
Organic Chemistry,5th Edition HC一H L.G.Wade,Jr. H Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Tools for Study HC+一H H To determine a reaction's mechanism,look at: >Equilibrium constant >Free energy change >Enthalpy >Entropy >Bond dissociation energy >Kinetics >Activation energy => Chapter 4 2
Chapter 4 2 Tools for Study • To determine a reaction’s mechanism, look at: ➢Equilibrium constant ➢Free energy change ➢Enthalpy ➢Entropy ➢Bond dissociation energy ➢Kinetics ➢Activation energy =>
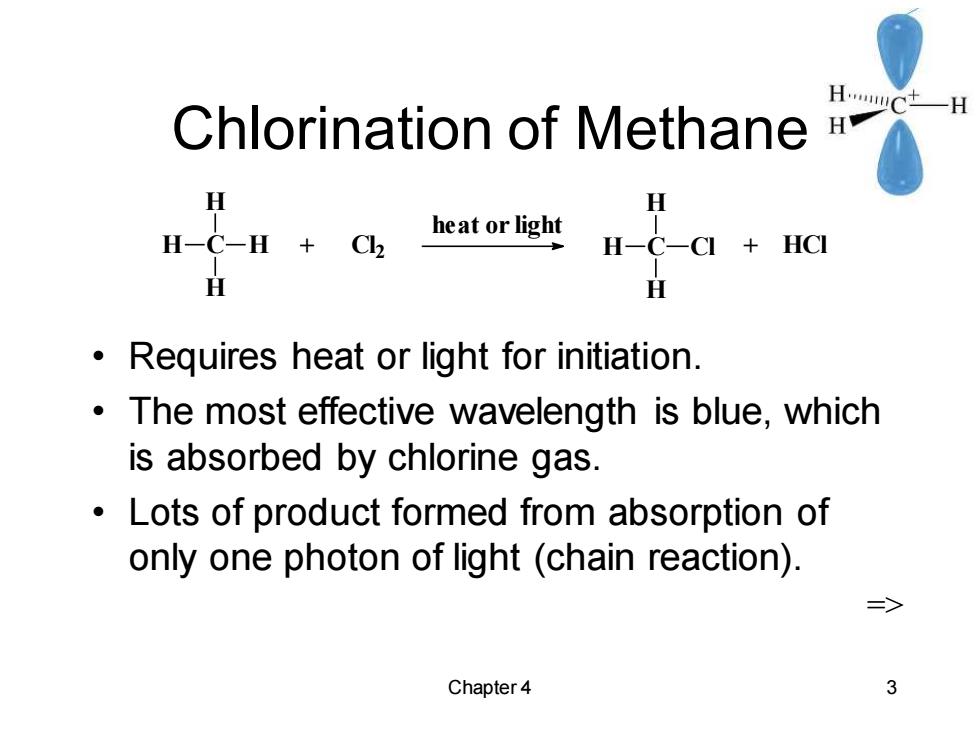
Chlorination of Methane HwC+一H H H H-C-H+Ck heat or light H-C-CI HCI H Requires heat or light for initiation. The most effective wavelength is blue,which is absorbed by chlorine gas. Lots of product formed from absorption of only one photon of light(chain reaction). Chapter 4 3
Chapter 4 3 Chlorination of Methane • Requires heat or light for initiation. • The most effective wavelength is blue, which is absorbed by chlorine gas. • Lots of product formed from absorption of only one photon of light (chain reaction). => C H H H H + Cl 2 heat or light C H H H Cl + HCl

HC一H Free-Radical Chain Reaction Initiation generates a reactive intermediate. Propagation:the intermediate reacts with a stable molecule to produce another reactive intermediate(and a product molecule). Termination:side reactions that destroy the reactive intermediate. > Chapter4 4
Chapter 4 4 Free-Radical Chain Reaction • Initiation generates a reactive intermediate. • Propagation: the intermediate reacts with a stable molecule to produce another reactive intermediate (and a product molecule). • Termination: side reactions that destroy the reactive intermediate. =>
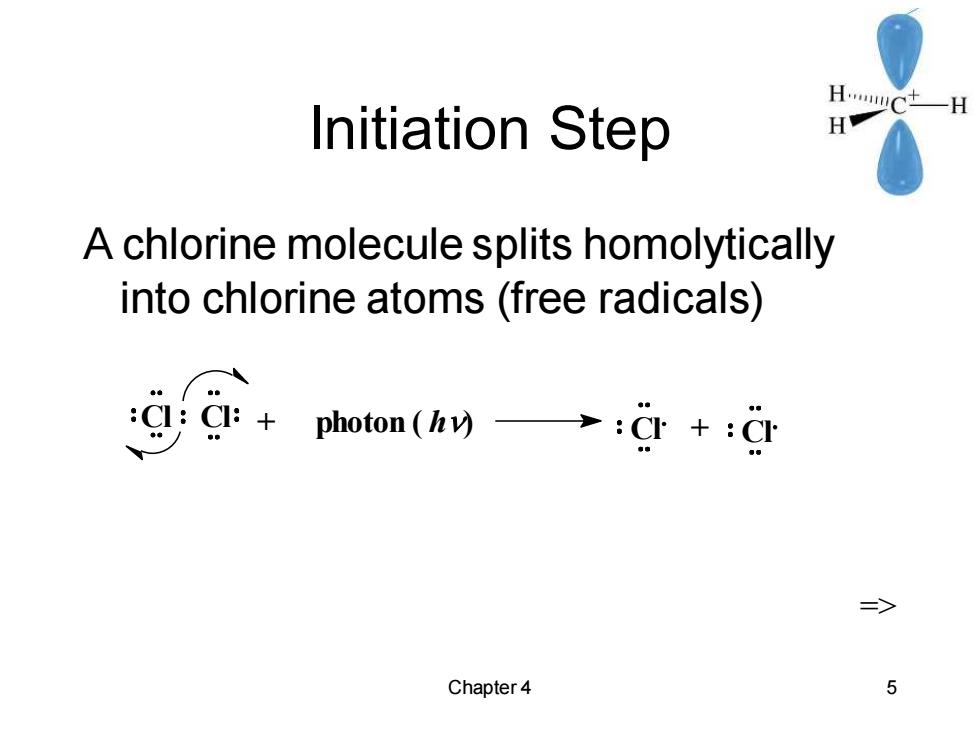
Initiation Step HC一H H A chlorine molecule splits homolytically into chlorine atoms (free radicals) gg:+photon(hy→:g+:d 三> Chapter 4 5
Chapter 4 5 Initiation Step A chlorine molecule splits homolytically into chlorine atoms (free radicals) => Cl Cl + photon ( h) Cl + Cl