MC AC MC AC Pe PMC D=MR MR Q. Quantity Cvc Quantity (a) ) Comparison of Monopolistically Competitive Equilibrium and Perfectly Competitive Equilibrium
Comparison of Monopolistically Competitive Equilibrium and Perfectly Competitive Equilibrium

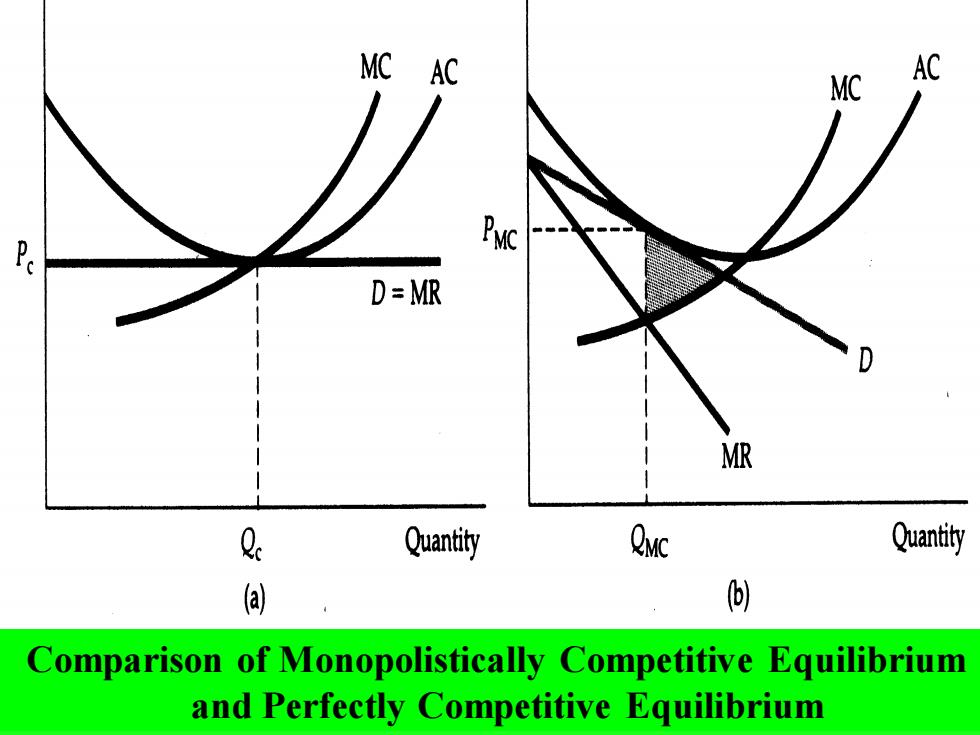
Under perfect competition,as in (a),price equals marginal cost, but under monopolistic competition,price exceeds marginal cost, so there is a deadweight loss as shown by the shaded area in (b). In both type of markets,entry occurs until profits are driven to zero
Under perfect competition, as in (a), price equals marginal cost, but under monopolistic competition, price exceeds marginal cost, so there is a deadweight loss as shown by the shaded area in (b). In both type of markets, entry occurs until profits are driven to zero

Under perfect competition,the demand curve facing the firm is horizontal,so the zero-profit point occurs at the point of minimum average cost. Under monopolistic competition the demand curve is downward sloping,so the zero-profit point is to the left of the point of minimum average cost. In evaluating monopolistic competition,these inefficiencies must be balanced (against the gains to consumers from product diversity
Under perfect competition, the demand curve facing the firm is horizontal, so the zero-profit point occurs at the point of minimum average cost. Under monopolistic competition the demand curve is downward sloping, so the zero-profit point is to the left of the point of minimum average cost. In evaluating monopolistic competition, these inefficiencies must be balanced (抵消) against the gains to consumers from product diversity

12.2 Oligopoly Nash equilibrium-Set of strategies or actions in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors'actions. Duopoly-Market in which two firms compete with each other. Cournot model-Oligopoly model in which firms produce a homogeneous good,each firm treats the output of its competitors as fixed,and all firms decide simultaneously how much to produce
12.2 Oligopoly Nash equilibrium - Set of strategies or actions in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors’ actions. Duopoly - Market in which two firms compete with each other. Cournot model - Oligopoly model in which firms produce a homogeneous good, each firm treats the output of its competitors as fixed, and all firms decide simultaneously how much to produce
Pi D1(0) MR1(0) MC1 MR1(75) MR1(50)D1(75) p50 12.5 25 50 75 Q1 Firm 1's Output Decision
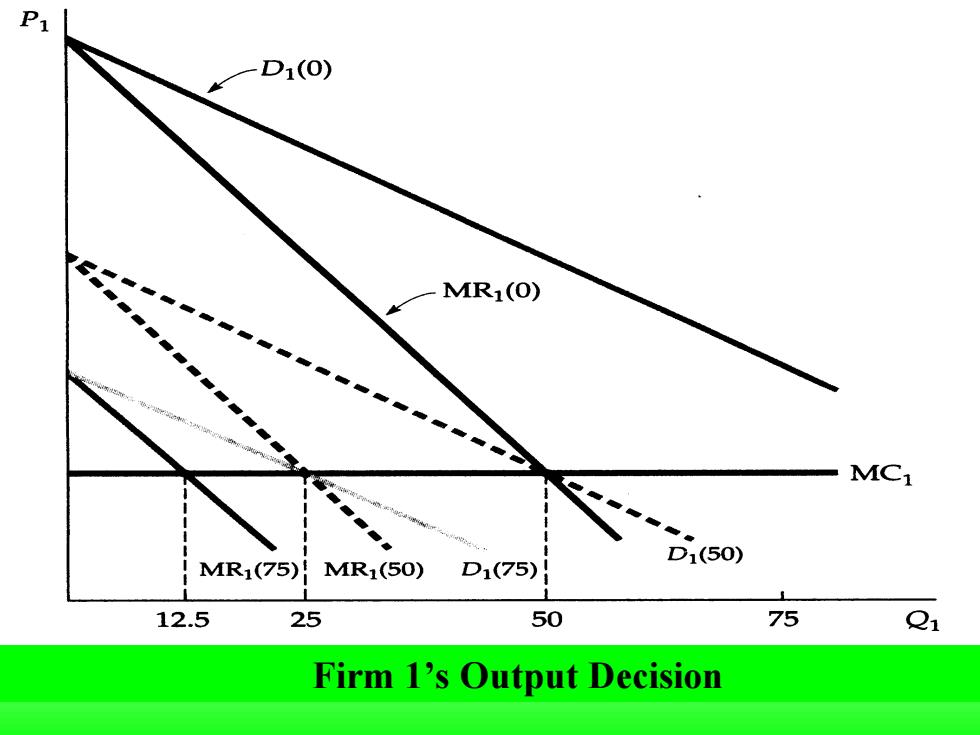
Firm 1’s Output Decision