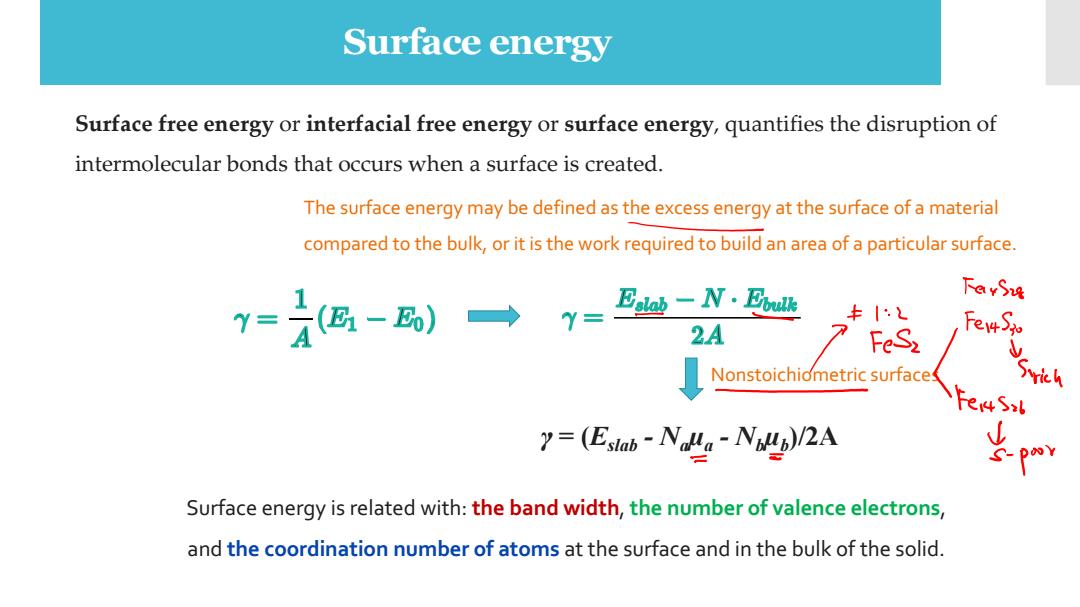
Surface energy Surface free energy or interfacial free energy or surface energy,quantifies the disruption of intermolecular bonds that occurs when a surface is created. The surface energy may be defined as the excess energy at the surface of a material compared to the bulk,or it is the work required to build an area of a particular surface. 下GvS4 y=-)一→ 2A FeS2 Nonstoichiometric surface 7=(E,ab-Na。Na/2A Surface energy is related with:the band width,the number of valence electrons, and the coordination number of atoms at the surface and in the bulk of the solid
Surface energy Surface free energy or interfacial free energy or surface energy, quantifies the disruption of intermolecular bonds that occurs when a surface is created. The surface energy may be defined as the excess energy at the surface of a material compared to the bulk, or it is the work required to build an area of a particular surface. Surface energy is related with: the band width, the number of valence electrons, and the coordination number of atoms at the surface and in the bulk of the solid. γ = (Eslab - Naµa - Nbµb )/2A Nonstoichiometric surfaces
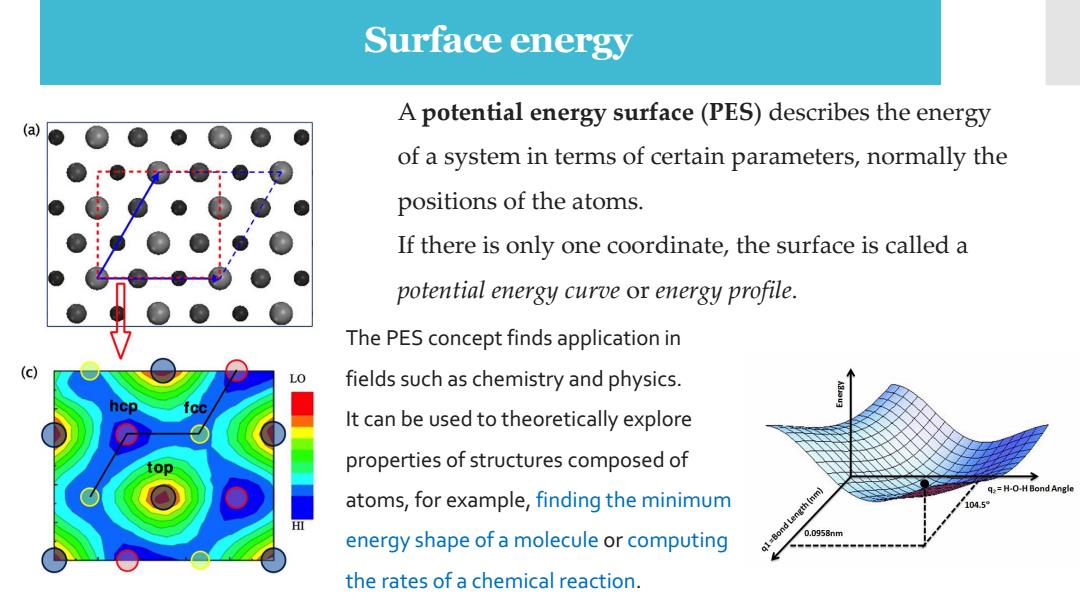
Surface energy A potential energy surface(PES)describes the energy of a system in terms of certain parameters,normally the positions of the atoms. If there is only one coordinate,the surface is called a potential energy curve or energy profile. The PES concept finds application in LO fields such as chemistry and physics. It can be used to theoretically explore top properties of structures composed of q=H-O-H Bond Angle atoms,for example,finding the minimum 104.5 energy shape of a molecule or computing g1=Bond Length (nm) 0.0958nm the rates of a chemical reaction
Surface energy A potential energy surface (PES) describes the energy of a system in terms of certain parameters, normally the positions of the atoms. If there is only one coordinate, the surface is called a potential energy curve or energy profile. The PES concept finds application in fields such as chemistry and physics. It can be used to theoretically explore properties of structures composed of atoms, for example, finding the minimum energy shape of a molecule or computing the rates of a chemical reaction
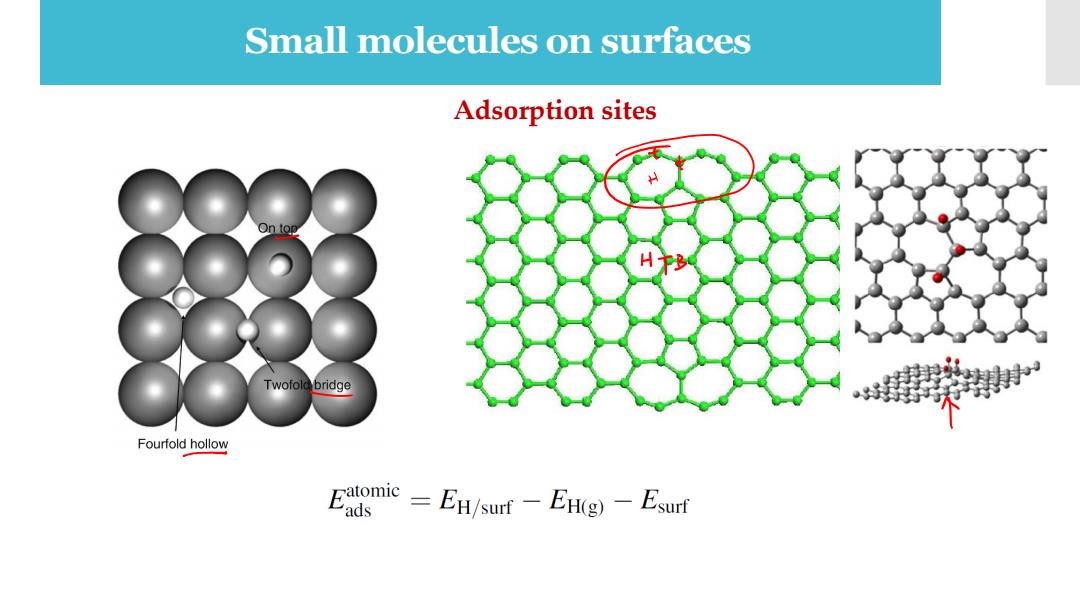
Small molecules on surfaces Adsorption sites H Twofold bridge Fourfold hollow Eagmie-EH/sur-EHg)-Esurt
Small molecules on surfaces Adsorption sites