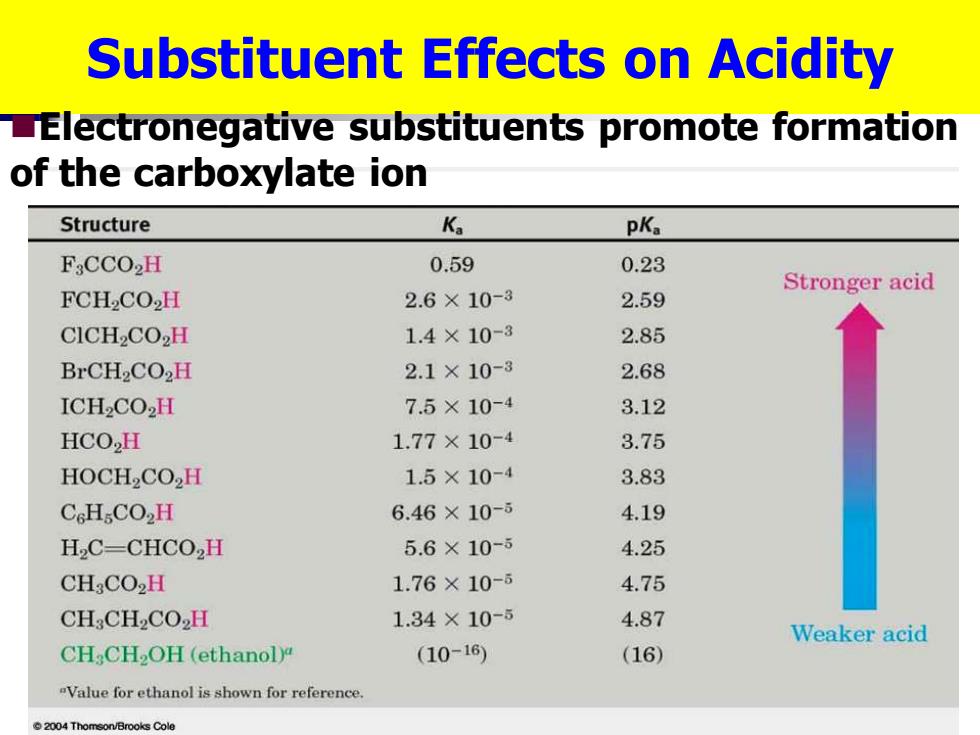
Substituent Effects on Acidity LElectronegative substituents promote formation of the carboxylate ion Structure K pKa F:CCO2H 0.59 0.23 Stronger acid FCH2CO2H 2.6×10-3 2.59 CICH2CO2H 1.4×10-3 2.85 BrCH2CO2H 2.1×10-3 2.68 ICH2CO2H 7.5×10-4 3.12 HCO,H 1.77×10-4 3.75 HOCH2CO2H 1.5×10-4 3.83 CcHCO2H 6.46×10-ǒ 4.19 H,C-CHCO,H 5.6×10-5 4.25 CH:CO2H 1.76×10-6 4.75 CH:CH2CO2H 1.34×10-5 4.87 Weaker acid CH CH2OH(ethanol) (10-16) (16) "Value for ethanol is shown for reference 004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
Substituent Effects on Acidity ◼Electronegative substituents promote formation of the carboxylate ion
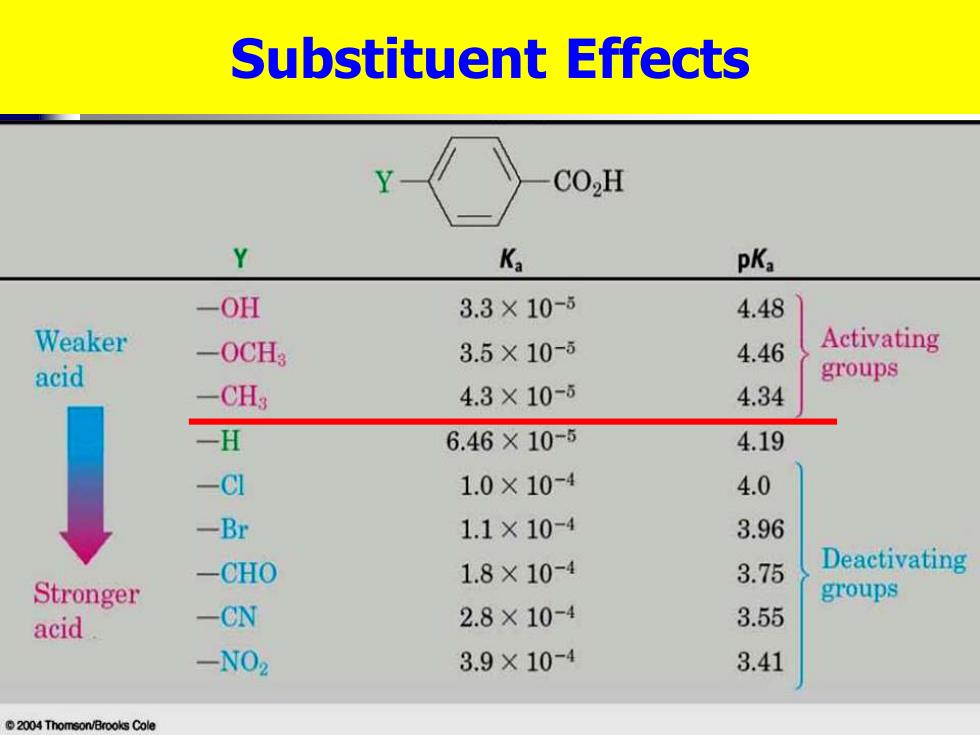
Substituent Effects CO,H Y Ka pKa -OH 3.3×10-5 4.48 Weaker -0CH3 3.5X10-5 4.46 Activating acid groups -CH3 4.3×10-6 4.34 一H 6.46×10-5 4.19 -CI 1.0×10-4 4.0 -Br 1.1×10-4 3.96 -CHO 1.8×10-4 3.75 Deactivating Stronger groups acid -CN 2.8×10-4 3.55 -N02 3.9×10-4 3.41 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
Substituent Effects
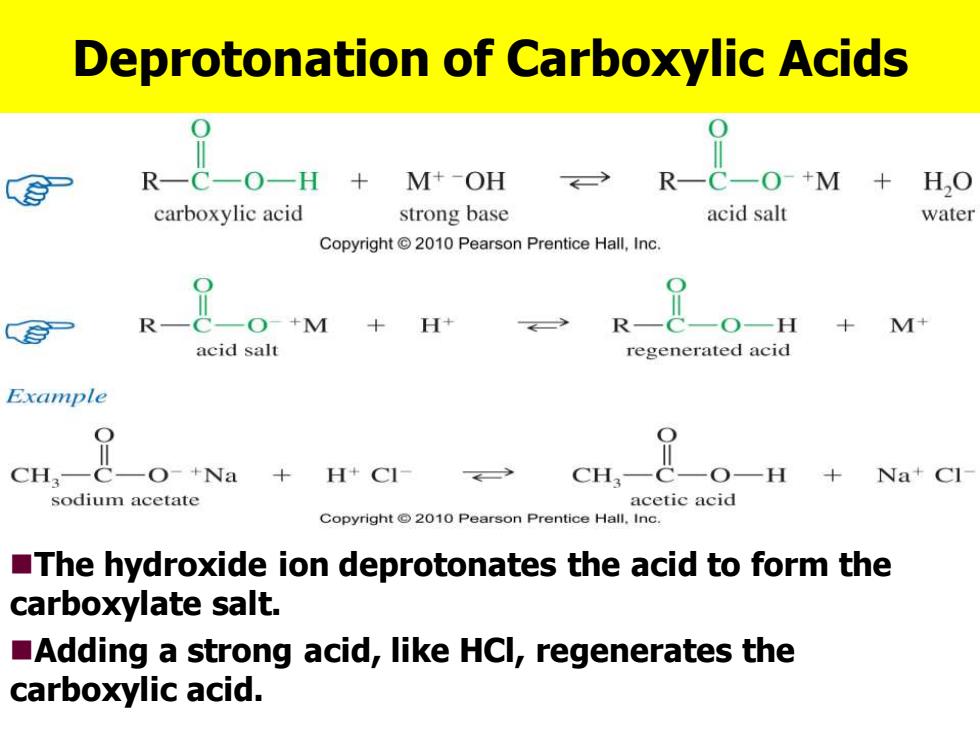
Deprotonation of Carboxylic Acids R一C一O+M H,O carboxylic acid strong base acid salt water Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. 二O+M+ +M+ acid salt regenerated acid Example CH,— O-+Na +H+C1 cH, ,O- +Na+Cl sodium acetate acetic acid Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc. The hydroxide ion deprotonates the acid to form the carboxylate salt. Adding a strong acid,like HCl,regenerates the carboxylic acid
Deprotonation of Carboxylic Acids ◼The hydroxide ion deprotonates the acid to form the carboxylate salt. ◼Adding a strong acid, like HCl, regenerates the carboxylic acid

Hydrolysis of Fats and Oils 0 cH,-0-&M CH2-OH o-iMM 0 OH/H,O CH-0-0 CH-OH 0 hydrolysis 0 CH2-0-c_ CH2-OH o-c fat or oil glycerol fatty acid salts (soap) Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The basic hydrolysis of fat and oils produces soap,known as saponification
Hydrolysis of Fats and Oils • The basic hydrolysis of fat and oils produces soap,known as saponification
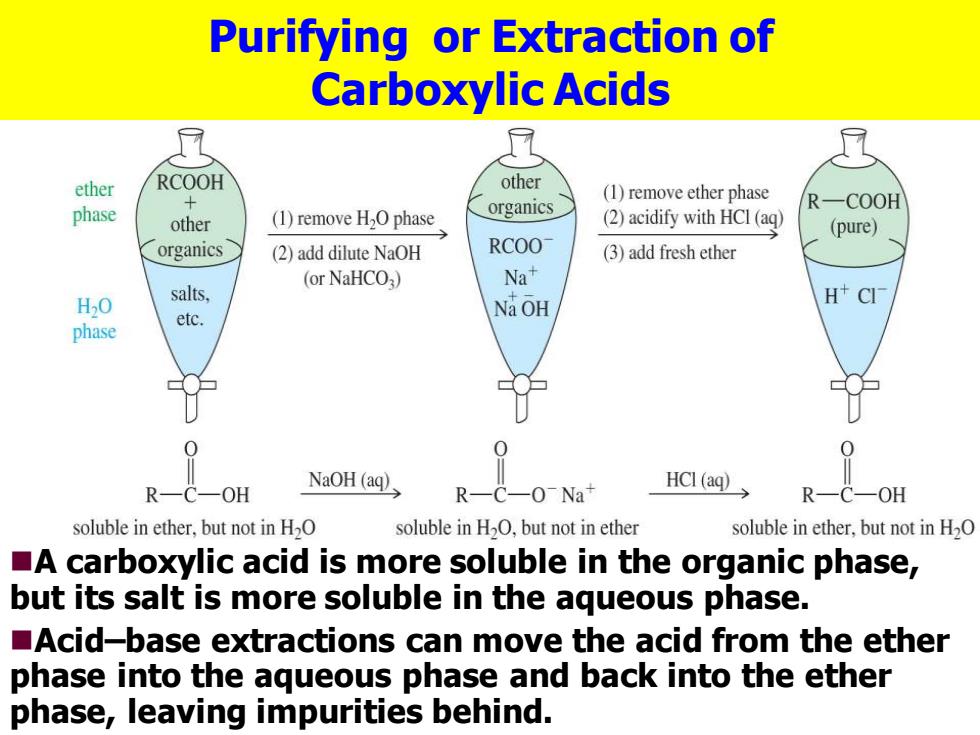
Purifying or Extraction of Carboxylic Acids ether RCOOH other (1)remove ether phase organics R一COOH phase other (1)remove H2O phase (2)acidify with HCI(aq) (pure) organics (2)add dilute NaOH RCOO (3)add fresh ether (or NaHCO3) Na+ H2O salts, Na OH H CI etc. phase R-C—OH NaOH (aq) R-C-0-Na+ HCI(aq) R—C soluble in ether,but not in H2O soluble in H2O,but not in ether soluble in ether,but not in H2O A carboxylic acid is more soluble in the organic phase, but its salt is more soluble in the aqueous phase. Acid-base extractions can move the acid from the ether phase into the aqueous phase and back into the ether phase,leaving impurities behind
Purifying or Extraction of Carboxylic Acids ◼A carboxylic acid is more soluble in the organic phase, but its salt is more soluble in the aqueous phase. ◼Acid–base extractions can move the acid from the ether phase into the aqueous phase and back into the ether phase, leaving impurities behind