
Lecture 7:Radiation Between Surfaces
Lecture 7: Radiation Between Surfaces
Introduction Definition:energy emitted by matter that is at a finite temperature Nature of thermal radiation ■ all matters radiate it is dependent on the temperature and nature of the material The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Introduction Definition: energy emitted by matter that is at a finite temperature Nature of thermal radiation all matters radiate it is dependent on the temperature and nature of the material The Electromagnetic Spectrum

X Rays Microwave Gamma rays hermal radiation 10-5 104 10-3 102 101 10 102 103 10 2(4m) FIGURE 12.3 Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation

Frequency and wavelength of the electromagnetic waves v=c/九 Transparent,semitransparent,and opaque materials Two features:spectral and directional distribution
Frequency and wavelength of the electromagnetic waves Transparent, semitransparent, and opaque materials Two features: spectral and directional distribution c /
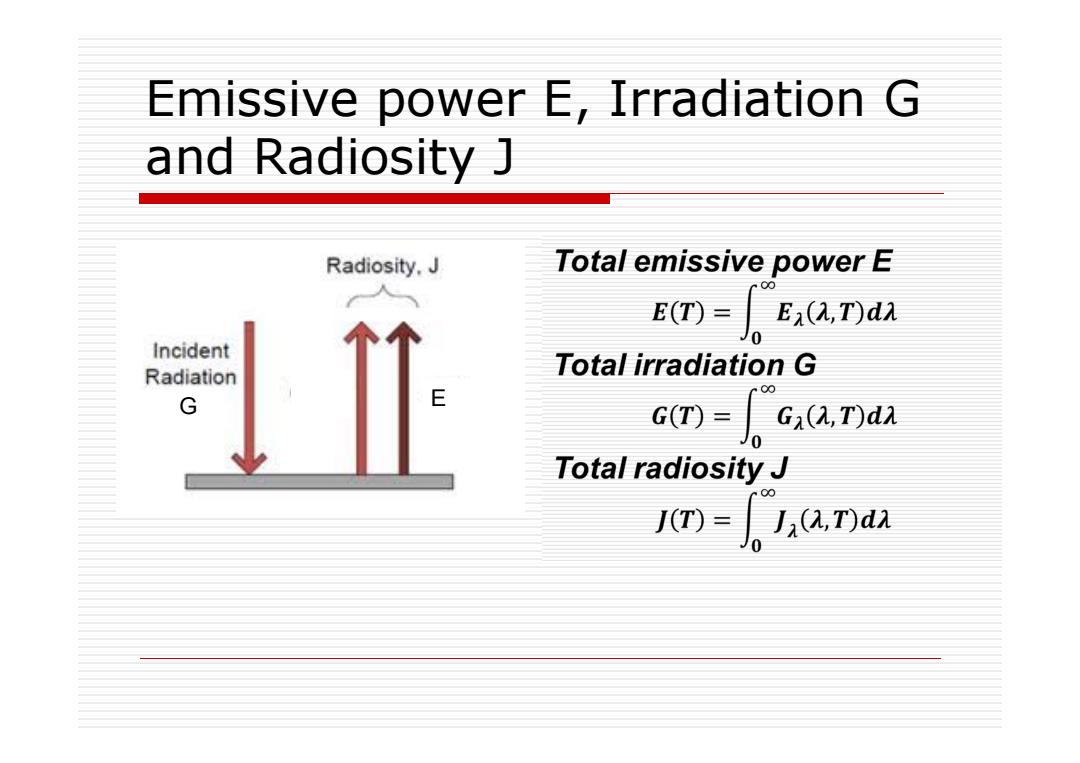
Emissive power E,Irradiation G and Radiosity J Radiosity.J Total emissive power E 00 E(T)= E(A,T)da Incident Radiation Total irradiation G 00 G G(T)= Gi(A,T)da Total radiosity J J(T)= J(A,T)da
Emissive power E, Irradiation G and Radiosity J G E