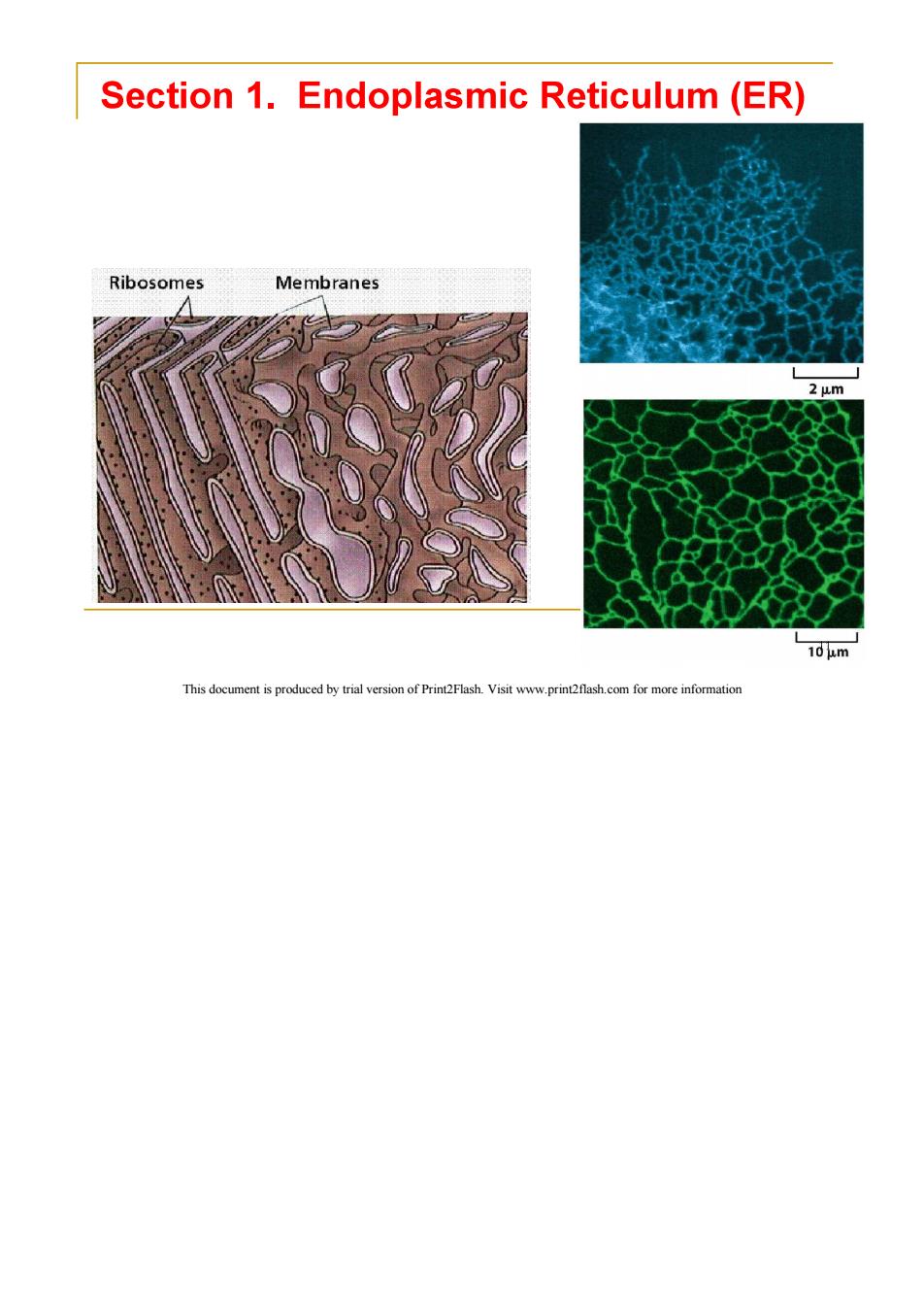
Section 1.Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Ribosomes Membranes 2 um 10um This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

1.1 The structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) ER is a network of membrane-enclosed tubules and sacs (cisternae)that extends from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm. ER is the largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells. Its membrane may account for about half of all cell membranes. The space enclosed by the ER may represent about 10%of the total cell volume. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
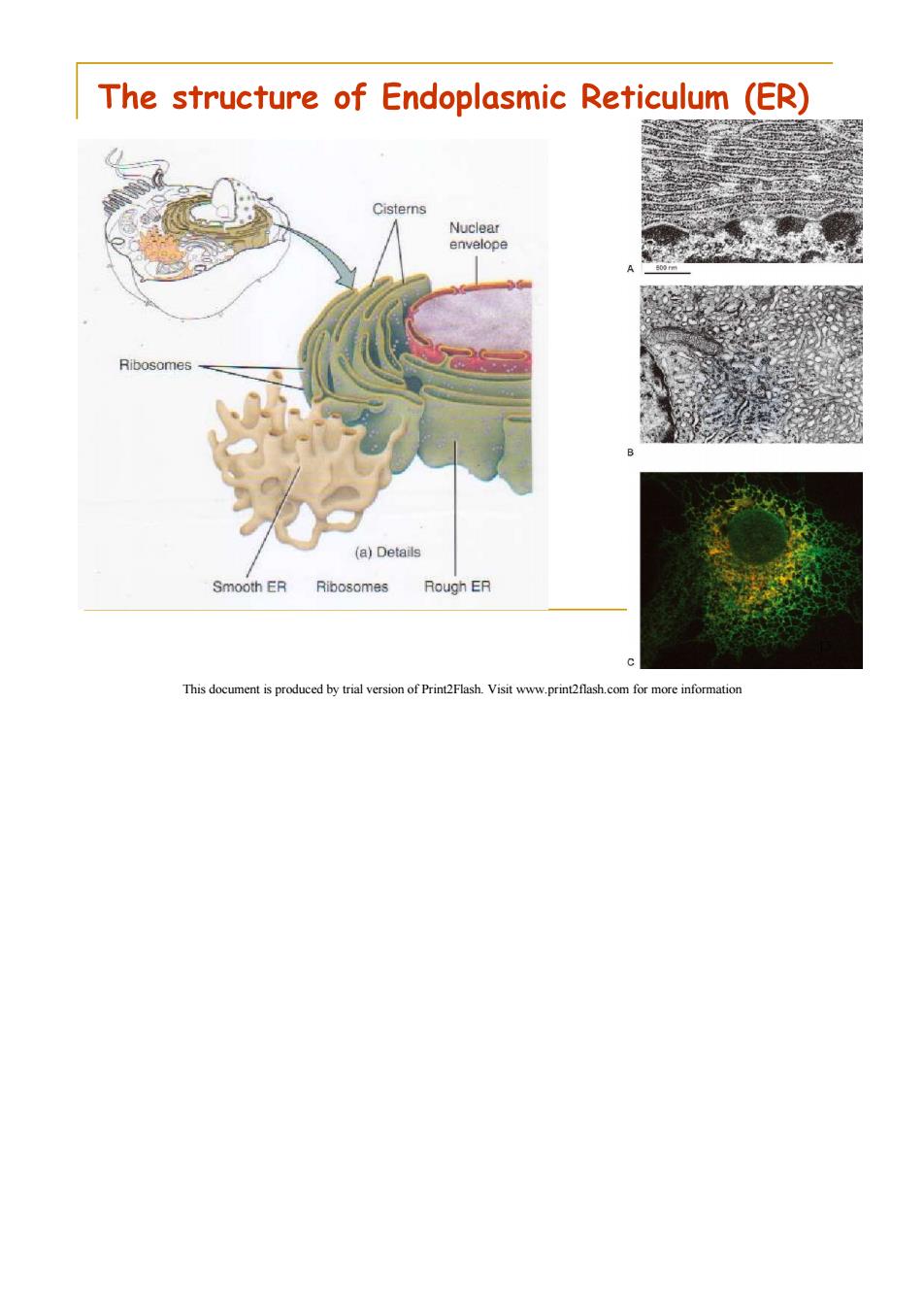
The structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Cisterns Nuclear envelope Ribosomes (a)Details Smooth ER Ribosomes Rough ER This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
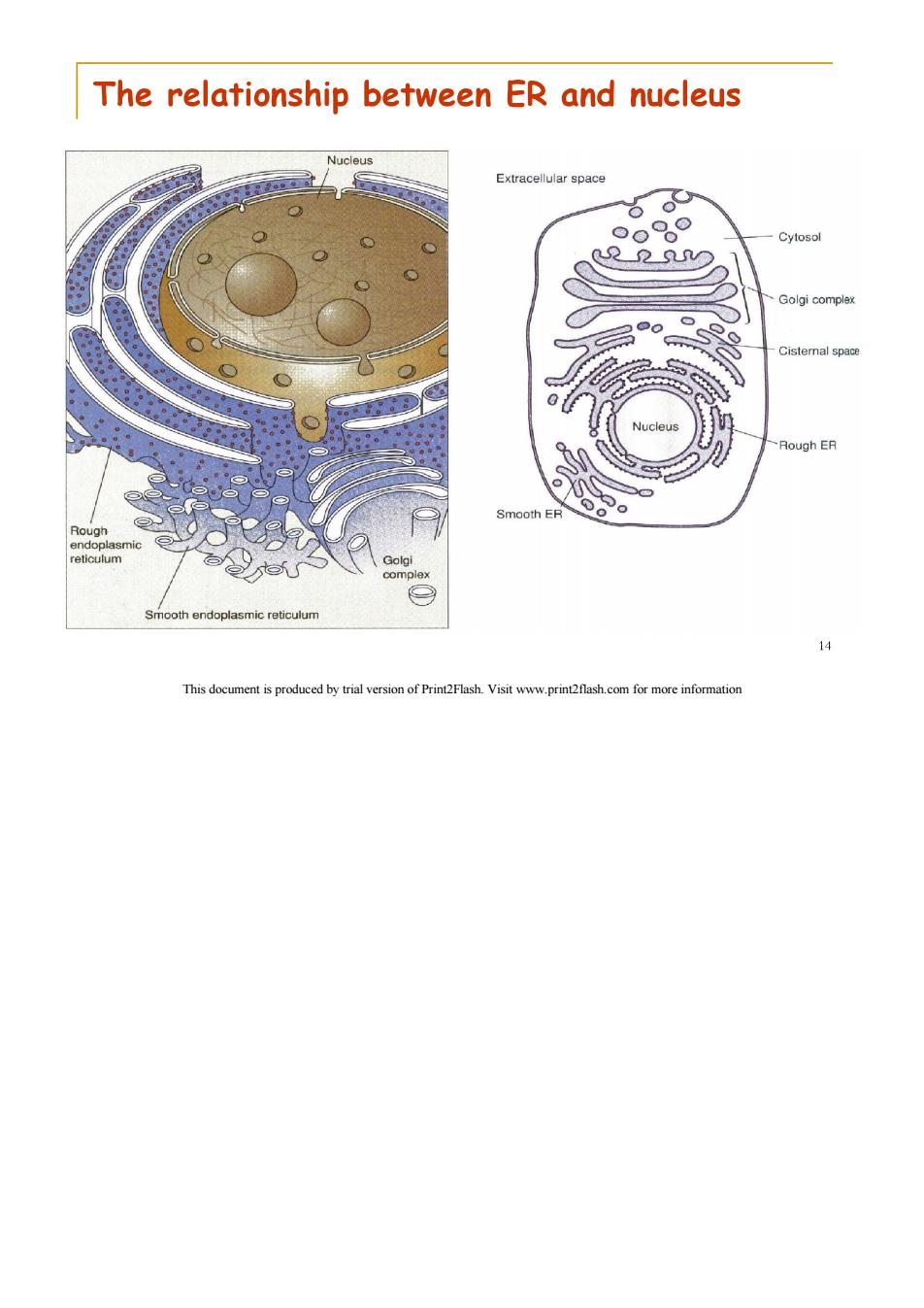
The relationship between ER and nucleus Nucleus Extracellular space 9o Cytosol 22 Golgi complex Cisternal space Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER Rough endoolasmic reticulum Golgi Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 14 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Morphological structure of rER and sER (形态结构) rough ER smooth ER ER lumen rER has ribosomes on the cytosolic side of continuous, flattened sacs(cisternae);sER is an interconnecting network of tubular membrane elements. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information