
The Use of High-Energy Protons in Cancer Therapy 王鹏程印
The Use of High-Energy Protons in Cancer Therapy

A Man A Vision In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000)suggested*: Protons can be used clinically Accelerators are available Maximum radiation dose can be placed into the tumor Proton therapy provides sparing of normal tissues Modulator wheels can spread narrow Bragg peak Robert Wilson *Wilson,R.R.(1946),"Radiological use of fast protons,"Radiology 47,487
A Man - A Vision • In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested*: – Protons can be used clinically – Accelerators are available – Maximum radiation dose can be placed into the tumor – Proton therapy provides sparing of normal tissues – Modulator wheels can spread narrow Bragg peak *Wilson, R.R. (1946), “Radiological use of fast protons,” Radiology 47, 487

History of Proton Beam Therapy 1946 R.Wilson suggests use of protons 1954 First treatment of pituitary tumors 1958 First use of protons as a neurosurgical tool 1967 First large-field proton treatments in Sweden 1974 Large-field fractionated proton treatments program begins at HCL,Cambridge,MA 1990 First hospital-based proton treatment center opens at Loma Linda University Medical Center
History of Proton Beam Therapy • 1946 R. Wilson suggests use of protons • 1954 First treatment of pituitary tumors • 1958 First use of protons as a neurosurgical tool • 1967 First large-field proton treatments in Sweden • 1974 Large-field fractionated proton treatments program begins at HCL, Cambridge, MA • 1990 First hospital-based proton treatment center opens at Loma Linda University Medical Center

World Wide Proton Treatments* Dubna(1967) 172 CANADA GER POL Moscow (1969) 3414 St.Petersburg (1969)1029 NORTH UNITED STATES Uppsala(1957): 309 CHINA HCL(1961) PSI(1984) 3935 LLUMC (1990) 6174 Clatterbridge(1989):1033 Chiba (1979) 133 INDIA 6174 Nice(1991): 1590 Tsukuba (1983) 700 Orsay (1991): 1894 Kashiwa (1998) 75 Berlin(1998) 166 A N。6 BRAZIL AUSTRALIA NAC(1993) 0/72H SOUTH PACIFIC ATLANTIE 398 *from:Particles,Newsletter (Ed J.Sisterson),No.28.July 2001
World Wide Proton Treatments* LLUMC (1990) 6174 HCL (1961) 6174 Uppsala (1957): 309 PSI (1984): 3935 Clatterbridge(1989): 1033 Nice (1991): 1590 Orsay (1991): 1894 Berlin (1998): 166 Chiba (1979) 133 Tsukuba (1983) 700 Kashiwa (1998) 75 NAC (1993) 398 Dubna (1967) 172 Moscow (1969) 3414 St. Petersburg (1969) 1029 *from: Particles, Newsletter (Ed J. Sisterson), No. 28. July 2001
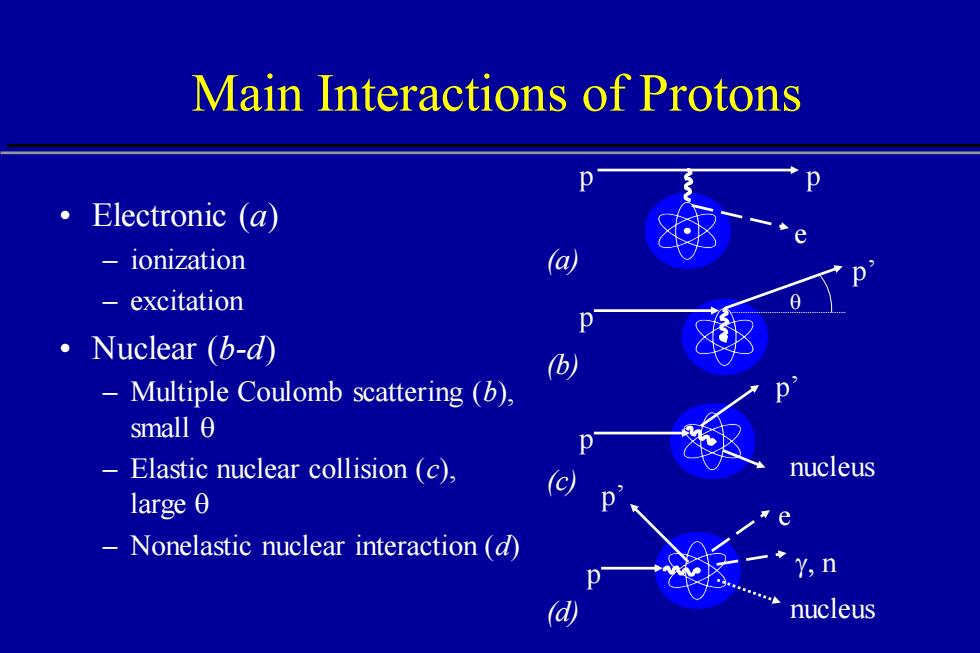
Main Interactions of Protons ·Electronic(a) ionization 一 excitation ·Nuclear(b-d Multiple Coulomb scattering (b). small 0 Elastic nuclear collision (c), nucleus large 0 Nonelastic nuclear interaction (d) Y,n d nucleus
Main Interactions of Protons • Electronic (a) – ionization – excitation • Nuclear (b-d) – Multiple Coulomb scattering (b), small q – Elastic nuclear collision (c), large q – Nonelastic nuclear interaction (d) e p p p’ p p p’ nucleus g, n p’ p e nucleus (b) (c) (d) (a) q