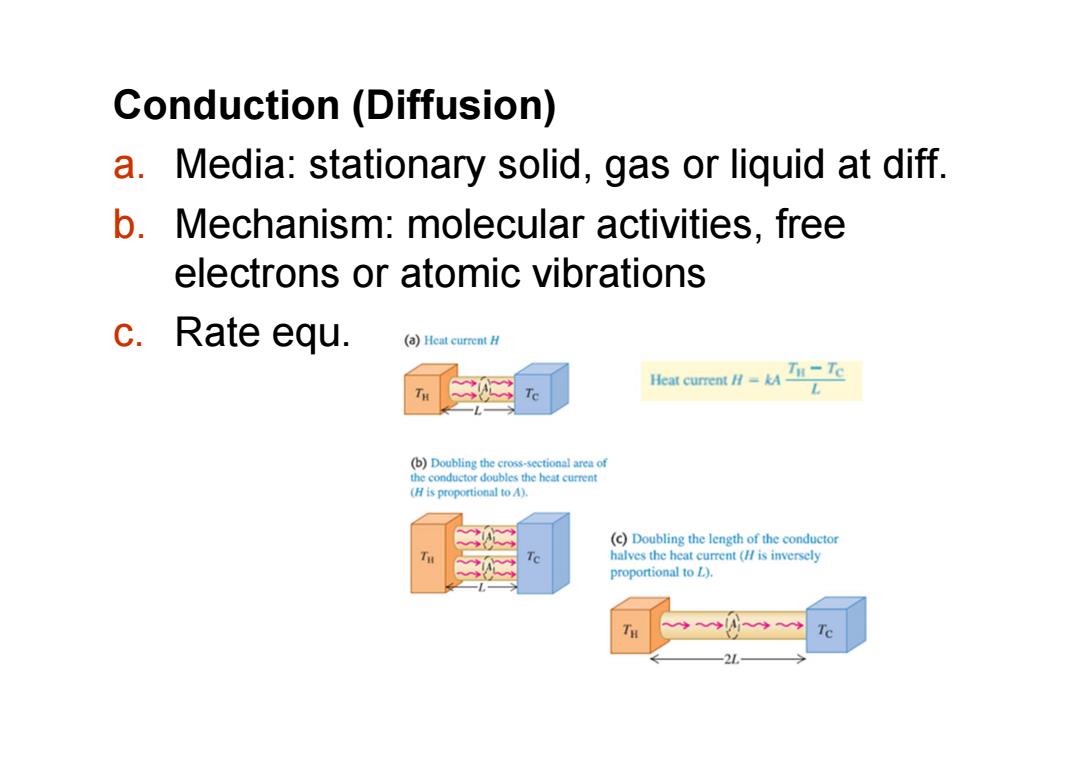
Conduction(Diffusion) a.Media:stationary solid,gas or liquid at diff b.Mechanism:molecular activities,free electrons or atomic vibrations c.Rate equ. (a))Heat current H Heat cument Ik Ti-Tc (b)Doubling the cross-sectional area of the conductor doubles the heat current (H is proportional to A). (c)Doubling the length of the conductor halves the heat current (is inversely proportional to L). Tc
Conduction (Diffusion) a. Media: stationary solid, gas or liquid at diff. b. Mechanism: molecular activities, free electrons or atomic vibrations c. Rate equ
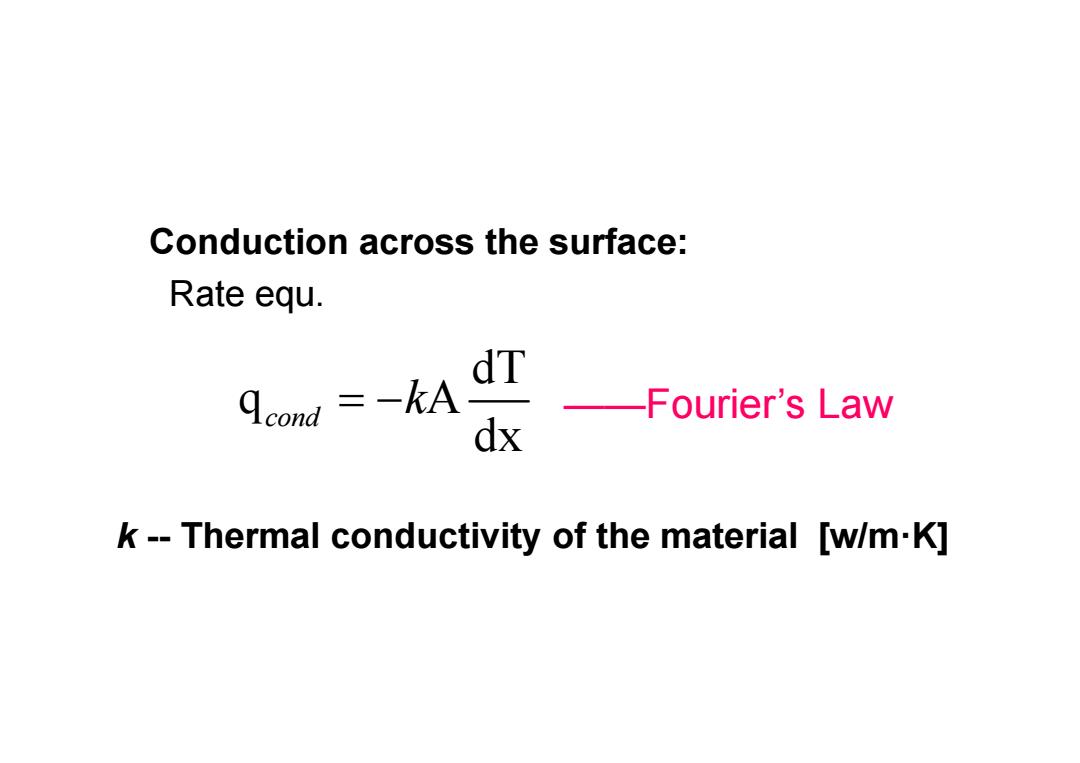
Conduction across the surface: Rate equ. cond =-kA dT -Fourier's Law dx k--Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m.K]
Conduction across the surface: Rate equ. ——Fourier’s Law dT q A dx cond k k -- Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m·K]
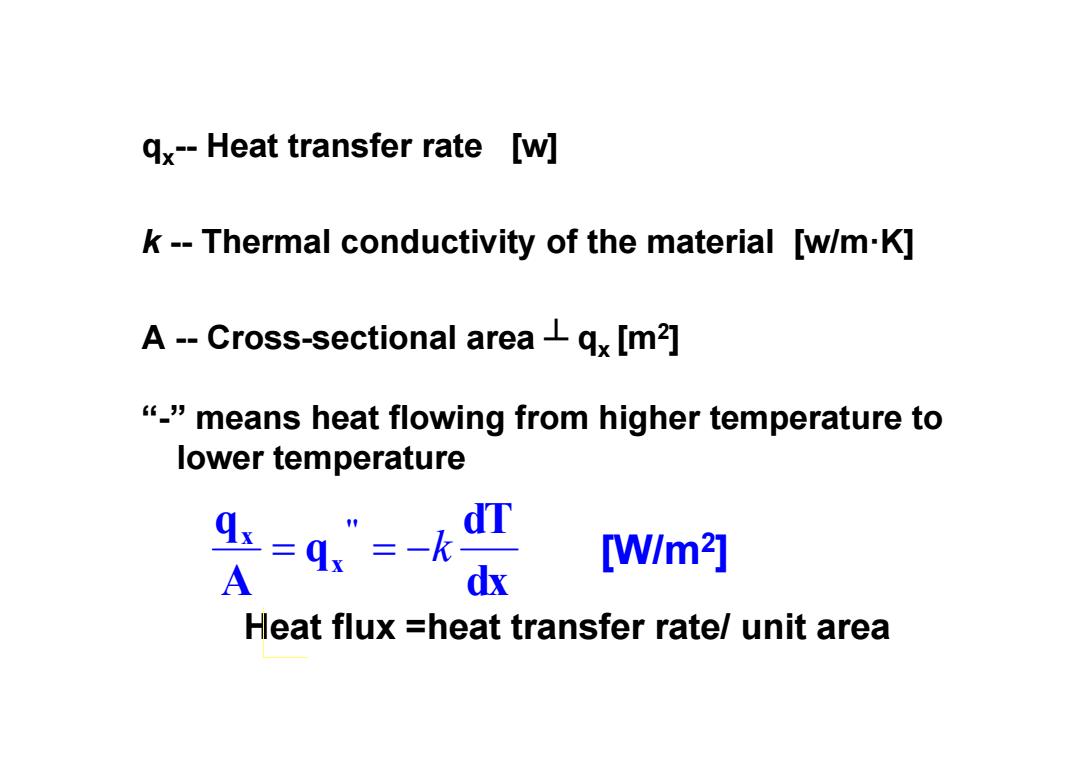
qx--Heat transfer rate [w] k--Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m-K] A--Cross-sectional areaqx [m2] "means heat flowing from higher temperature to lower temperature dT =q”=-k [W/m2] A dx Heat flux =heat transfer rate/unit area
qx-- Heat transfer rate [w] k -- Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m·K] A -- Cross-sectional area ┴ qx [m2] “-” means heat flowing from higher temperature to lower temperature dx dT q Aq '' x x k [W/m2] Heat flux =heat transfer rate/ unit area

Convection a Media:between solid moving fluid b.Mechanism:Bulk motion effects c.Rate equ. q=hA(T、-Ta) Newton's law of cooling
Convection a Media: between solid & moving fluid b. Mechanism: Bulk motion effects c. Rate equ. Newton’s law of cooling hA(T T ) s q
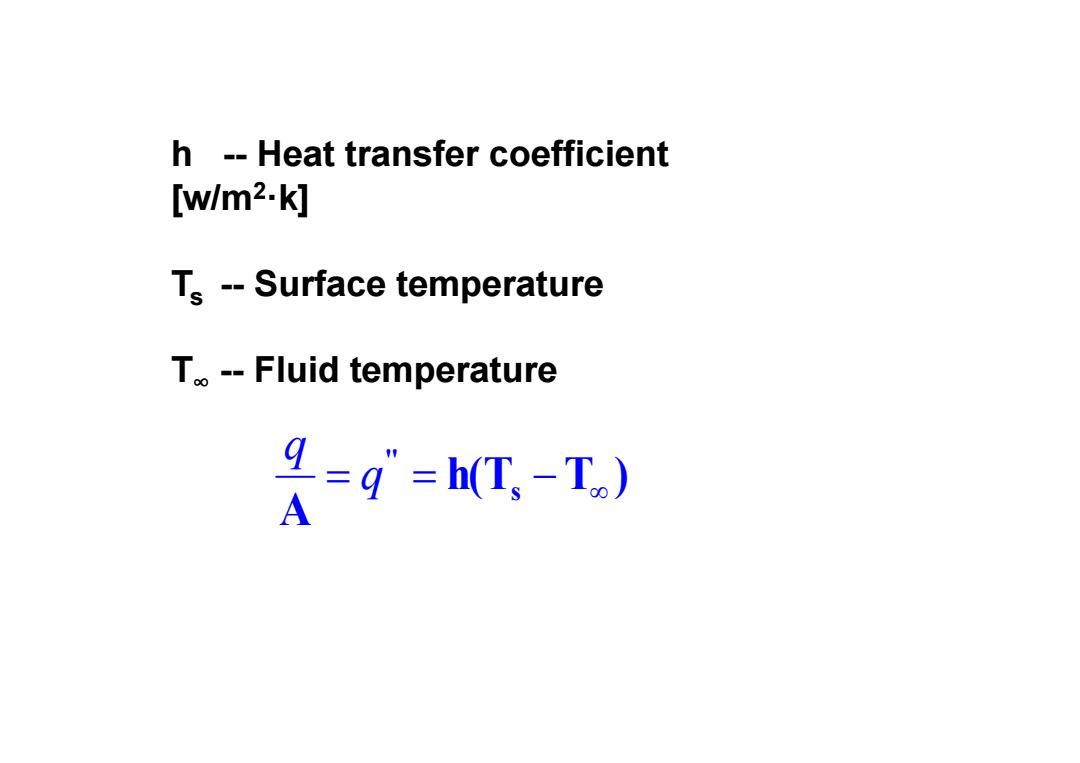
h--Heat transfer coefficient [w/m2.k] Ts--Surface temperature T--Fluid temperature =q”=hT,-T) A
h -- Heat transfer coefficient [w/m 2·k] Ts -- Surface temperature T ∞ -- Fluid temperature h(T T ) A s '' q q