
Analog Modulation Conventional AM
Analog Modulation Conventional AM
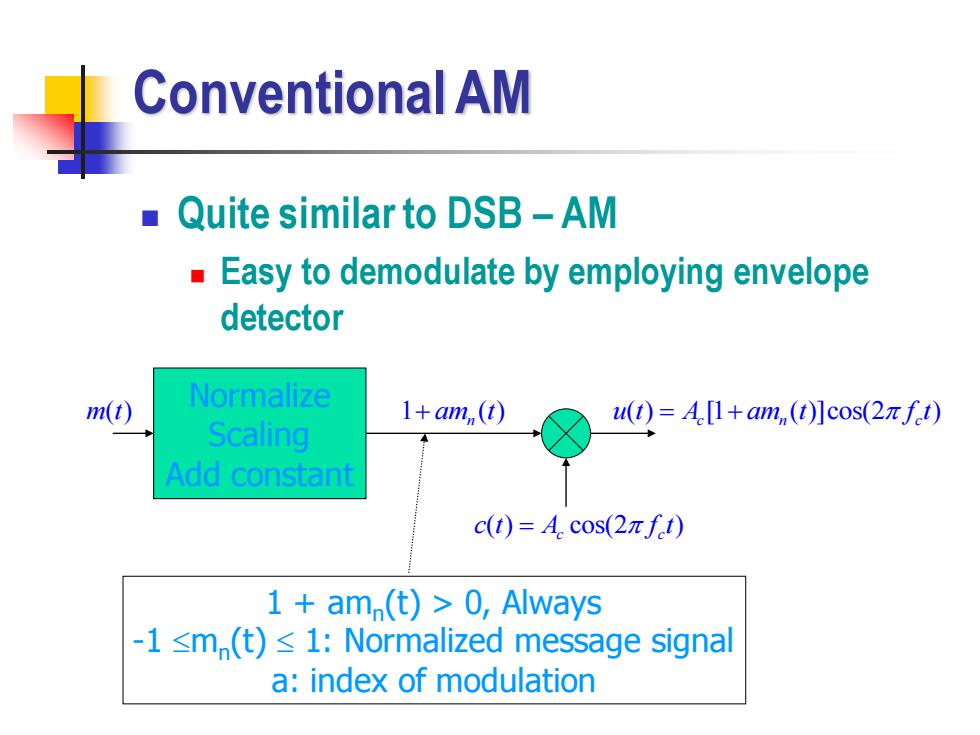
Conventional AM Quite similar to DSB-AM Easy to demodulate by employing envelope detector m(t) Normalize 1+am,(t) u(t)=A[1+am,(t)]cos(2nft) Scaling Add constant c(t)=Acos(2πft) 1 am(t)>0,Always -1≤m(t)≤l:Normalized message signal a:index of modulation
Conventional AM ◼ Quite similar to DSB – AM ◼ Easy to demodulate by employing envelope detector ( ) cos(2 ) c c c t A f t = ( ) [1 ( )]cos(2 ) 1 ( ) + am t n u t A am t f t = + c n c Normalize Scaling Add constant m t( ) 1 + amn (t) > 0, Always -1 mn (t) 1: Normalized message signal a: index of modulation
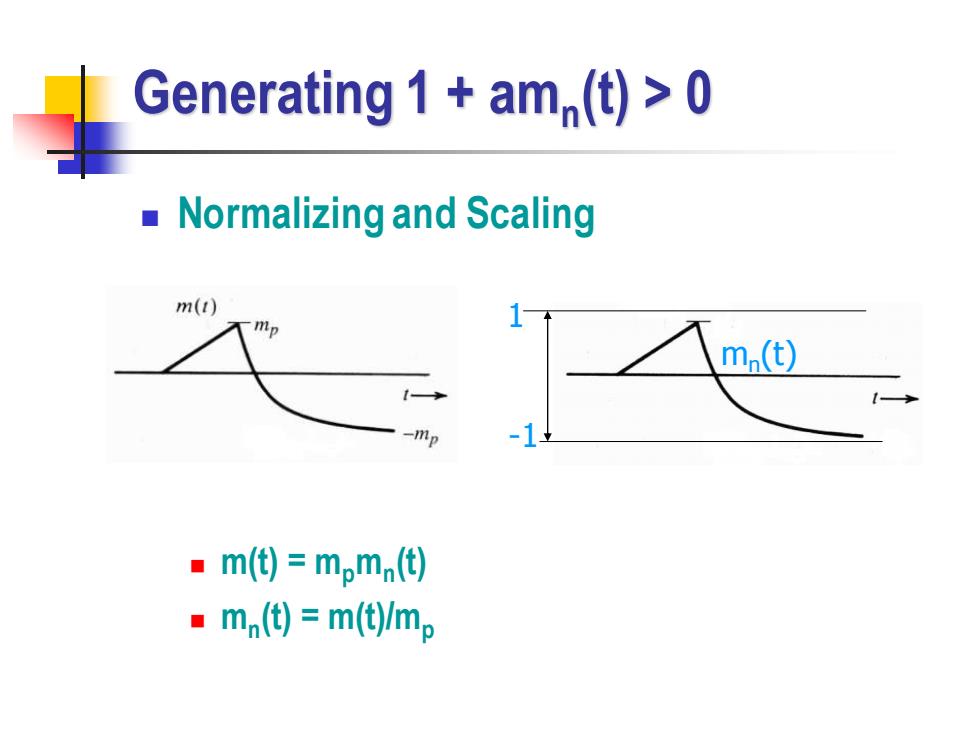
Generating 1 am(t)>0 Normalizing and Scaling m(t) mp m(t) -mp m(t)=mpmn(t) ·mn()=m(mp
Generating 1 + amn (t) > 0 ◼ Normalizing and Scaling ◼ m(t) = mpmn (t) ◼ mn (t) = m(t)/mp mn (t) 1 -1
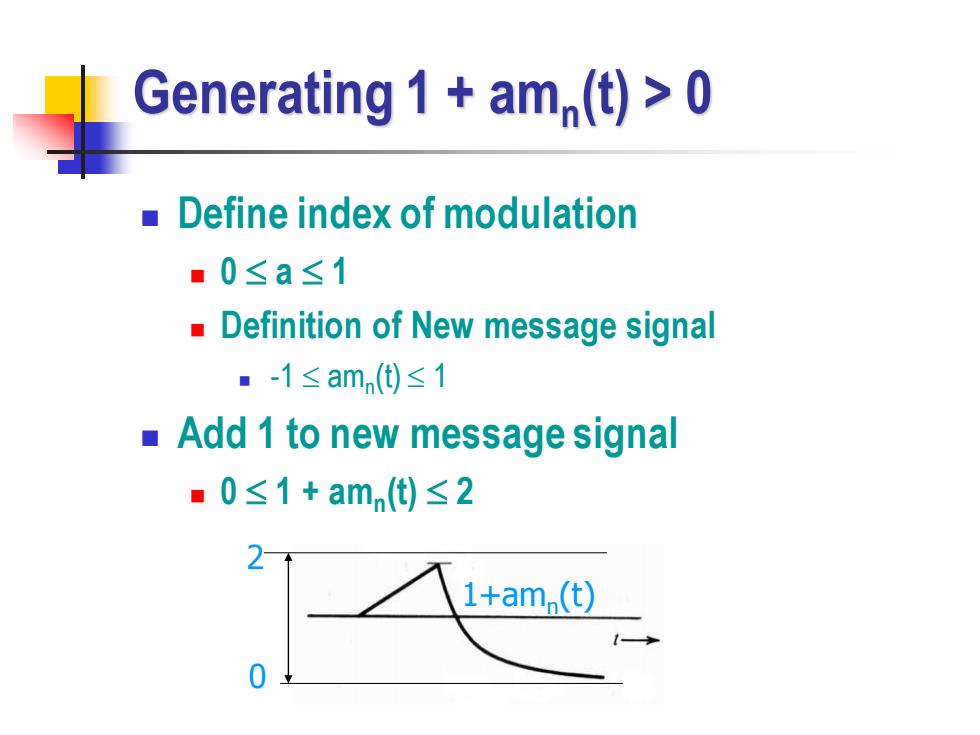
Generating 1+am(t)>0 Define index of modulation ■0≤a≤1 Definition of New message signal m-1≤am()≤1 Add 1 to new message signal ■ ■0≤1+am)≤2 1+am.(t) 0
Generating 1 + amn (t) > 0 ◼ Define index of modulation ◼ 0 a 1 ◼ Definition of New message signal ◼ -1 amn (t) 1 ◼ Add 1 to new message signal ◼ 0 1 + amn (t) 2 1+amn (t) 2 0
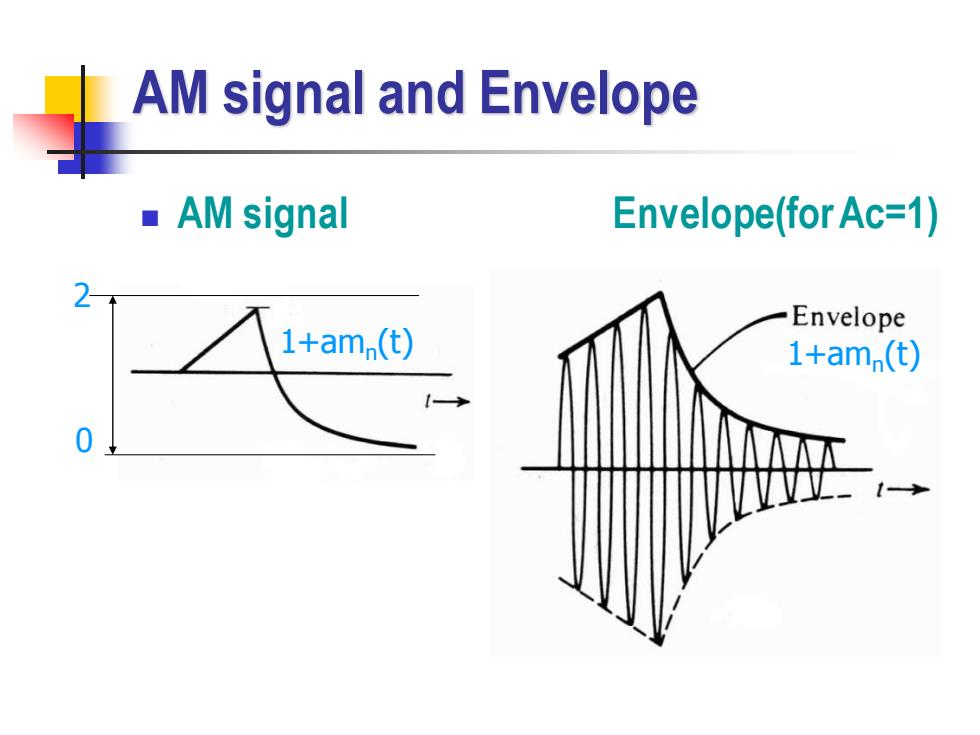
AM signal and Envelope AM signal Envelope(for Ac=1) 2 Envelope 1+am.(t) 1+am (t) 0
AM signal and Envelope ◼ AM signal Envelope(for Ac=1) 1+amn (t) 2 0 1+amn (t)