
Chapter 11 Applications of Digital Signal Processing
Chapter 11 Applications of Digital Signal Processing

Spectral Analysis of Signals Spectral analysis is concerned with the determination of frequency contents of a continuous-time signal ga(t)using DSP methods It involves the determination of either the energy spectrum or the power spectrum of the signal If ga(t)is sufficiently bandlimited,spectral characteristics of its discrete-time equivalent g[n]should provide a good estimate of spectral characteristics of ga(t)
Spectral Analysis of Signals • Spectral analysis is concerned with the determination of frequency contents of a continuous-time signal ga(t) using DSP methods • It involves the determination of either the energy spectrum or the power spectrum of the signal • If ga(t) is sufficiently bandlimited, spectral characteristics of its discrete-time equivalent g[n] should provide a good estimate of spectral characteristics of ga(t)
Spectral Analysis of Signals In most cases,ga(t)is defined for-oo<t<oo Thus,gn is of infinite extent,and defined for -co<n<oo Hence,ga(t)is first passed through an analog anti-aliasing filter whose output is then sampled to generate gn Assumptions:(1)Effect of aliasing can be ignored,(2)A/D conversion noise can be neglected
Spectral Analysis of Signals • In most cases, ga(t) is defined for-∞<t<∞ • Thus, g[n] is of infinite extent, and defined for -∞<n<∞ • Hence, ga(t) is first passed through an analog anti-aliasing filter whose output is then sampled to generate g[n] • Assumptions: (1) Effect of aliasing can be ignored, (2) A/D conversion noise can be neglected

Spectral Analysis of Signals Three types of spectral analysis- 1)Spectral analysis of stationary sinusoidal signals 2)Spectral analysis of of nonstationary signals with time-varying parameters 3)Spectral analysis of random signals
Spectral Analysis of Signals • Three types of spectral analysis - • 1) Spectral analysis of stationary sinusoidal signals • 2) Spectral analysis of of nonstationary signals with time-varying parameters • 3) Spectral analysis of random signals
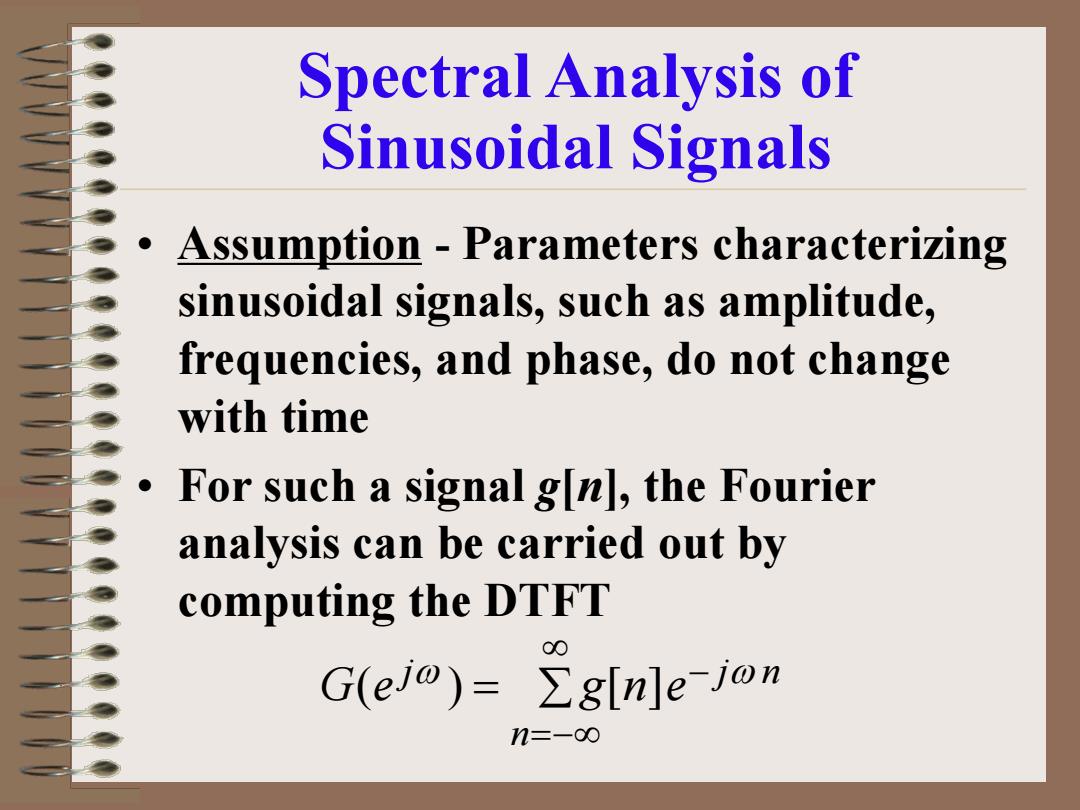
Spectral Analysis of Sinusoidal Signals Assumption -Parameters characterizing sinusoidal signals,such as amplitude, frequencies,and phase,do not change with time For such a signal g[n],the Fourier analysis can be carried out by computing the DTFT G(ejo)=∑g[nle-jon n=-o∞
Spectral Analysis of Sinusoidal Signals • Assumption - Parameters characterizing sinusoidal signals, such as amplitude, frequencies, and phase, do not change with time • For such a signal g[n], the Fourier analysis can be carried out by computing the DTFT = ∑ ∞ =−∞ − n j j n G e g n e ω ω ( ) [ ]