
Lecture 2 196 Introduction of Lithium Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.03
Introduction of Lithium Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.03 Lecture 2

Content /986 Important Terms of batteries Why lithium batteries? Necessity,and advantage Different types of lithium batteries Primary and secondary/rechargeable ·Working mechanism How they store charges 2
2 Content • Important Terms of batteries • Why lithium batteries? • Necessity, and advantage • Different types of lithium batteries • Primary and secondary/rechargeable • Working mechanism • How they store charges
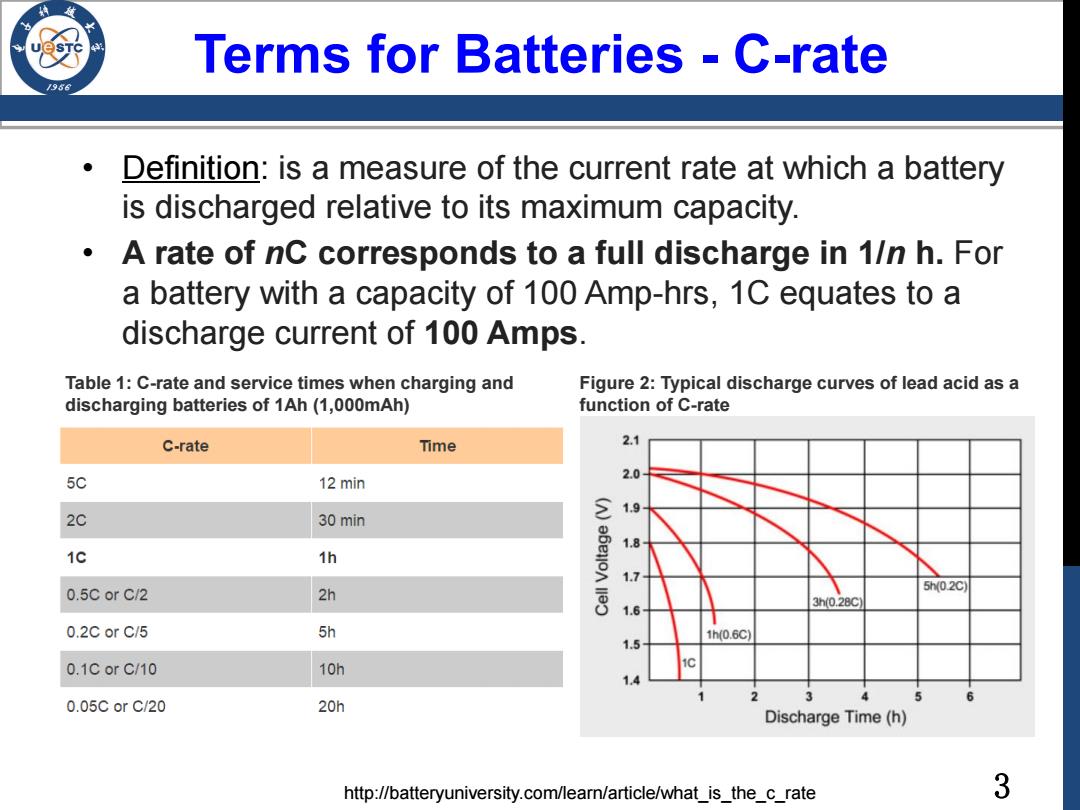
Terms for Batteries -C-rate Definition:is a measure of the current rate at which a battery is discharged relative to its maximum capacity. A rate of nC corresponds to a full discharge in 1/n h.For a battery with a capacity of 100 Amp-hrs,1C equates to a discharge current of 100 Amps. Table 1:C-rate and service times when charging and Figure 2:Typical discharge curves of lead acid as a discharging batteries of 1Ah(1,000mAh) function of C-rate C-rate Time 2.1 5C 2.0 12 min 1.9 2C 30 min 1.8 1c 1h 1.7 0.5C or C/2 2h 5h0.2c 3h0.28c 1.6 0.2C or C/5 5h 1h(0.6C) 1.5 0.1CorC/10 10h 1.4 0.05CorC/20 20h Discharge Time (h) http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/what_is_the_c_rate 3
3 Terms for Batteries - C-rate • Definition: is a measure of the current rate at which a battery is discharged relative to its maximum capacity. • A rate of nC corresponds to a full discharge in 1/n h. For a battery with a capacity of 100 Amp-hrs, 1C equates to a discharge current of 100 Amps. Table 1: C-rate and service times when charging and discharging batteries of 1Ah (1,000mAh) Figure 2: Typical discharge curves of lead acid as a function of C-rate http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/what_is_the_c_rate

Terms for Batteries Over discharge: Definition:during discharge,if the battery continues to discharge even beyond the discharge voltage limit the reversibility of both electrode materials will be damaged,leading to a decreased battery capacity Overcharge: Definition:during charge,if the battery continues to charge even after the capacity is full,the battery would likely to suffer from deformation or electrolyte leakage with a significantly deteriorated performance. 4
4 Terms for Batteries • Over discharge: • Definition: during discharge, if the battery continues to discharge even beyond the discharge voltage limit, the reversibility of both electrode materials will be damaged, leading to a decreased battery capacity . • Overcharge: • Definition: during charge, if the battery continues to charge even after the capacity is full, the battery would likely to suffer from deformation or electrolyte leakage with a significantly deteriorated performance
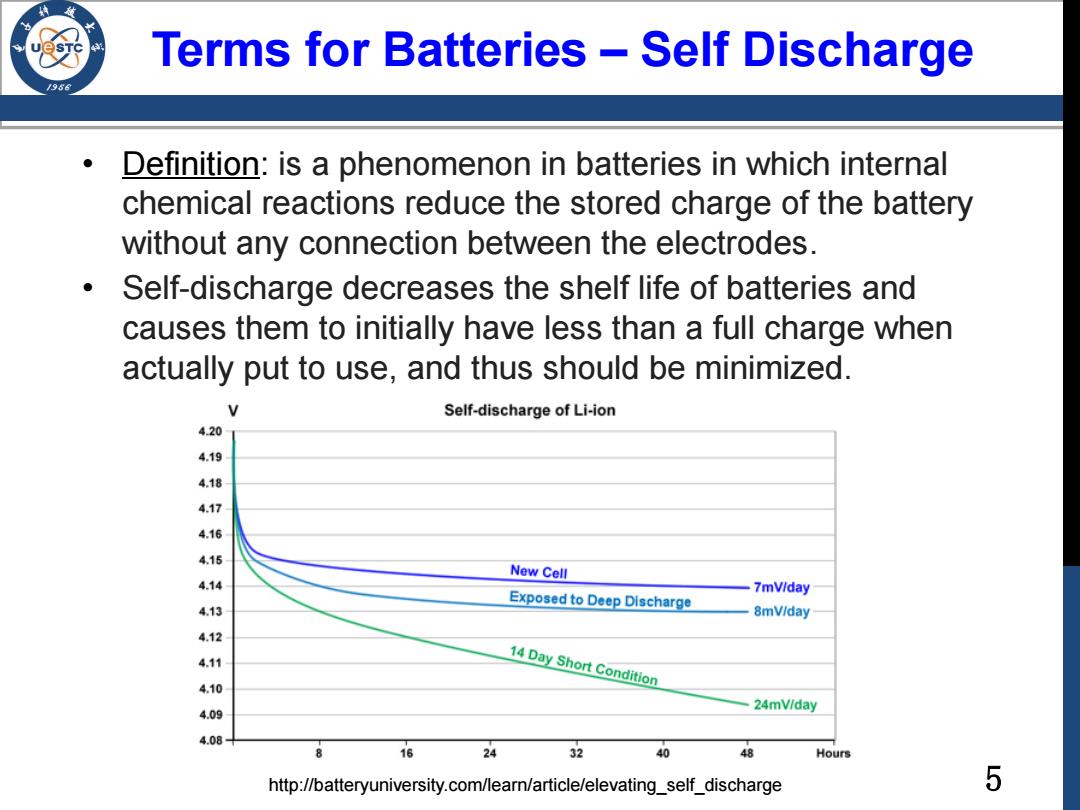
Terms for Batteries -Self Discharge /98 Definition:is a phenomenon in batteries in which internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes. Self-discharge decreases the shelf life of batteries and causes them to initially have less than a full charge when actually put to use,and thus should be minimized. Self-discharge of Li-ion 4.20 New Cell Exposed to Deep Discharge 7mViday 8mV/day 410 14 Day Short Condition 409 24mV/day 4.08 8 16 24 32 40 48 Hours http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/elevating_self_discharge 5
5 Terms for Batteries – Self Discharge • Definition: is a phenomenon in batteries in which internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes. • Self-discharge decreases the shelf life of batteries and causes them to initially have less than a full charge when actually put to use, and thus should be minimized. http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/elevating_self_discharge