
教师教案 (2020一2021学年第一学期) 课程名称:工程力学 授课学时:48学时 授课班级:2019级 任课教师:谢晓梅 教师职称:副教授 教师所在学院:航空航天学院 电子科技大学教务处
教 师 教 案 (2020 — 2021 学年 第 一 学期) 课 程 名 称:工程力学 授 课 学 时:48 学时 授 课 班 级:2019 级 任 课 教 师:谢晓梅 教 师 职 称:副教授 教师所在学院:航空航天学院 电子科技大学教务处
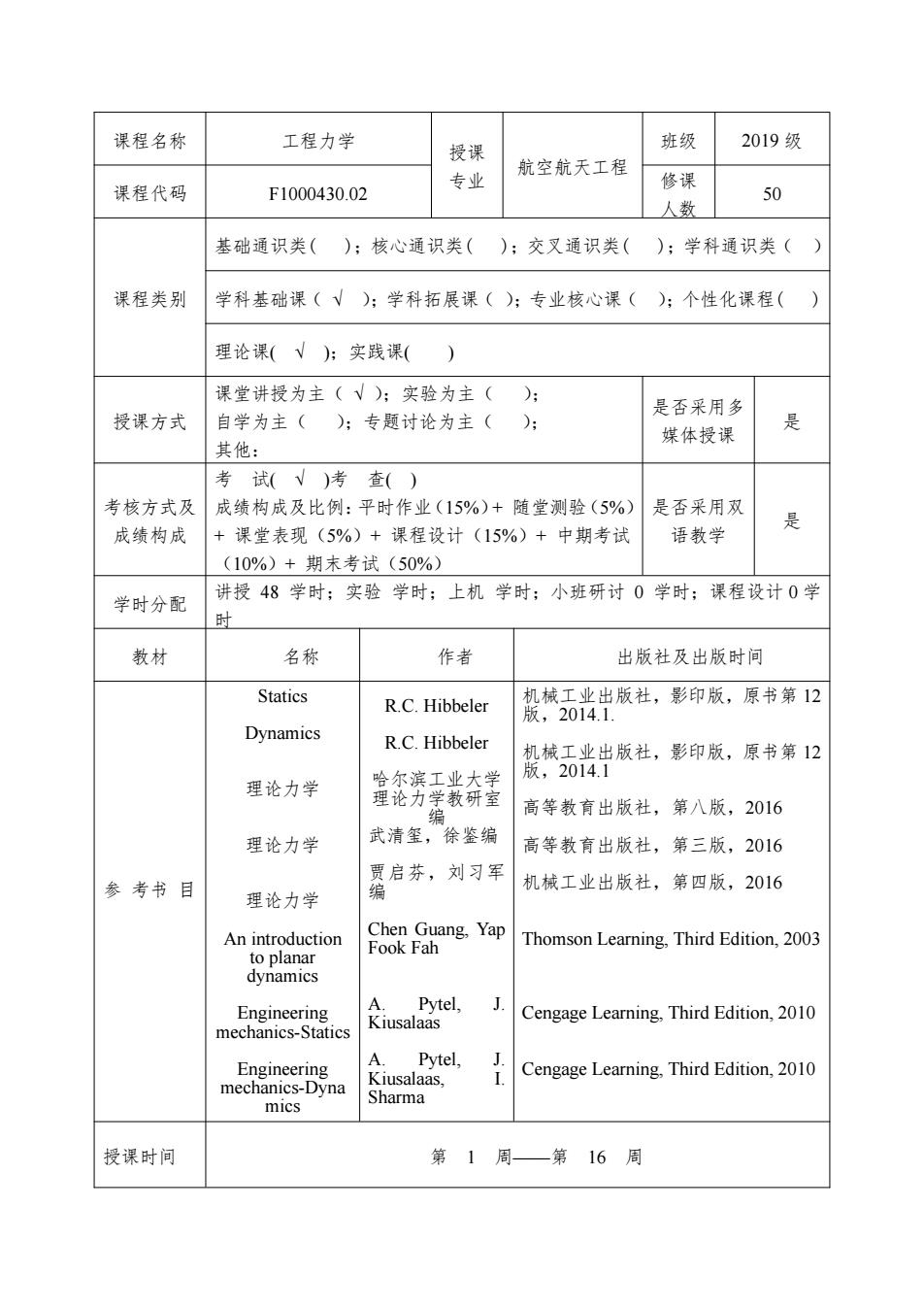
课程名称 工程力学 授课 班级 2019级 专业 航空航天工程 课程代码 F1000430.02 修课 50 人数 基础通识类();核心通识类( );交叉通识类( );学科通识类() 课程类别 学科基础课(√):学科拓展课();专业核心课();个性化课程( 理论课(√):实践课() 课堂讲授为主(V);实验为主(): 授课方式 是否采用多 自学为主():专题讨论为主(): 媒体授课 是 其他: 考试(V)考查() 考核方式及 成绩构成及比例:平时作业(15%)+随堂测验(5%) 是否采用双 成绩构成 +课堂表现(5%)+课程设计(15%)+中期考试 语教学 是 (10%)+期末考试(50%) 学时分配 讲授48学时;实验学时;上机学时;小班研讨0学时;课程设计0学 时 教材 名称 作者 出版社及出版时间 Statics R.C.Hibbeler 机械工业出版社,影印版,原书第12 版,2014.1. Dynamics R.C.Hibbeler 机械工业出版社,影印版,原书第12 版,2014.1 理论力学 哈尔滨工业大学 理论力学教研室 编 高等教育出版社,第八版,2016 理论力学 武清玺,徐鉴编 高等教育出版社,第三版,2016 贾启芬,刘习军 参考书目 理论力学 机械工业出版社,第四版,2016 An introduction Chen Guang,Yap Fook Fah Thomson Learning,Third Edition,2003 to planar dynamics Engineering A.Pytel, J. Cengage Learning,Third Edition,2010 mechanics-Statics Kiusalaas Engineering A. Pytel, J Kiusalaas, Cengage Learning,Third Edition,2010 mechanics-Dyna mics Sharma 授课时间 第1周一第16周
课程名称 工程力学 授课 专业 航空航天工程 班级 2019 级 课程代码 F1000430.02 修课 人数 50 课程类别 基础通识类( );核心通识类( );交叉通识类( );学科通识类( ) 学科基础课( √ );学科拓展课( );专业核心课( );个性化课程( ) 理论课( √ );实践课( ) 授课方式 课堂讲授为主( √ );实验为主( ); 自学为主( );专题讨论为主( ); 其他: 是否采用多 媒体授课 是 考核方式及 成绩构成 考 试( √ )考 查( ) 成绩构成及比例:平时作业(15%)+ 随堂测验(5%) + 课堂表现(5%)+ 课程设计(15%)+ 中期考试 (10%)+ 期末考试(50%) 是否采用双 语教学 是 学时分配 讲授 48 学时;实验 学时;上机 学时;小班研讨 0 学时;课程设计 0 学 时 教材 名称 作者 出版社及出版时间 参 考书 目 Statics Dynamics 理论力学 理论力学 理论力学 An introduction to planar dynamics Engineering mechanics-Statics Engineering mechanics-Dyna mics R.C. Hibbeler R.C. Hibbeler 哈尔滨工业大学 理论力学教研室 编 武清玺,徐鉴编 贾启芬,刘习军 编 Chen Guang, Yap Fook Fah A. Pytel, J. Kiusalaas A. Pytel, J. Kiusalaas, I. Sharma 机械工业出版社,影印版,原书第 12 版,2014.1. 机械工业出版社,影印版,原书第 12 版,2014.1 高等教育出版社,第八版,2016 高等教育出版社,第三版,2016 机械工业出版社,第四版,2016 Thomson Learning, Third Edition, 2003 Cengage Learning, Third Edition, 2010 Cengage Learning, Third Edition, 2010 授课时间 第 1 周——第 16 周

Statics Introduction 一、教学内容及要求 教学内容(2学时): What is Mechanics? What is Engineering Mechanics? Why to study? What to study? How do we learn this course well? Textbook and Reference About Bilingual Teaching 教学要求: To understand history of mechanics; To understand relationship between mechanics and engineering; To understand objective,contents of this course. 二、教学重点、难点及解决办法 教学重点和难点是让学生了解为什么要学习这门课程?这门课程学习什 么?这门课程如何学习?通过课堂介绍力学发展史,力学在工程中的应用,工程 力学的研究内容和方法,使学生了解本课程的内涵和概貌,学习内容、学习方法。 三、教学设计 开篇从什么是力学导入到力学的发展史、力学在工程中的应用,从而让学生 了解学习力学的重要性,在此基础上介绍本课程的学习内容、学习方法、考核方 式、学习资源。在讲授力学发展的历史脉络过程中,介绍涌现出的国内外标志性 人物(亚里士多德、伽利略、牛顿、欧拉、拉格朗日、冯·卡门、钱学森、钱伟 长、郭永怀、周培源等),推荐一些有关力学史发展的课外阅读资料;在介绍力 学在工程中的应用时,结合本专业的特点,通过我国探月工程、北斗导航、导弹 等航空航天领域取得的重大突破来激发学生对本课程的学习兴趣。 四、作业 自学第一章 五、参考资料 [1]Statics(静力学).R.C.Hibbeler.机械工业出版社,影印版,第十二版, 2014. [2]Dynamics(动力学).R.C.Hibbeler.机械工业出版社,影印版,第十二
Statics Introduction 一、教学内容及要求 教学内容(2 学时): What is Mechanics? What is Engineering Mechanics? Why to study? What to study? How do we learn this course well? Textbook and Reference About Bilingual Teaching 教学要求: To understand history of mechanics; To understand relationship between mechanics and engineering; To understand objective, contents of this course. 二、教学重点、难点及解决办法 教学重点和难点是让学生了解为什么要学习这门课程?这门课程学习什 么?这门课程如何学习?通过课堂介绍力学发展史,力学在工程中的应用,工程 力学的研究内容和方法,使学生了解本课程的内涵和概貌,学习内容、学习方法。 三、教学设计 开篇从什么是力学导入到力学的发展史、力学在工程中的应用,从而让学生 了解学习力学的重要性,在此基础上介绍本课程的学习内容、学习方法、考核方 式、学习资源。在讲授力学发展的历史脉络过程中,介绍涌现出的国内外标志性 人物(亚里士多德、伽利略、牛顿、欧拉、拉格朗日、冯·卡门、钱学森、钱伟 长、郭永怀、周培源等),推荐一些有关力学史发展的课外阅读资料;在介绍力 学在工程中的应用时,结合本专业的特点,通过我国探月工程、北斗导航、导弹 等航空航天领域取得的重大突破来激发学生对本课程的学习兴趣。 四、作业 自学第一章 五、参考资料 [1] Statics(静力学). R.C. Hibbeler. 机械工业出版社,影印版,第十二版, 2014.[2] Dynamics(动力学). R.C. Hibbeler. 机械工业出版社,影印版,第十二

版,2014 六、教学后记 通过绪论部分的讲解和学习,学生通对力学发展史,力学在工程(特别是航 空航天工程中)应用及本专业中有待进一步研究的力学问题的学习,让学生体会 到科学家用于探索真理的精神,为祖国当前在航空航天领域中彰显的科技实力感 到自豪,增强学生的民族自豪感,同时也激发学生的学习兴趣。 本章内容整合到《工程力学》概论一节中,要求学生课后自学。但从作业情 况来看,较多的学生对单位换算及指数表达方式存在问题,特别是对Prefiⅸ不理 解。在第二章上课前,对出错较多的问题进行讲解。 Chapter 1 General Principles 一、教学内容及要求 教学内容(0学时): 1.1 Mechanics 1.2 Units of Measurement 1.3 The international System of Units 1.4 Numerical Calculation 1.5General Procedure for Analysis 教学要求: To provide an introduction to the basic quantities and idealizations of mechanics. To give a statement of Newton's Laws of Motion and Gravitation To review the principles for applying the SI system of units To examine the standard procedures for performing numerical calculations To present a general guide for solving problems. 二、教学重点、难点及解决办法 Mechanics,units,numerical calculation and general procedure for analysis. Explain what is mechanics,statics,kinematics and kinetics.Work with one types of units.Round the final answer appropriately.Apply problem-solving strategies. 三、教学设计 本章主要采用课下自学,课上练习的方式进行。通过本章的学习,建议学生 了解以下两点: 1.The language of engineering mechanics is mathematics.Consequently, make sure you review/re-read the necessary mathematical notation/concepts as they arise in your mechanics course(trying to review all of the necessary mathematics at once is not recommended-there's just too much to digest at one time).You should aim to achieve fluency in basic mathematical techniques/notation so that your learning of mechanics is not distracted by trying to remember things which your instructor assumes you know e.g.,how to solve linear systems of algebraic equations
版,2014 六、教学后记 通过绪论部分的讲解和学习,学生通对力学发展史,力学在工程(特别是航 空航天工程中)应用及本专业中有待进一步研究的力学问题的学习,让学生体会 到科学家用于探索真理的精神,为祖国当前在航空航天领域中彰显的科技实力感 到自豪,增强学生的民族自豪感,同时也激发学生的学习兴趣。 本章内容整合到《工程力学》概论一节中,要求学生课后自学。但从作业情 况来看,较多的学生对单位换算及指数表达方式存在问题,特别是对 Prefix 不理 解。在第二章上课前,对出错较多的问题进行讲解。 Chapter 1 General Principles 一、教学内容及要求 教学内容(0 学时): 1.1 Mechanics 1.2 Units of Measurement 1.3 The international System of Units 1.4 Numerical Calculation 1.5General Procedure for Analysis 教学要求: To provide an introduction to the basic quantities and idealizations of mechanics. To give a statement of Newton’s Laws of Motion and Gravitation To review the principles for applying the SI system of units To examine the standard procedures for performing numerical calculations. To present a general guide for solving problems. 二、教学重点、难点及解决办法 Mechanics, units, numerical calculation and general procedure for analysis. Explain what is mechanics, statics, kinematics and kinetics. Work with one types of units. Round the final answer appropriately. Apply problem-solving strategies. 三、教学设计 本章主要采用课下自学,课上练习的方式进行。通过本章的学习,建议学生 了解以下两点: 1. The language of engineering mechanics is mathematics. Consequently, make sure you review/re-read the necessary mathematical notation/concepts as they arise in your mechanics course (trying to review all of the necessary mathematics at once is not recommended—there’s just too much to digest at one time). You should aim to achieve fluency in basic mathematical techniques/notation so that your learning of mechanics is not distracted by trying to remember things which your instructor assumes you know e.g., how to solve linear systems of algebraic equations

how to perform basic vector algebra,differentiation and integration etc. 2.Remember that in solving problems from engineering mechanics you are solving real practical problems and producing real data with physical significance. Thus,you are responsible for making sure your results are correct,consistent and well-presented.Get into the habit of doing this now so that it will become second nature by the time you graduate.In the world of professional engineering you have a responsibility to your profession and to the many people that will use the product you will help to design,manufacture or implement. 四、作业 P16:1-6 Review questions:True or False? 1.The subject called Statics studies only bodies which are at rest. 2.A particle has a mass but negligible shape/size. 3.A rigid body has a mass but negligible shape/size. 4.Newton's three laws of motion can be proved mathematically 5.Weight is a property of matter that does not change from one location to another. 6.In the SI system of units,the newton is a derived unit. 7.When performing numerical calculations,the final answer should be reported to three significant figures. 8.In an equation it's permitted to have different terms expressed in different units.This is referred to as dimensionally inhomogeneous. Answers:1.F;2.T,3.F;4.F;5.F;6.T;7.T;8.F. 五、参考资料 Statics.R.C.Hibbeler.机械工业出版社,影印版,原书第12版,2014.01 六、教学后记 本章的基本原理是学生在先修课程中已经学习过和接触过,因此本章采用自 学的方式进行。学生结合课件及本章思考题进行学习和总结,在一定程度上培养 学生自主学习能力。 Chapter 2 Force vector 一、教学内容及要求 教学内容(2学时): 2.1 Scalars and Vectors(标量和矢量) 2.2 Vector Operations(矢量运算) 2.3 Vector addition of forces(力的矢量合成) 2.4 Addition of a system of coplanar forces(平面力系的合成) 2.5 Cartesian vectors(笛卡尔矢量) 2.6 Addition of Cartesian vectors(笛卡尔矢量的合成)
how to perform basic vector algebra, differentiation and integration etc. 2. Remember that in solving problems from engineering mechanics you are solving real practical problems and producing real data with physical significance. Thus, you are responsible for making sure your results are correct, consistent and well-presented. Get into the habit of doing this now so that it will become second nature by the time you graduate. In the world of professional engineering you have a responsibility to your profession and to the many people that will use the product you will help to design, manufacture or implement. 四、作业 P16:1-6 Review questions: True or False? 1. The subject called Statics studies only bodies which are at rest. 2. A particle has a mass but negligible shape/size. 3. A rigid body has a mass but negligible shape/size. 4. Newton’s three laws of motion can be proved mathematically. 5. Weight is a property of matter that does not change from one location to another. 6. In the SI system of units, the newton is a derived unit. 7. When performing numerical calculations, the final answer should be reported to three significant figures. 8. In an equation it’s permitted to have different terms expressed in different units. This is referred to as dimensionally inhomogeneous. Answers: 1. F; 2. T; 3. F; 4. F; 5. F; 6. T; 7. T; 8. F. 五、参考资料 Statics. R.C. Hibbeler. 机械工业出版社,影印版,原书第 12 版,2014.01. 六、教学后记 本章的基本原理是学生在先修课程中已经学习过和接触过,因此本章采用自 学的方式进行。学生结合课件及本章思考题进行学习和总结,在一定程度上培养 学生自主学习能力。 Chapter 2 Force vector 一、教学内容及要求 教学内容(2 学时): 2.1 Scalars and Vectors(标量和矢量) 2.2 Vector Operations(矢量运算) 2.3 Vector addition of forces(力的矢量合成) 2.4 Addition of a system of coplanar forces(平面力系的合成) 2.5 Cartesian vectors(笛卡尔矢量) 2.6 Addition of Cartesian vectors(笛卡尔矢量的合成)