
9.2 The Efficiency of a Competitive Market Economic efficiency-Maximization of aggregate consumer and producer surplus. Market failure-Situation in which an unregulated competitive market is inefficient because prices fail to provide proper signals to consumers and producers. Externality-Action taken by either a producer or a consumer which affects other producers or consumers but is not accounted for by the market price
9.2 The Efficiency of a Competitive Market ❑ Economic efficiency-Maximization of aggregate consumer and producer surplus. ❑ Market failure-Situation in which an unregulated competitive market is inefficient because prices fail to provide proper signals to consumers and producers. ❑ Externality-Action taken by either a producer or a consumer which affects other producers or consumers but is not accounted for by the market price
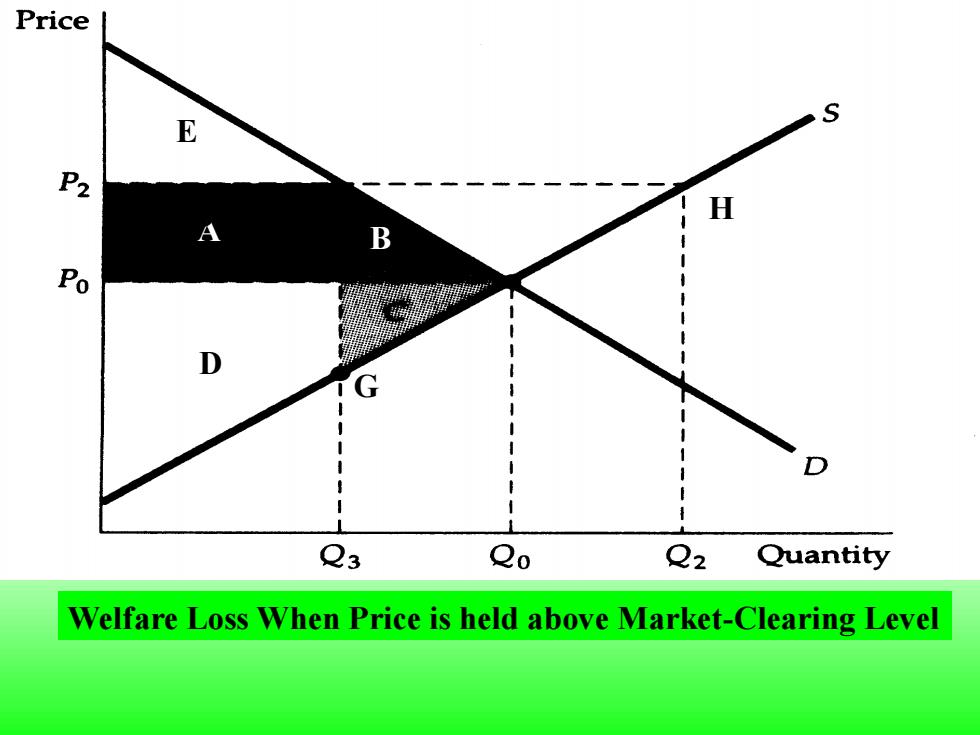
Price E P2 H Po D Q3 Qo Q2 Quantity Welfare Loss When Price is held above Market-Clearing Level
Welfare Loss When Price is held above Market-Clearing Level A B D D E G H

When price is regulated to be no lower than P2,only Q3 will be demanded.If Q;is produced,the deadweight loss is given by triangles B and C.At price P2,producers would like to produce more than Q:.If they do,the deadweight loss will be even larger
When price is regulated to be no lower than P2 , only Q3 will be demanded. If Q3 is produced, the deadweight loss is given by triangles B and C. At price P2 , producers would like to produce more than Q3 . If they do, the deadweight loss will be even larger
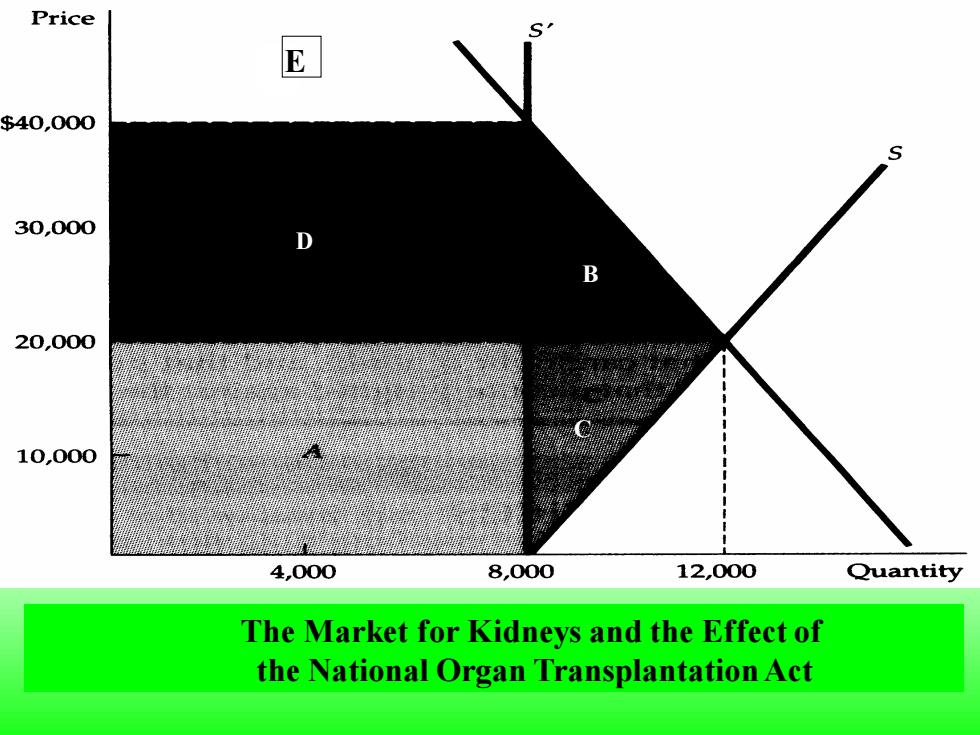
Price E $40,000 30,000 D B 20,000 10,000 4,000 8,000 12,000 Quantity The Market for Kidneys and the Effect of the National Organ Transplantation Act
The Market for Kidneys and the Effect of the National Organ Transplantation Act C B D EED

The market-clearing price is $20,000;at this price,about 12,000 kidneys per year would be supplied.The act effectively makes the price zero.About 8000 kidneys per year are still donated; this constrained supply is shown as S'.The loss to suppliers is given by rectangle A and triangle C. If consumer received kidney at no cost,their gain would be given by rectangle A less triangle B
The market-clearing price is $20,000; at this price, about l2,000 kidneys per year would be supplied. The act effectively makes the price zero. About 8000 kidneys per year are still donated; this constrained supply is shown as S'. The loss to suppliers is given by rectangle A and triangle C. If consumer received kidney at no cost, their gain would be given by rectangle A less triangle B