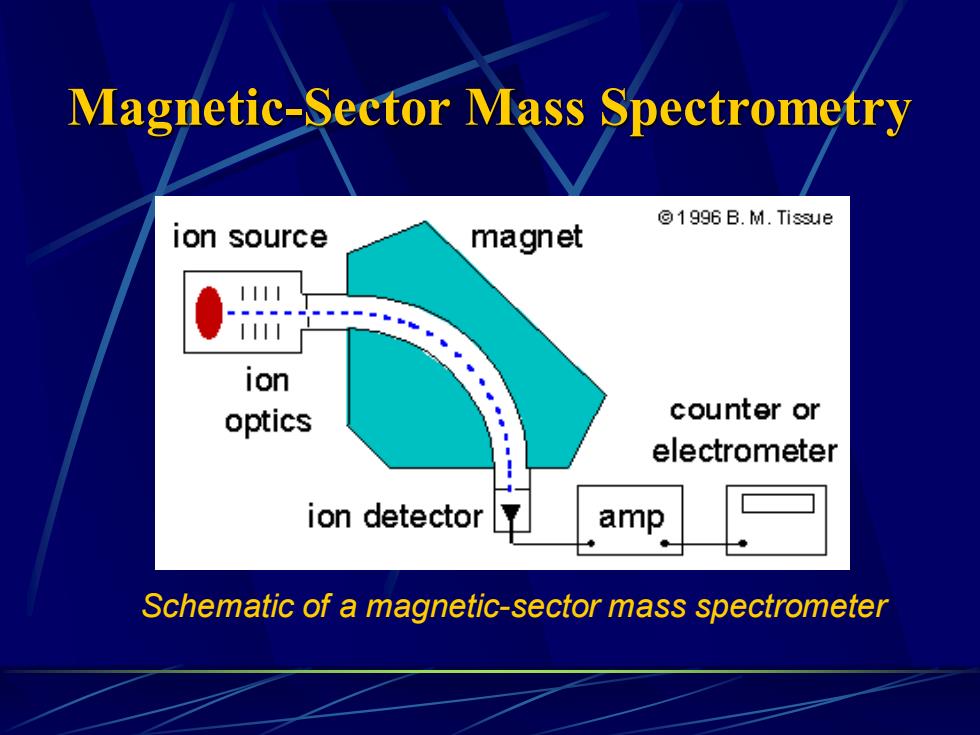
Magnetic-Sector Mass Spectrometry 1996 B.M.Tissue ion source magnet 1111 1111 ion optics counter or electrometer ion detector amp Schematic of a magnetic-sector mass spectrometer
Magnetic-Sector Mass Spectrometry Schematic of a magnetic-sector mass spectrometer

Theory The ion optics in the ion-source chamber of a mass spectrometer extract and accelerate ions to a kinetic energy given by: KE.=0.5 mv2=ev where m is the mass of the ion,v is it's velocity,e is the charge of the ion and V is the applied voltage of the ion optics. The ions enter the flight tube between the poles of a magnet and are deflected by the magnetic field,H.Only ions of mass-to-charge ratio that have equal centrifugal and centripetal forces pass through the flight tube: mv2/r=Hev centrifugal=centripetal forces. Where r is the radius of curvature of the ion path: r=mv/eH This equation shows that the m/e of the ions that reach the detector can be varied by changing either H or V
Theory The ion optics in the ion-source chamber of a mass spectrometer extract and accelerate ions to a kinetic energy given by: K.E. = 0.5 mv2 = eV where m is the mass of the ion, v is it's velocity, e is the charge of the ion and V is the applied voltage of the ion optics. The ions enter the flight tube between the poles of a magnet and are deflected by the magnetic field, H. Only ions of mass-to-charge ratio that have equal centrifugal and centripetal forces pass through the flight tube: mv2 / r = Hev centrifugal = centripetal forces. Where r is the radius of curvature of the ion path: r= mv / eH This equation shows that the m/e of the ions that reach the detector can be varied by changing either H or V

三、部件 进样系统, 扩散法 适用于气体或挥发性液体(P213-图13一2 直接插入探针法 适用于低挥发度样品,对易分解样品,通常使 用衍生法转化为稳定化合物后分析
三、部 件 (一)进样系统, 扩散法 适用于气体或挥发性液体(P213-图13-2) 直接插入探针法 适用于低挥发度样品,对易分解样品,通常使 用衍生法转化为稳定化合物后分析

(二)离子源或电离室 将试样中的原子、分子电离成离子,其性能影响质谱仪 的灵敏度和分辨率本领。 电子轰击源(Electron1 onization,EI): 电加热 La或W,2000℃其能量为10-70eV。高速电子与分子 发生碰撞,若电子能量大于试样品分子的电离电位, 将引致:M+e(高速)→M+,+2e(低速 M:偶数电子有机化合物M+.带奇数电子的阳离子 能量>70eV时,还发生进一步键的断裂,形成各种低质 量碎片的正离子与中性自由基。 用以有机化合物的结构鉴定。 常得到不易辨认的分子离子蜂
(二)离子源或电离室 将试样中的原子、分子电离成离子,其性能影响质谱仪 的灵敏度和分辨率本领。 1. 电子轰击源(Electron Ionization, EI):电加热 La或W,2000℃ 其能量为10-70ev。高速电子与分子 发生碰撞,若电子能量大于试样品分子的电离电位, 将引致:M+e- (高速)→M +. +2e(低速) M:偶数电子有机化合物 M+. 带奇数电子的阳离子 能量>70ev时,还发生进一步键的断裂,形成各种低质 量碎片的正离子与中性自由基。 用以有机化合物的结构鉴定。 常得到不易辨认的分子离子峰
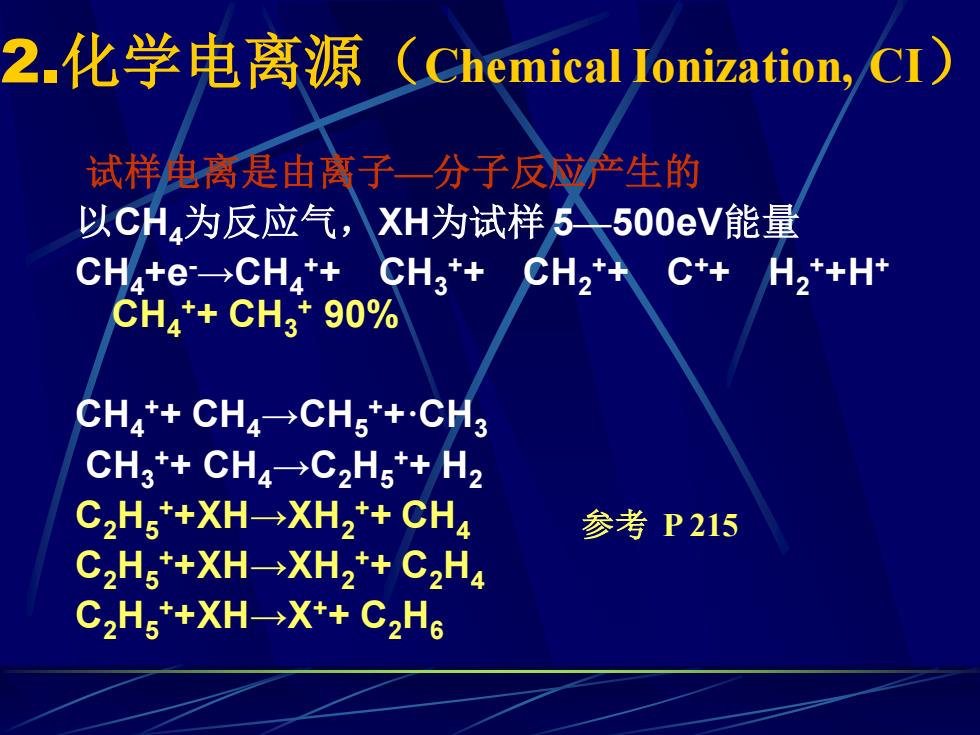
2.化学电离源 (Chemical Ionization,CI) 试样电离是由离子一分子反应产生的 以CH4为反应气, XH为试样5500eV能量 CH4te→CH4+CH3+ CH2*+ C++H2++H+ CHa*+CH3*90% CH4+CH4→CH5*+·CH3 CH3+CH4→C2H5*+H2 C2H写*+XH→XH2*+CH4 参考P215 C2H写*+XH→XH2*+C2H4 C2H写*+XH-→X*+C2H6
2.化学电离源(Chemical Ionization, CI) 试样电离是由离子—分子反应产生的 以CH4为反应气,XH为试样 5—500eV能量 CH4+e-→CH4 ++ CH3 ++ CH2 ++ C++ H2 ++H+ CH4 ++ CH3 + 90% CH4 ++ CH4→CH5 ++·CH3 CH3 ++ CH4→C2H5 ++ H2 C2H5 ++XH→XH2 ++ CH4 C2H5 ++XH→XH2 ++ C2H4 C2H5 ++XH→X++ C2H6 参考 P 215