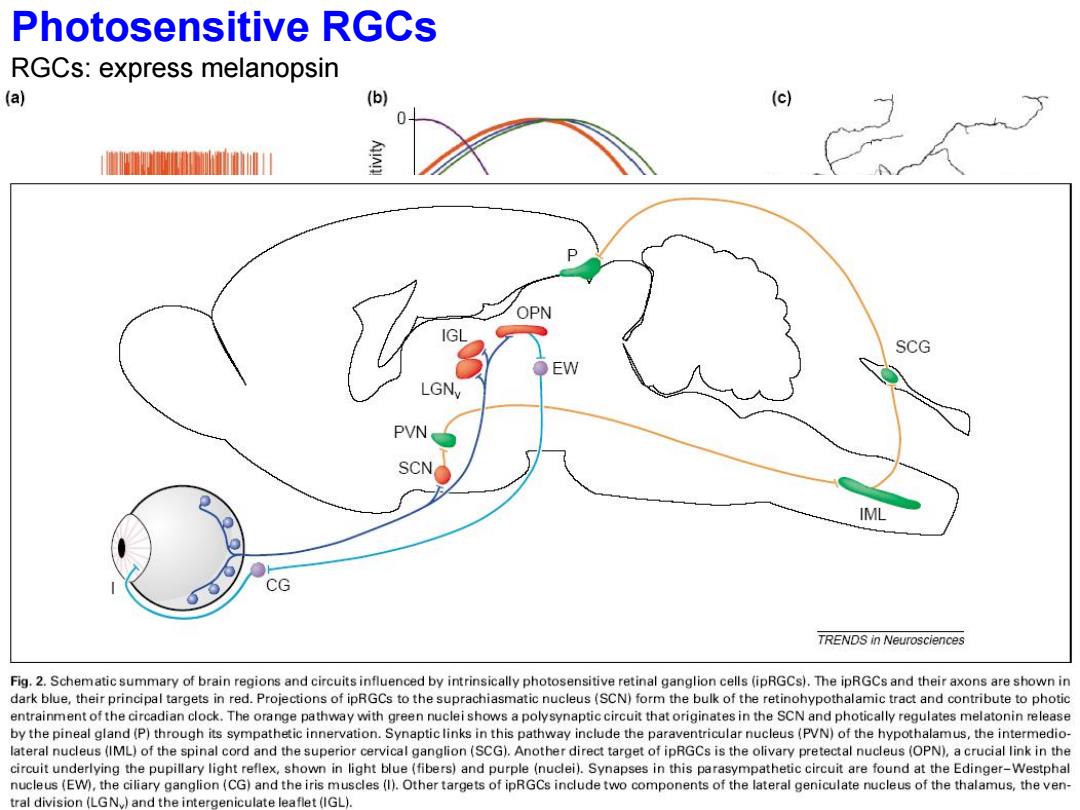
Photosensitive RGCs RGCs:express melanopsin (a) (b) (c) 室 OPN SCG LGNy PVN SCN o IML CG TRENDS in Neurosciences Fig.2.Schematic summary of brain regions and circuits influenced by intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs).The ipRGCs and their axons are shown in dark blue,their principal targets in red.Projections of ipRGCs to the suprachiasmatic nucleus(SCN)form the bulk of the retinohypothalamic tract and contribute to photic entrainment of the circadian clock.The orange pathway with green nuclei shows a polysynaptic circuit that originates in the SCN and photically regulates melatonin release by the pineal gland(P)through its sympathetic innervation.Synaptic links in this pathway include the paraventricular nucleus(PVN)of the hypothalamus,the intermedio- lateral nucleus(IML)of the spinal cord and the superior cervical ganglion(SCG).Another direct target of ipRGCs is the olivary pretectal nucleus (OPN),a crucial link in the circuit underlying the pupillary light reflex,shown in light blue(fibers)and purple(nuclei).Synapses in this parasympathetic circuit are found at the Edinger-Westphal nucleus(EW),the ciliary ganglion(CG)and the iris muscles(I).Other targets of ipRGCs include two components of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus,the ven- tral division(LGN.)and the intergeniculate leaflet(IGL)
Photosensitive RGCs RGCs: express melanopsin
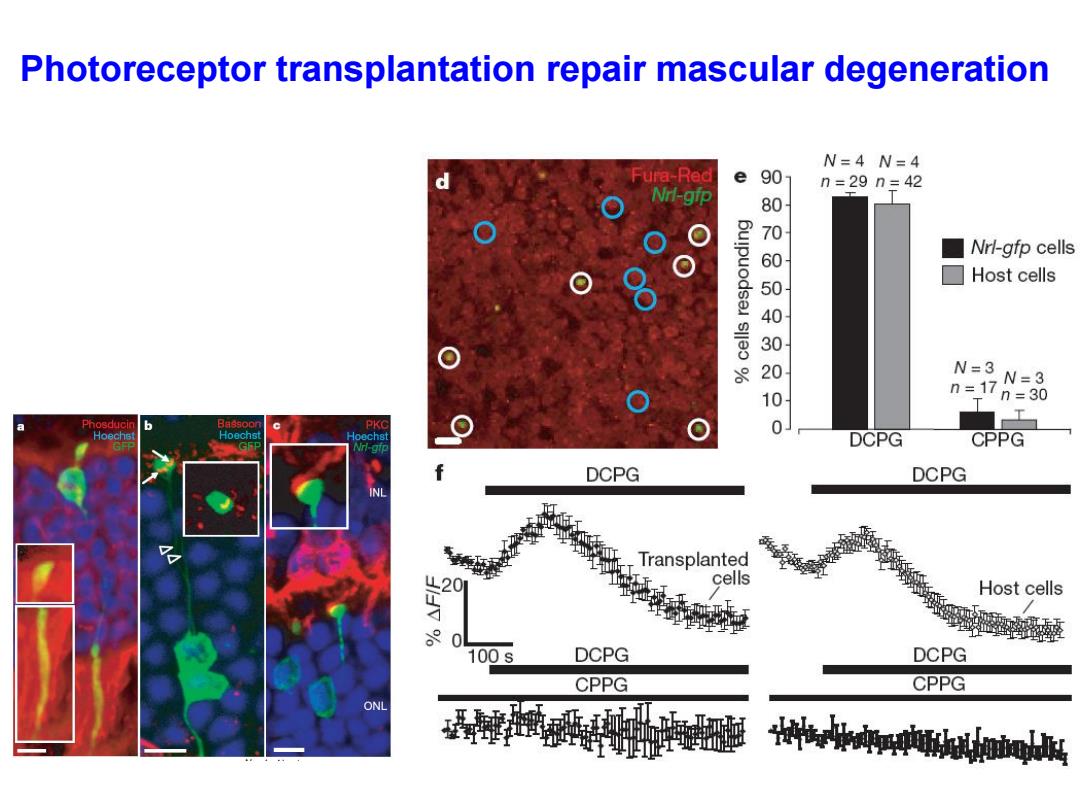
Photoreceptor transplantation repair mascular degeneration N=4N=4 ura-Red e 90 n=29n=42 Nrl-gip 00010000 Nrl-gfp cells ☐Host cells N=3 n=17 N=3 =30 T Phosducin Bassoor Hoechs Hoechst DCPG CPPG DCPG DCPG INL Transplanted cells Host cells 0 100s DCPG DCPG CPPG CPPG ONL e.ireoboigd
Photoreceptor transplantation repair mascular degeneration
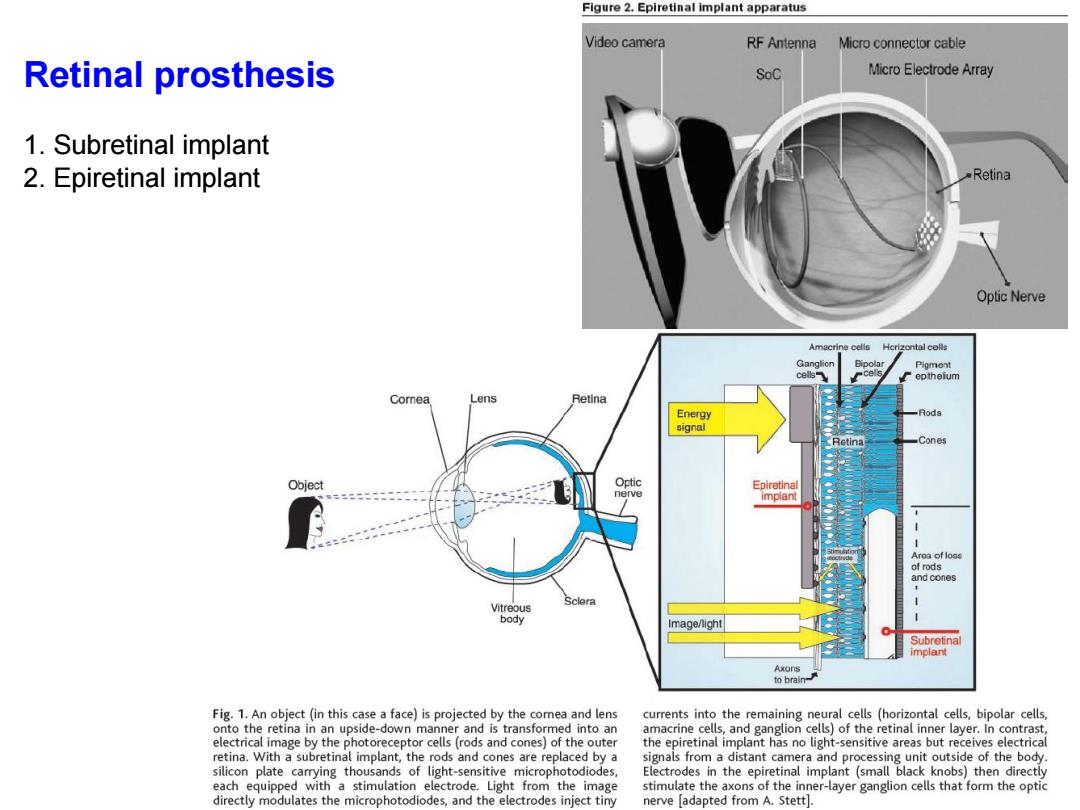
Figure 2.Epiretinal implant apparatus Video camera RF Antenna Micro connector cable Retinal prosthesis SoC Micro Electrode Array 1.Subretinal implant 2.Epiretinal implant Retina Optic Nerve Hcrizontal colls Pigment eptheium Comnea Lens Retina Energy 月ods signal Retina Cones Object Optic Epiretinal nerve implant Aroa of loas of rods and cones Sclera Vitreous body Image/light Subretinal implant Axons to brain- Fig.1.An object (in this case a face)is projected by the cornea and lens currents into the remaining neural cells (horizontal cells,bipolar cells, onto the retina in an upside-down manner and is transformed into an amacrine cells,and ganglion cells)of the retinal inner layer.In contrast. electrical image by the photoreceptor cells(rods and cones)of the outer the epiretinal implant has no light-sensitive areas but receives electrical retina.With a subretinal implant,the rods and cones are replaced by a signals from a distant camera and processing unit outside of the body. silicon plate carrying thousands of light-sensitive microphotodiodes, Electrodes in the epiretinal implant (small black knobs)then directly each equipped with a stimulation electrode.Light from the image stimulate the axons of the inner-layer ganglion cells that form the optic directly modulates the microphotodiodes,and the electrodes inject tiny nerve adapted from A.Stett
Retinal prosthesis 1. Subretinal implant 2. Epiretinal implant
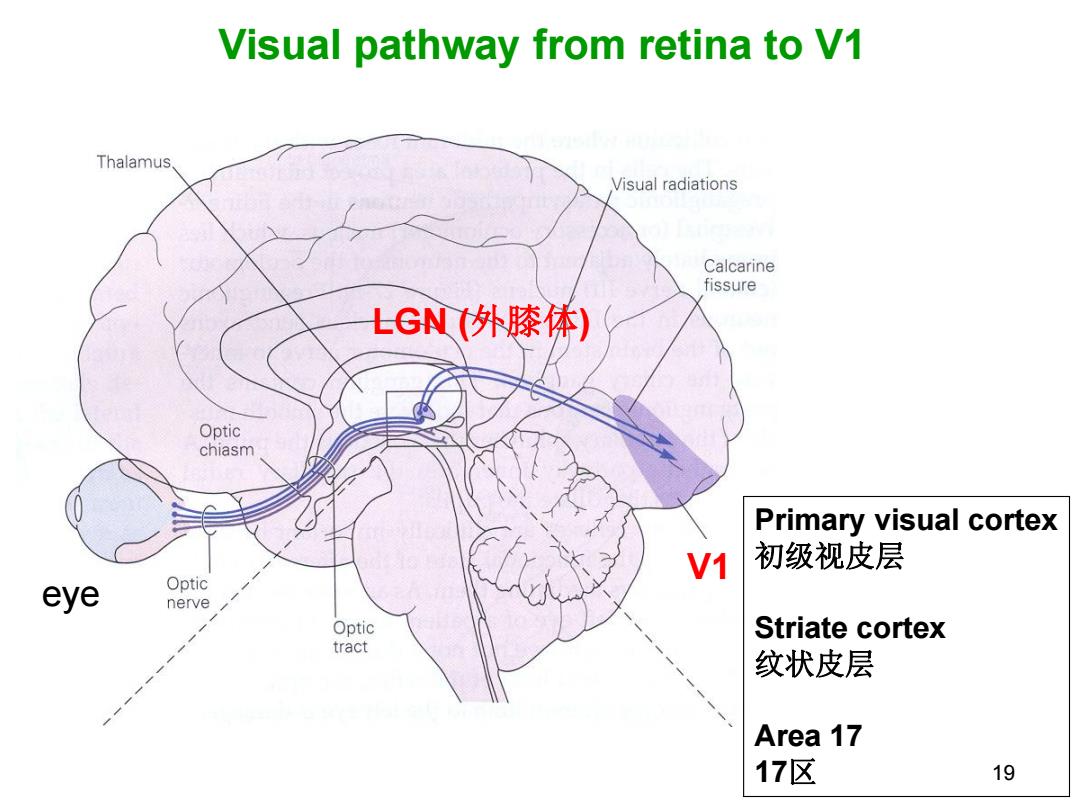
Visual pathway from retina to V1 Thalamus. Visual radiations Calcarine fissure LGN(外膝体) Optic chiasm Primary visual cortex V1 初级视皮层 eye Optic nerve Optic Striate cortex tract 纹状皮层 Area 17 17区 19
19 Visual pathway from retina to V1 eye LGN (外膝体) V1 Primary visual cortex 初级视皮层 Striate cortex 纹状皮层 Area 17 17区