
Why discount? Most Markov reward and decision processes are discounted.Why? Mathematically convenient to discount rewards Avoids infinite returns in cyclic Markov processes Uncertainty about the future may not be fully represented If the reward is financial,immediate rewards may earn more interest than delayed rewards Animal/human behaviour shows preference for immediate reward It is sometimes possible to use undiscounted Markov reward processes(i.e.Y=1),e.g.if all sequences terminate. 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Why discount?
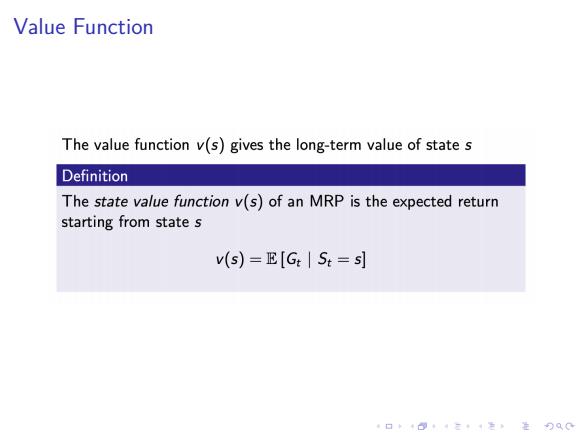
Value Function The value function v(s)gives the long-term value of state s Definition The state value function v(s)of an MRP is the expected return starting from state s v(s)=E[GS:=s] 口·三4,进分双0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Value Function
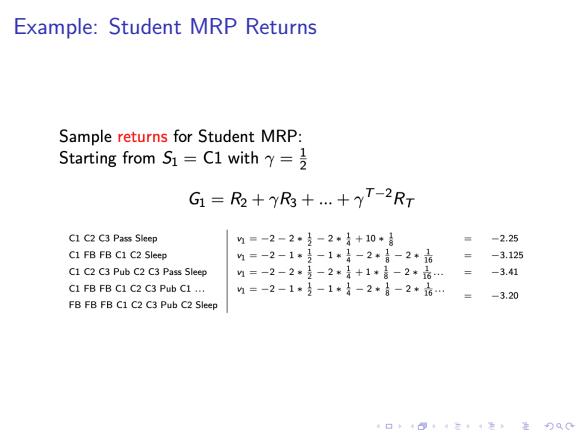
Example:Student MRP Returns Sample returns for Student MRP: Starting from S1 C1 with G1=R2+yR3+...+T-2RT Cl C2 C3 Pass Sleep n=-2-2·}-2*}+10*} -2.25 C1 FB FB C1 C2 Sleep 4=-2-1*是-1*}-2*青-2*6 = -3.125 C1 C2 C3 Pub C2 C3 Pass Sleep n=-2-2*是-2*}+1*言-2*品 -3.41 C1 FBFB C1 C2 C3 Pub C1... h=-2-1*3-1*}-2*日-2*6… -3.20 FBFBFB C1 C2 C3 Pub C2 Sleep 4口卡404三·1=生0C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Example: Student MRP Returns
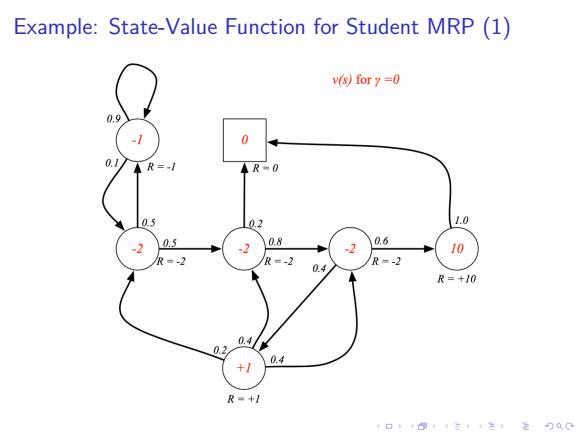
Example:State-Value Function for Student MRP(1) v(s)for y=0 0.9 0 0.1 AR-0 0.5 1.0 0.8 0.6 10 -2 R=-2 R=+10 0. 0.2 +1 0.4 R=+1 口卡+8·三色进分双0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Example: State-Value Function for Student MRP (1)
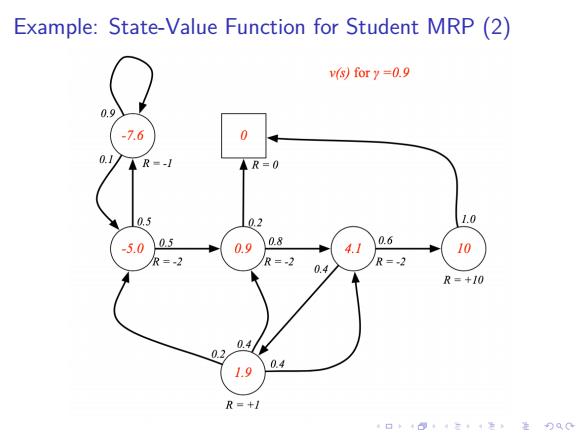
Example:State-Value Function for Student MRP(2) v(s)for y=0.9 0.9 -7.6 2 0.1 AR=-1 4R=0 0.5 L02 1.0 -5.0 05 0.9 0.8 4.1 0.6 10 R=-2 R=-2 R=-2 0.4 R=+10 0.4 0.2 0.4 1.9 R=+1 口◆4日4三·1=,生9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Example: State-Value Function for Student MRP (2)