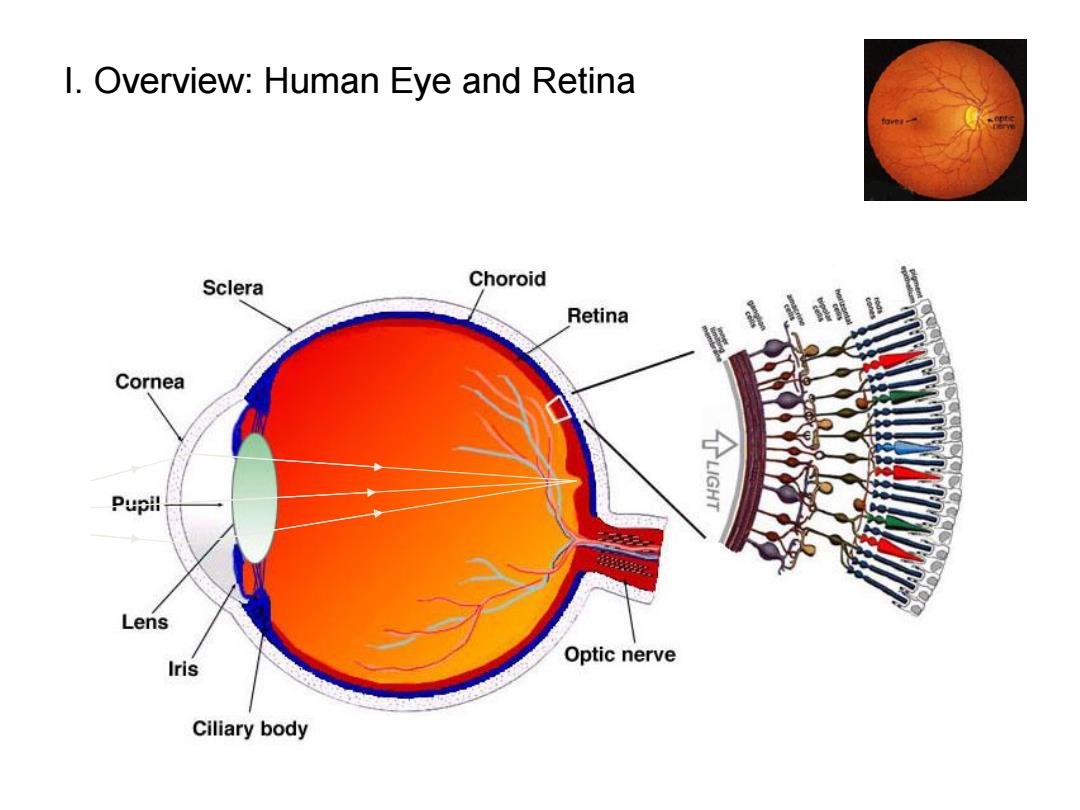
I.Overview:Human Eye and Retina Sclera Choroid Retina A移 Cornea Pupil % Lens Iris Optic nerve Ciliary body
I. Overview: Human Eye and Retina
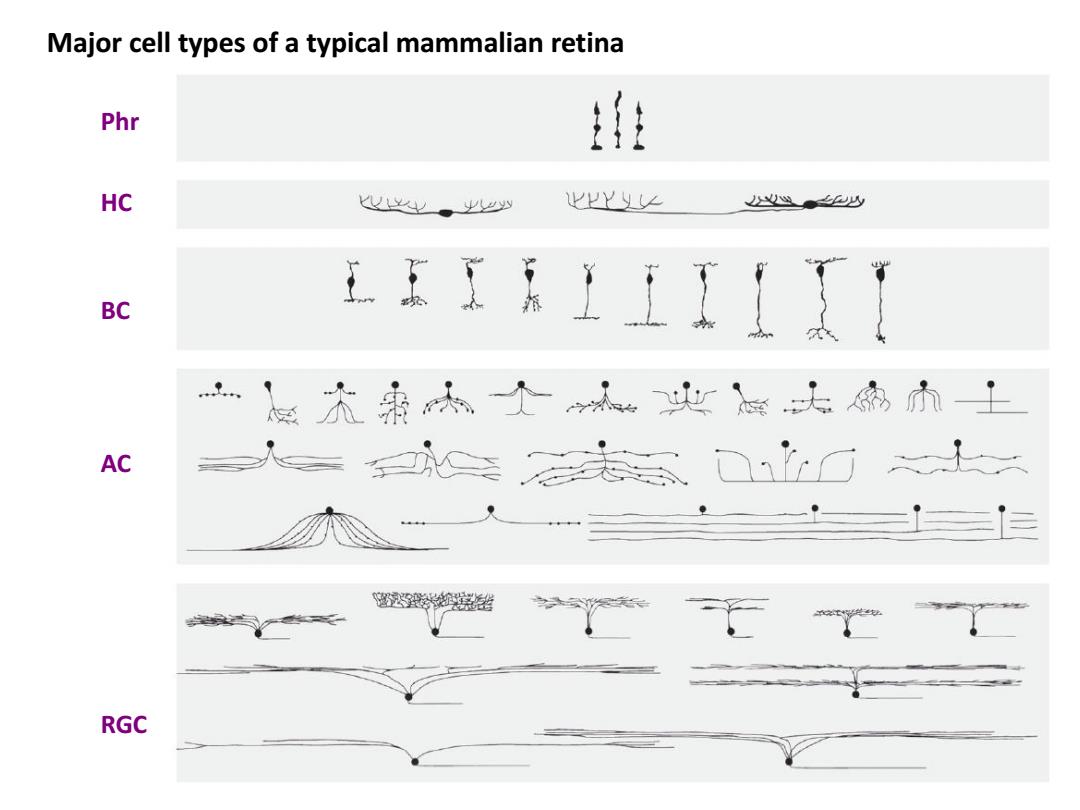
Major cell types of a typical mammalian retina Phr : HC Uy。岁少 Yy∠ ●少 BC E住A上1I【 六最六人地大扇小土 AC 人一装念0口 名 RGC
Major cell types of a typical mammalian retina Phr HC BC AC RGC
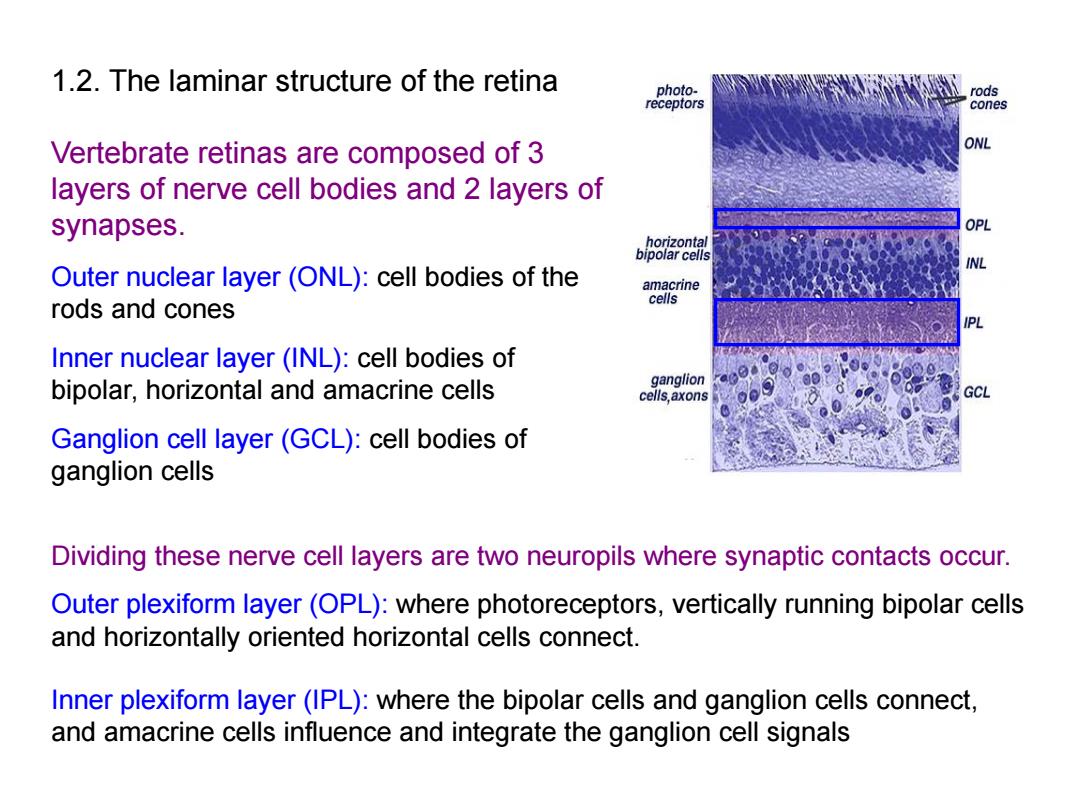
1.2.The laminar structure of the retina photo- rods receptors cones Vertebrate retinas are composed of 3 ONL layers of nerve cell bodies and 2 layers of synapses. OPL horizontal bipolar cells INL Outer nuclear layer(ONL):cell bodies of the amacrine rods and cones cells Inner nuclear layer(INL):cell bodies of bipolar,horizontal and amacrine cells ganglion cells,axons Ganglion cell layer(GCL):cell bodies of ganglion cells Dividing these nerve cell layers are two neuropils where synaptic contacts occur. Outer plexiform layer(OPL):where photoreceptors,vertically running bipolar cells and horizontally oriented horizontal cells connect. Inner plexiform layer(IPL):where the bipolar cells and ganglion cells connect, and amacrine cells influence and integrate the ganglion cell signals
1.2. The laminar structure of the retina Vertebrate retinas are composed of 3 layers of nerve cell bodies and 2 layers of synapses. Outer nuclear layer (ONL): cell bodies of the rods and cones Inner nuclear layer (INL): cell bodies of bipolar, horizontal and amacrine cells Ganglion cell layer (GCL): cell bodies of ganglion cells Dividing these nerve cell layers are two neuropils where synaptic contacts occur. Outer plexiform layer (OPL): where photoreceptors, vertically running bipolar cells and horizontally oriented horizontal cells connect. Inner plexiform layer (IPL): where the bipolar cells and ganglion cells connect, and amacrine cells influence and integrate the ganglion cell signals
Il.Photoreceptors
II. Photoreceptors
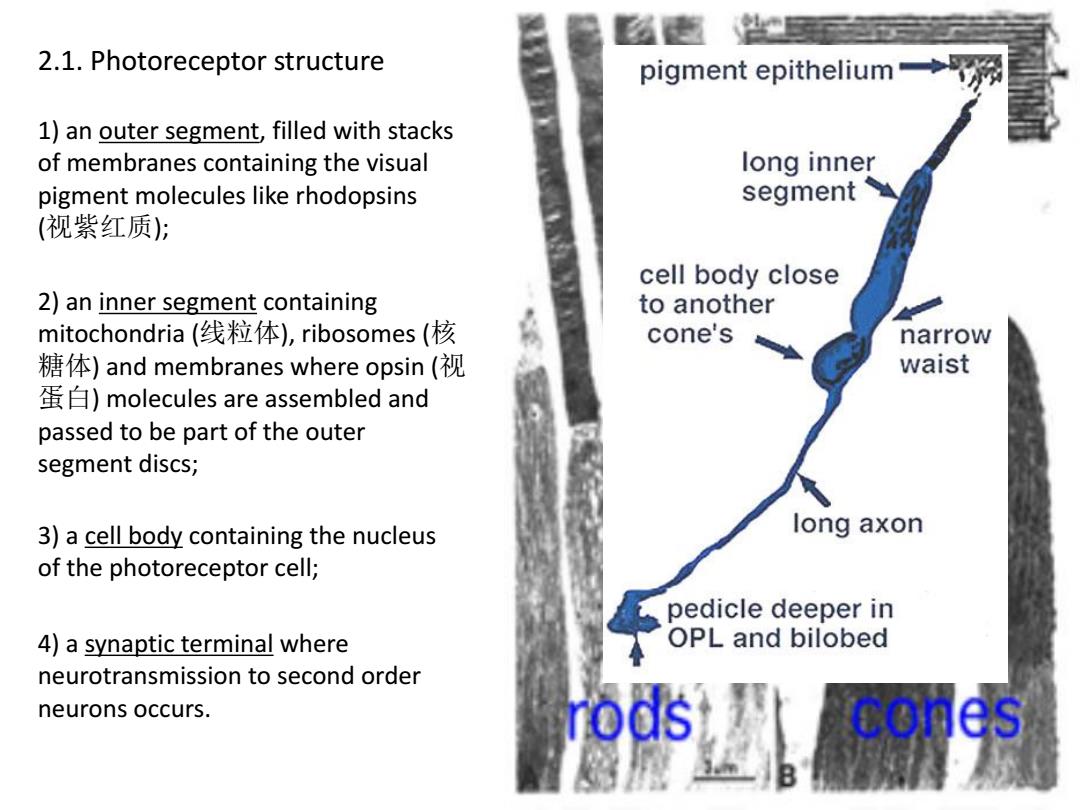
2.1.Photoreceptor structure pigment epithelium 1)an outer segment,filled with stacks of membranes containing the visual long inner pigment molecules like rhodopsins segment (视紫红质); cell body close 2)an inner segment containing to another mitochondria(线粒体),ribosomes(核 cone's narrow 糖体)and membranes where opsin(视 waist 蛋白)molecules are assembled and passed to be part of the outer segment discs; 3)a cell body containing the nucleus long axon of the photoreceptor cell; pedicle deeper in 4)a synaptic terminal where OPL and bilobed neurotransmission to second order neurons occurs. rods cones
2.1. Photoreceptor structure 1) an outer segment, filled with stacks of membranes containing the visual pigment molecules like rhodopsins (视紫红质); 2) an inner segment containing mitochondria (线粒体), ribosomes (核 糖体) and membranes where opsin (视 蛋白) molecules are assembled and passed to be part of the outer segment discs; 3) a cell body containing the nucleus of the photoreceptor cell; 4) a synaptic terminal where neurotransmission to second order neurons occurs