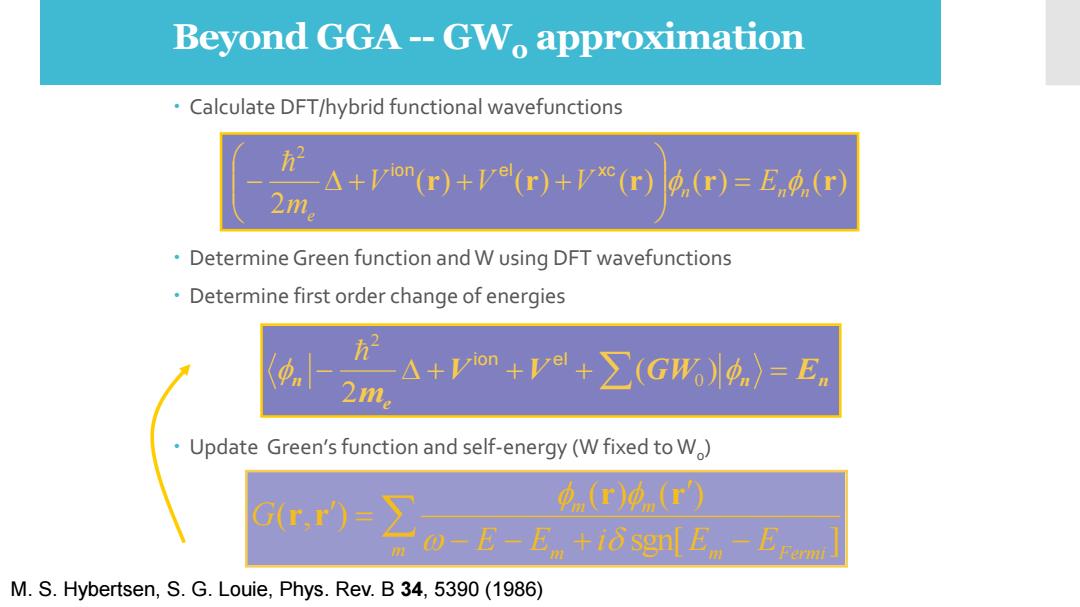
Beyond GGA--GW approximation Calculate DFT/hybrid functional wavefunctions A+Vion(r)+ve(r)+vx(r) p(r)=En(r) 2m Determine Green function and W using DFT wavefunctions Determine first order change of energies h" 21 △+Vom+V+∑(GW)p)=En Update Green's function and self-energy(W fixed to W) Gr,r)=∑ (r)0(r) 0-E-E +i sgnl En EFomi M.S.Hybertsen,S.G.Louie,Phys.Rev.B 34,5390(1986)
Beyond GGA -- GW0 approximation Calculate DFT/hybrid functional wavefunctions Determine Green function and W using DFT wavefunctions Determine first order change of energies Update Green’s function and self-energy (W fixed to W0 ) M. S. Hybertsen, S. G. Louie, Phys. Rev. B 34, 5390 (1986) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 r r r r r n n n e V V V E m = − + + + ion e l xc n n e n V V GW E m − + + +( ) = 2 0 2 ion e l − − + − = m m m Fermi m m E E i E E G sgn[ ] ( ) ( ) ( , ) r r r r
The Accuracy of DFT ·Atomic structures bond lengths and lattice constants are accurate to within 1-2% ·Energies several meVs;but depends on different functionals Vibrational frequencies within 5-10%accuracy
Atomic structures bond lengths and lattice constants are accurate to within 1-2% Energies several meVs; but depends on different functionals Vibrational frequencies within 5-10% accuracy The Accuracy of DFT
The limitations of DFT ·Band-gap problem HKS theorem is not valid for excited states; band-gaps in semiconductors and insulators are usually underestimated. ·Overbinding -LSDA:too small lattice constants,too large cohesive energies,too high bulk moduli; -The use of the GGA is mandatory for calculating adsorption energies,but the choice of the "correct"GGA is important. Neglect of strong correlations -Exchange-splitting underestimated for narrow d-and f-bands; Many transition-metal compounds are charge-transfer insulators,but DFT predicts metallic state. Neglect of van der Waals interactions -vdW forces are not included in any DFT functional; -Approximate expression of vdW forces on the basis of local polarizabilities derived from DFT
The limitations of DFT Band-gap problem - HKS theorem is not valid for excited states; - band-gaps in semiconductors and insulators are usually underestimated. Overbinding - LSDA: too small lattice constants, too large cohesive energies, too high bulk moduli; - The use of the GGA is mandatory for calculating adsorption energies, but the choice of the “correct” GGA is important. Neglect of strong correlations - Exchange-splitting underestimated for narrow d- and f-bands; - Many transition-metal compounds are charge-transfer insulators, but DFT predicts metallic state. Neglect of van der Waals interactions - vdW forces are not included in any DFT functional; - Approximate expression of vdW forces on the basis of local polarizabilities derived from DFT
Building models Cubo-Oh:M@Pt12 ody-centered cublc Face-centered cublc (b) Dual Catalytic Site side view La SroMnO, BaTiO, La SreMnO, 42
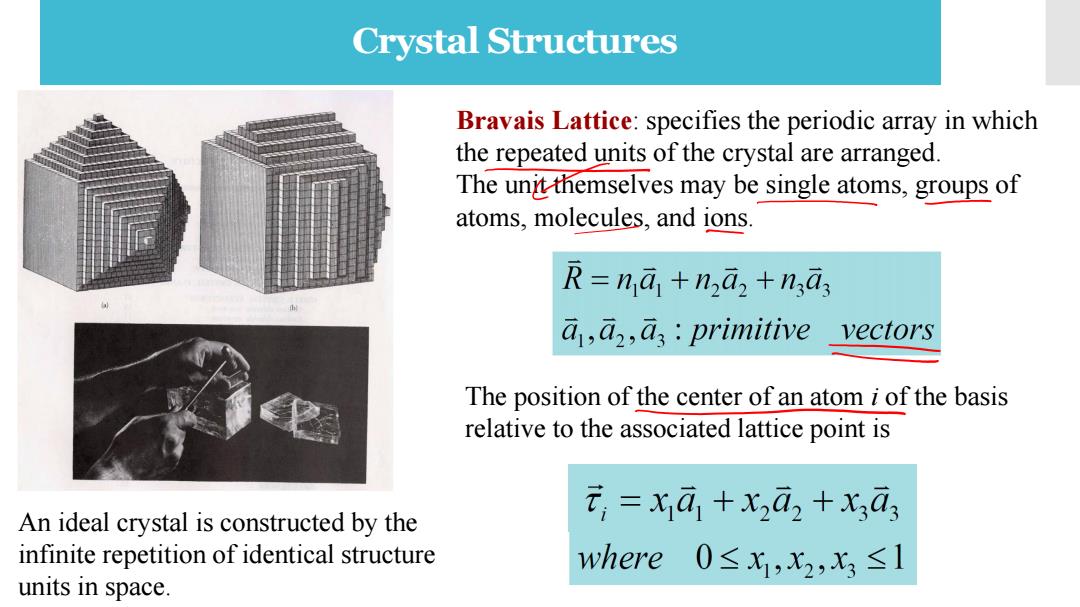
Crystal Structures Bravais Lattice:specifies the periodic array in which the repeated units of the crystal are arranged. The unit themselves may be single atoms,groups of atoms,molecules,and ions. R=na+naz+ngas a,a,as:primitive vectors The position of the center of an atom i of the basis relative to the associated lattice point is An ideal crystal is constructed by the t,=x1a1+x2ā2+X,ā3 infinite repetition of identical structure where0≤x,x2,x3≤1 units in space
Crystal Structures An ideal crystal is constructed by the infinite repetition of identical structure units in space. Bravais Lattice: specifies the periodic array in which the repeated units of the crystal are arranged. The unit themselves may be single atoms, groups of atoms, molecules, and ions. The position of the center of an atom i of the basis relative to the associated lattice point is