
Lecture 8 196 Anode Material for LIBs: Silicon Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04
Anode Material for LIBs: Silicon Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04 Lecture 8

Content /986 Introduction of silicon 0 Chemistry of silicon Reaction mechanisms of silicon anode 。Problems Synthesis and modification methods One literature example 2
2 Content • Introduction of silicon • Chemistry of silicon • Reaction mechanisms of silicon anode • Problems • Synthesis and modification methods • One literature example
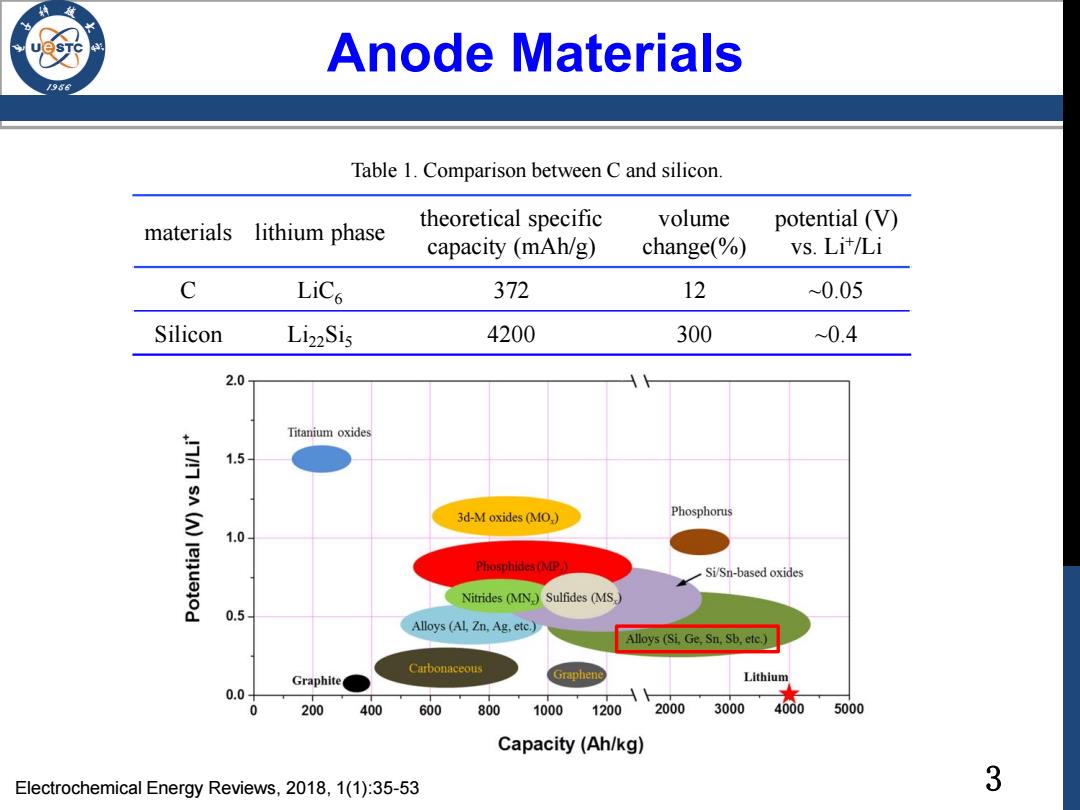
Anode Materials 936 Table 1.Comparison between C and silicon. materials lithium phase theoretical specific volume potential (V) capacity (mAh/g) change(%) vs.Lit/Li C LiCs 372 12 0.05 Silicon Li22Sis 4200 300 ~0.4 2.0 Titanium oxides 1.5 3d-M oxides(MO,) Phosphorus 1.0 Phosphides (MP. Si/Sn-based oxides Nitrides (MN,)Sulfides (MS,) 0.5 Alloys (AL,Zn.Ag.etc.) Alloys(Si.Ge,Sn,Sb,etc.) Carbonaceous Graphite Graphene Lithium 0.0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 2000 3000 4000 5000 Capacity(Ah/kg) Electrochemical Energy Reviews,2018,1(1):35-53 3
3 Anode Materials materials lithium phase theoretical specific capacity (mAh/g) volume change(%) potential (V) vs. Li+ /Li C LiC6 372 12 ~0.05 Silicon Li22Si5 4200 300 ~0.4 Table 1. Comparison between C and silicon. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2018, 1(1):35-53

Silicon Origin:widely distributed in dusts,sands,clay in the forms of silicon dioxide(silica)or silicates Characteristics:1.amorphous and crystalline silicon,2.diamond cubic crystal structure,3semiconductor (E=1.12 eV) Preparation:conversion of silica(SiO2) >Carbothermal reduction→SiO,+2C→Si+2CO2 SiC+SiO2→3Si+2C0 >Aluminothermal reduction-3 SiO,+4 Al->3 Si+2 Al2O3 quartz,agate,agate
4 Silicon • Origin:widely distributed in dusts, sands, clay in the forms of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates • Characteristics: 1. amorphous and crystalline silicon, 2. diamond cubic crystal structure, 3.semiconductor (Eg=1.12 eV) • Preparation:conversion of silica (SiO2 ) Carbothermal reduction → SiO2 + 2 C → Si + 2 CO2 SiC + SiO2 → 3 Si + 2 CO Aluminothermal reduction → 3 SiO2 + 4 Al → 3 Si + 2 Al2O3 quartz, agate, agate

Silicon Anode /98 The electrochemical reaction: >Si+4.4Li LiSi(fully lithiated state,each silicon atom can host 4.4 lithium atoms) Reversible process (lithiation/delithiation) >Lit ions insert into silicon and form Li-Si alloy(charge) Si→Li2.oSi→Li3sSi→Li44Si >Then deinsert from silicon and Li-Si dealloy (discharge) Li4,4Si→Li3sSi→Li2.oSi→Si 5
5 Silicon Anode • The electrochemical reaction: Si + 4.4Li+ ↔ Li4.4Si (fully lithiated state, each silicon atom can host 4.4 lithium atoms) • Reversible process (lithiation/delithiation) Li+ ions insert into silicon and form Li-Si alloy(charge) Si → Li2.0Si → Li3.5Si → Li4.4Si Then deinsert from silicon and Li-Si dealloy (discharge) Li4.4Si → Li3.5Si → Li2.0Si → Si