
Acute Leukemia
Acute Leukemia

Acute Leukemia ·Definition characterized by a huge(massive) accumulation of blastcells the infiltration of these blastcells result in 1 suppression of normal hematopoiesis lead to anemia,infection,bleeding 2 clinic manifestation related to involvement of organs outside BM
Acute Leukemia • Definition characterized by a huge(massive) accumulation of blastcells .the infiltration of these blastcells result in : 1 )suppression of normal hematopoiesis lead to anemia,infection,bleeding 2 )clinic manifestation related to involvement of organs outside BM

Acute Leukemia ·Classification: 1976 Morphologic Classifying by International FAB cooperative group 1980 MIC Morphology,Immunology, Cytogenetics 2001WH○
Acute Leukemia • Classification: 1976 Morphologic Classifying by International FAB cooperative group , 1980 MIC ,Morphology, Immunology, Cytogenetics 2001 WHO
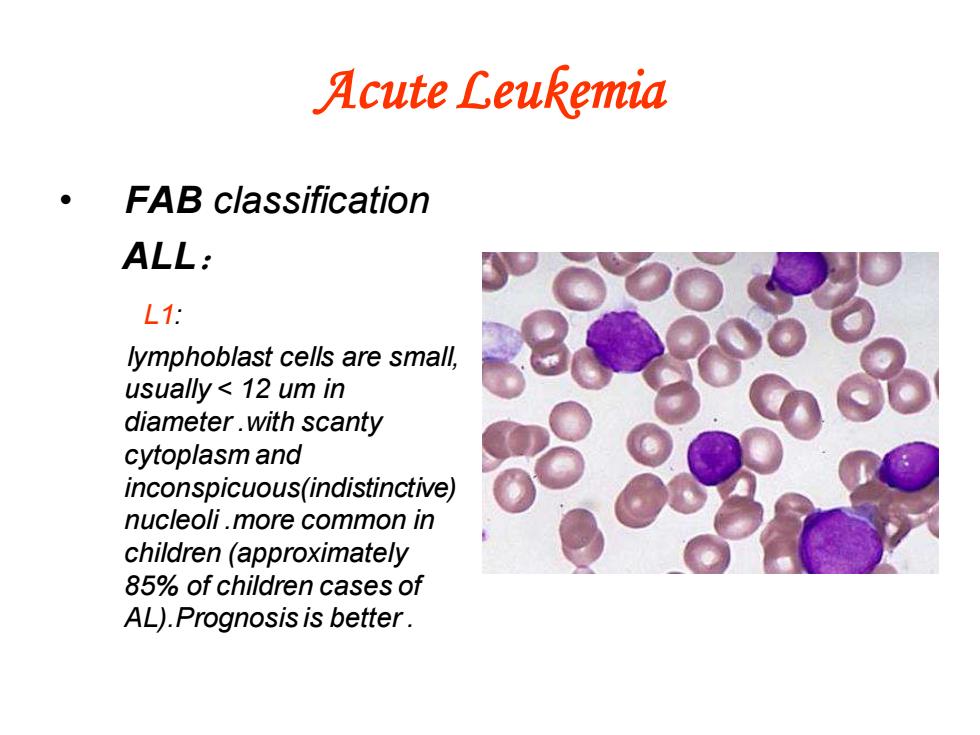
Acute Leukemia FAB classification ALL: L1: lymphoblast cells are small, usually 12 um in diameter.with scanty cytoplasm and inconspicuous(indistinctive) nucleoli.more common in children(approximately 85%of children cases of AL).Prognosis is better
Acute Leukemia • FAB classification ALL: L1: lymphoblast cells are small, usually < 12 um in diameter .with scanty cytoplasm and inconspicuous(indistinctive) nucleoli .more common in children (approximately 85% of children cases of AL).Prognosis is better

Acute Leukemia ALL L2: lymphoblasts are larger in size (>12um),have more prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm.more common in adult,worse in prognosis
Acute Leukemia ALL L2: lymphoblasts are larger in size (>12um),have more prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm .more common in adult ,worse in prognosis