
●Deadweight loss(无谓损失)-Net loss of total(consumer plus producer)surplus. The price of a good has been regulated to be no higher than Pmax,Which is below the market-clearing price Po. The gain to consumers is the difference between rectangle A and triangle B(A-B). The loss to producers is the sum of rectangle A and triangle C (A+C).Triangles B and C together measure the deadweight loss from price controls(B+C)
⚫ Deadweight loss (无谓损失) - Net loss of total (consumer plus producer)surplus. ◆The price of a good has been regulated to be no higher than Pmax, which is below the market-clearing price P0 . The gain to consumers is the difference between rectangle A and triangle B (A-B). The loss to producers is the sum of rectangle A and triangle C (A+C). Triangles B and C together measure the deadweight loss from price controls (B+C)
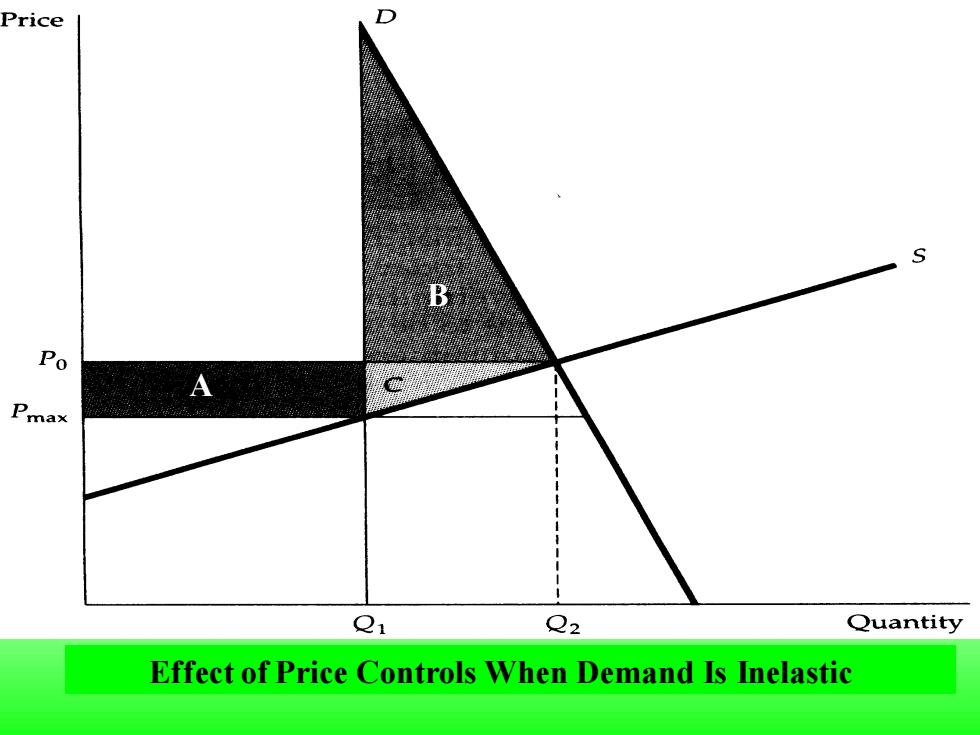
Price D S Po Pmax Q1 Q2 Quantity Effect of Price Controls When Demand Is Inelastic
Effect of Price Controls When Demand Is Inelastic B A

If demand is sufficiently inelastic,triangle B can be larger than rectangle A.In this case,consumers suffer a net loss from price controls
If demand is sufficiently inelastic, triangle B can be larger than rectangle A. In this case, consumers suffer a net loss from price controls
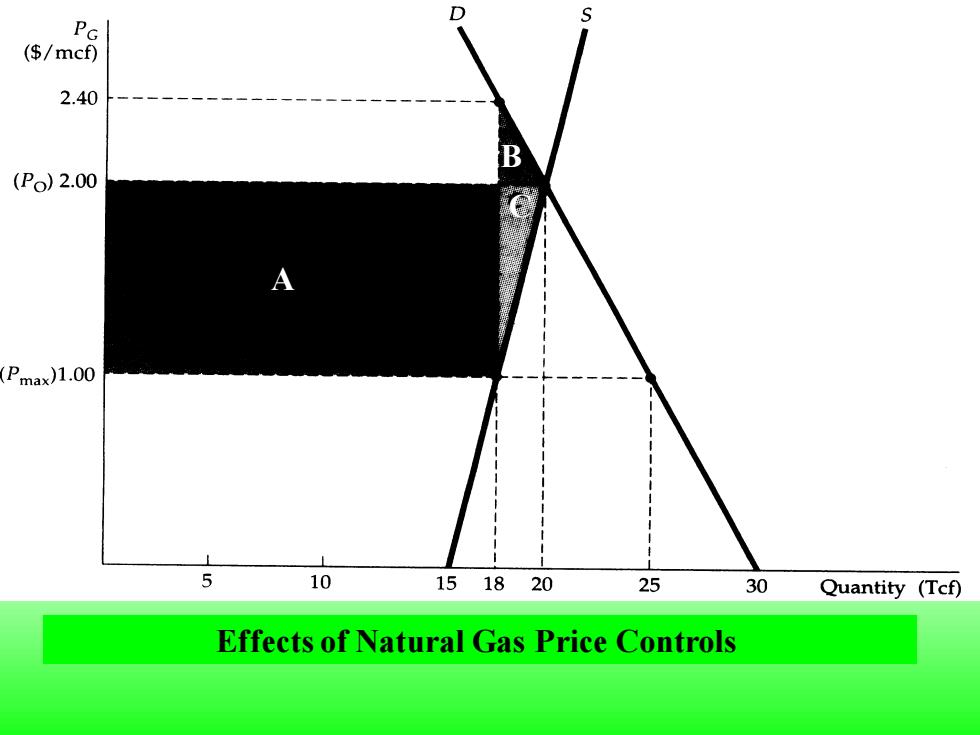
D PG ($/mcf) 2.40 B (Po)2.00 (Pmax)1.00 10 151820 25 30 Quantity (Tcf) Effects of Natural Gas Price Controls
Effects of Natural Gas Price Controls A A B C

The market-clearing price of natural gas is $2 per mef,and the maximum allowable price is $1.A shortage of 25-18=7 Tcf results.The gain to consumers is rectangle A minus triangle B, and the loss to producers is rectangle A plus triangle C
The market-clearing price of natural gas is $2 per mcf, and the maximum allowable price is $1. A shortage of 25-18 = 7 Tcf results. The gain to consumers is rectangle A minus triangle B, and the loss to producers is rectangle A plus triangle C