
微丝的功能 维持细胞形态,赋予质膜机械强度。微丝遍及胞质各 处,形成网络结构,维持细胞形状和赋予质膜机械强度。 细胞运动。胞质环流、阿米巴运动、变皱膜运动及吞噬 等,都与肌动蛋白相关。 冬微绒毛(microvillus)。是肠上皮细胞的指状突起,用以 增加肠上皮细胞表面积,以利于营养的快速吸收。 冬应力纤维(stress fiber)。介导细胞间或细胞与基质表 面的粘着。如粘着斑。 冬参与胞质分裂。收缩环由大量反向平行排列的微丝组 成,其收缩机制是肌动蛋白和肌球蛋白相对滑动。 冬肌肉收缩。动物所特有。 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 维持细胞形态,赋予质膜机械强度。微丝遍及胞质各 处,形成网络结构,维持细胞形状和赋予质膜机械强度。 细胞运动。胞质环流、阿米巴运动、变皱膜运动及吞噬 等,都与肌动蛋白相关。 微绒毛(microvillus)。是肠上皮细胞的指状突起,用以 增加肠上皮细胞表面积,以利于营养的快速吸收。 应力纤维(stress fiber)。介导细胞间或细胞与基质表 面的粘着。如粘着斑。 参与胞质分裂。收缩环由大量反向平行排列的微丝组 成,其收缩机制是肌动蛋白和肌球蛋白相对滑动。 肌肉收缩。动物所特有。 微丝的功能
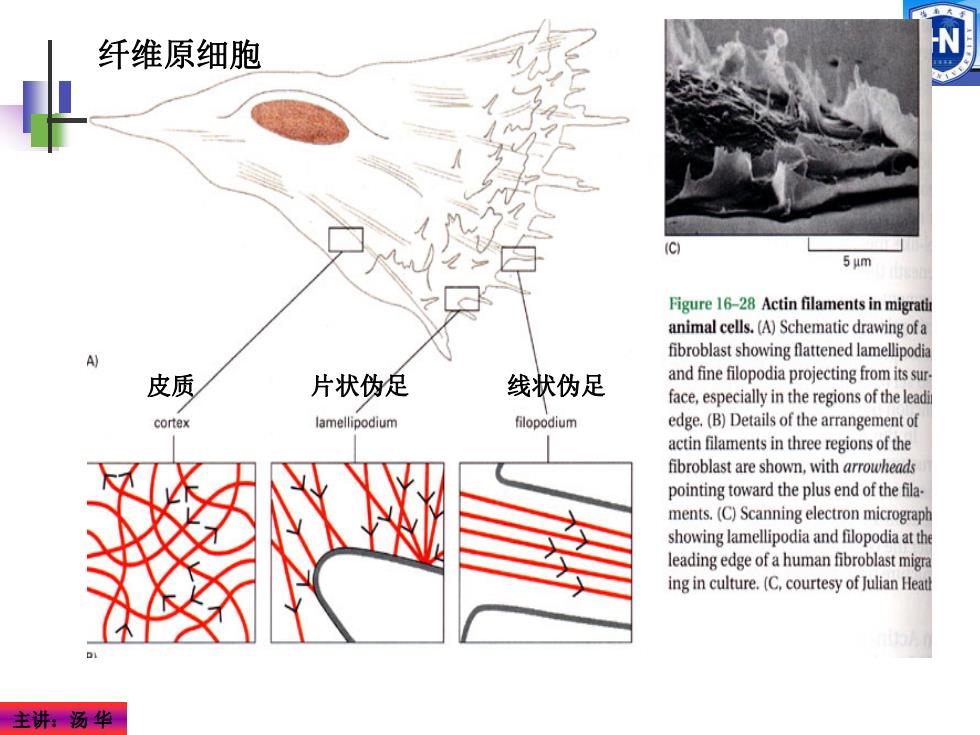
纤维原细胞 5μm Figure 16-28 Actin filaments in migrati animal cells.(A)Schematic drawing ofa fibroblast showing flattened lamellipodia 皮质 片状伪足 线状伪足 and fine filopodia projecting from its sur. face,especially in the regions of the leadi cortex lamellipodium filopodium edge.(B)Details of the arrangement of actin filaments in three regions of the fibroblast are shown,with arrowheads pointing toward the plus end of the fila. ments.(C)Scanning electron micrograph showing lamellipodia and filopodia at the leading edge of a human fibroblast migra ing in culture.(C.courtesy of Julian Heat 主讲汤华
主讲:汤 华 皮质 片状伪足 线状伪足 纤维原细胞
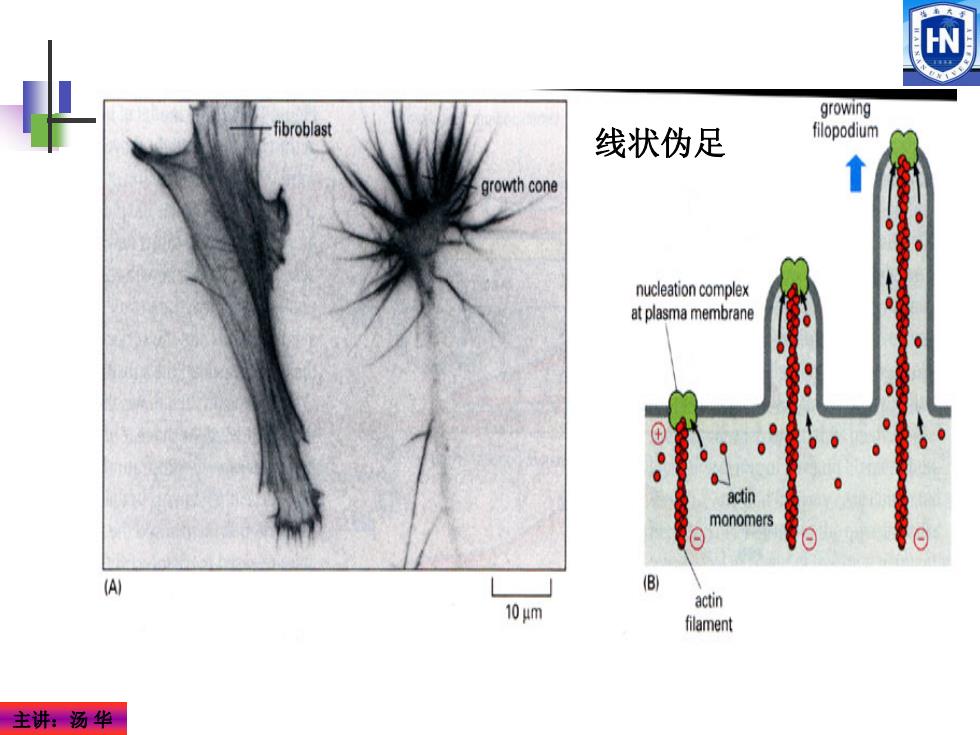
W growing fibroblast 线状伪足 filopodium growth cone nucleation complex at plasma membrane 0 0 0 actin monomers A B actin 10μm filament 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 线状伪足
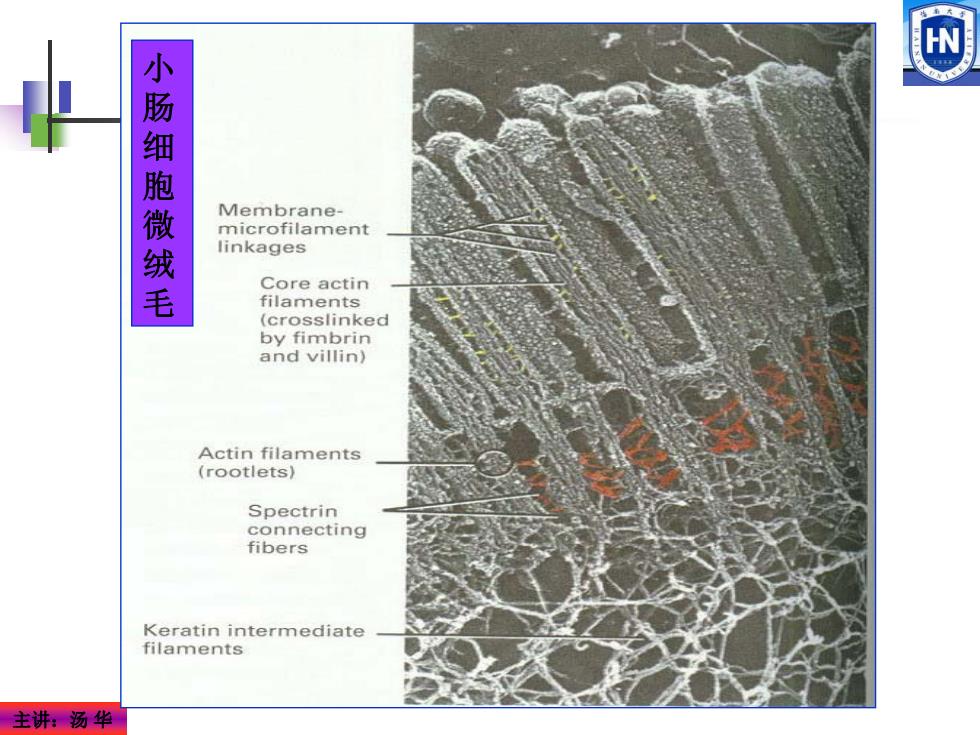
W 小 肠细 胞 Membrane- microfilament linkages 毛 Core actin filaments (crosslinked by fimbrin and villin) Actin filaments (rootlets) Spectrin connecting fibers Keratin intermediate filaments 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 小 肠 细 胞 微 绒 毛
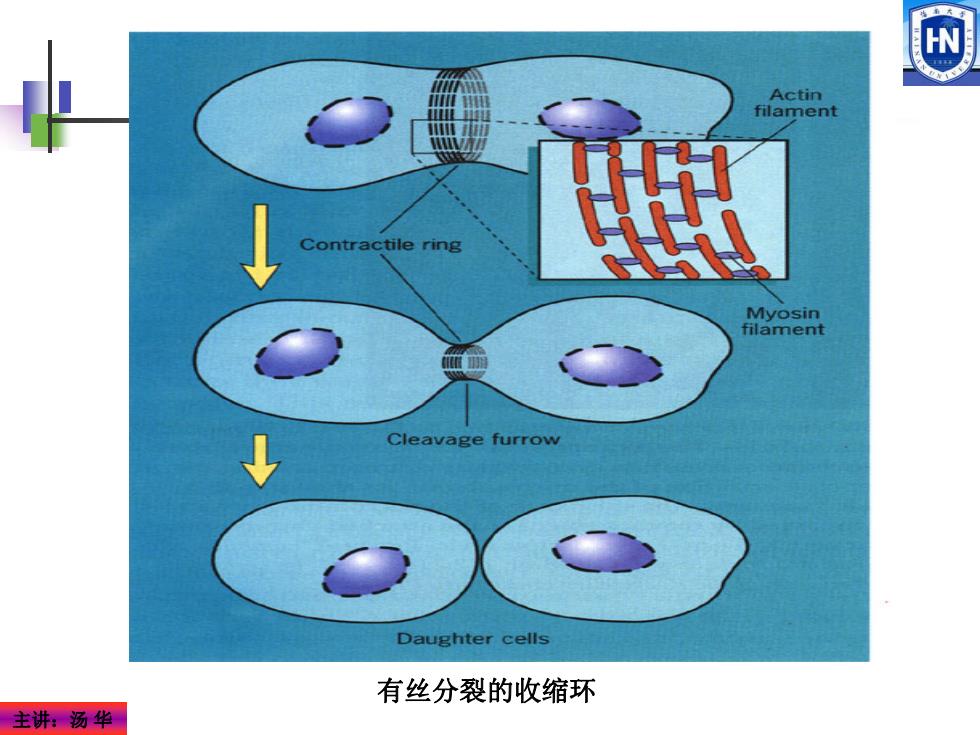
Actin filament Contractile ring Myosin filament 恤品 Cleavage furrow Daughter cells 有丝分裂的收缩环 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 有丝分裂的收缩环