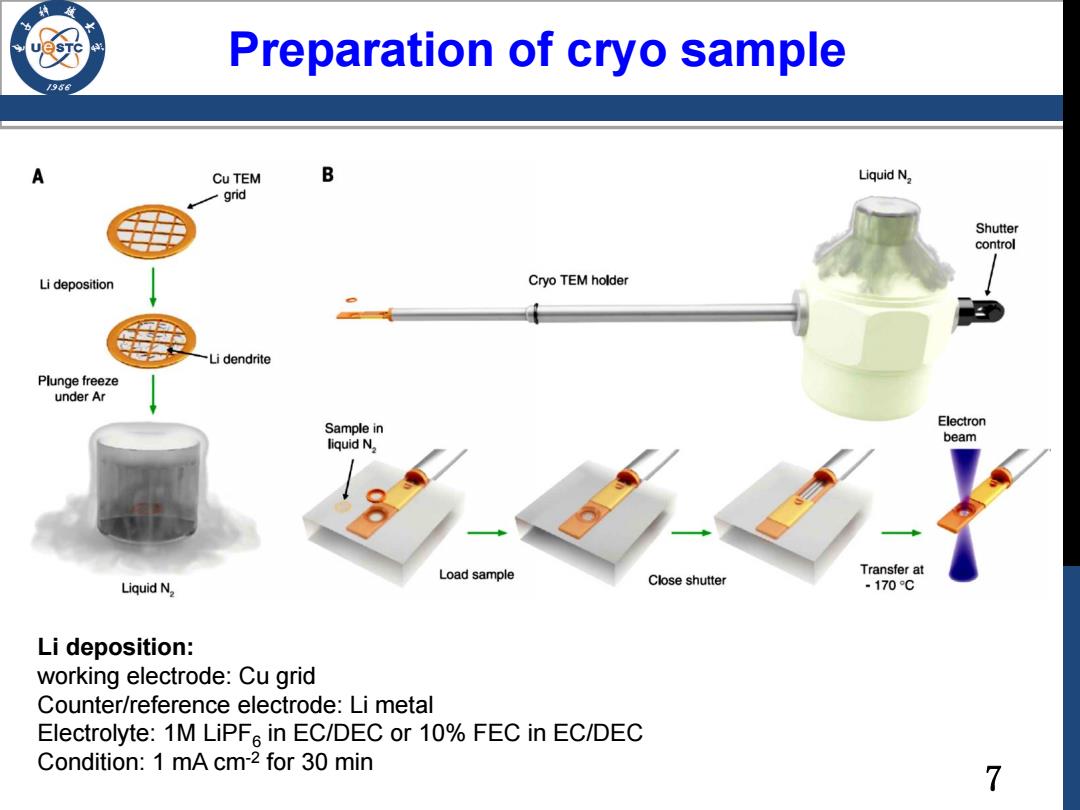
Preparation of cryo sample /98 A Cu TEM B Liquid N2 -grid Shutter control Li deposition Cryo TEM holder Li dendrite Plunge freeze under Ar Sample in Electron liquid N. beam Load sample Transfer at Liquid N2 Close shutter -170C Li deposition: working electrode:Cu grid Counter/reference electrode:Li metal Electrolyte:1M LiPF in EC/DEC or 10%FEC in EC/DEC Condition:1 mA cm-2 for 30 min 7
7 Preparation of cryo sample Li deposition: working electrode: Cu grid Counter/reference electrode: Li metal Electrolyte: 1M LiPF6 in EC/DEC or 10% FEC in EC/DEC Condition: 1 mA cm-2 for 30 min
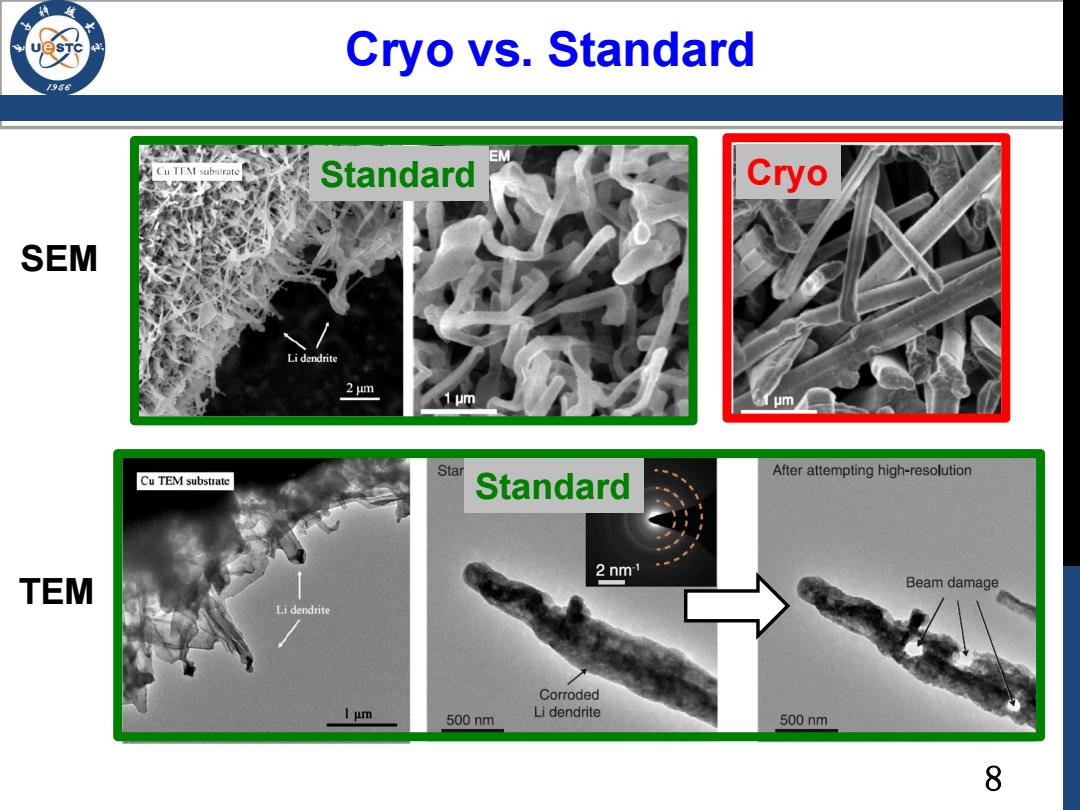
Cryo vs.Standard /986 医M EM Cu TTM subsirate Standard Cryo SEM Li dendrite 2 um 1μm um After attempting high-resolution Cu TEM substrate Star Standard 2 nm TEM Beam damage Li dendrite Corroded 1μm 500nm Li dendrite 500nm 8
8 Cryo vs. Standard SEM TEM Standard Cryo Standard