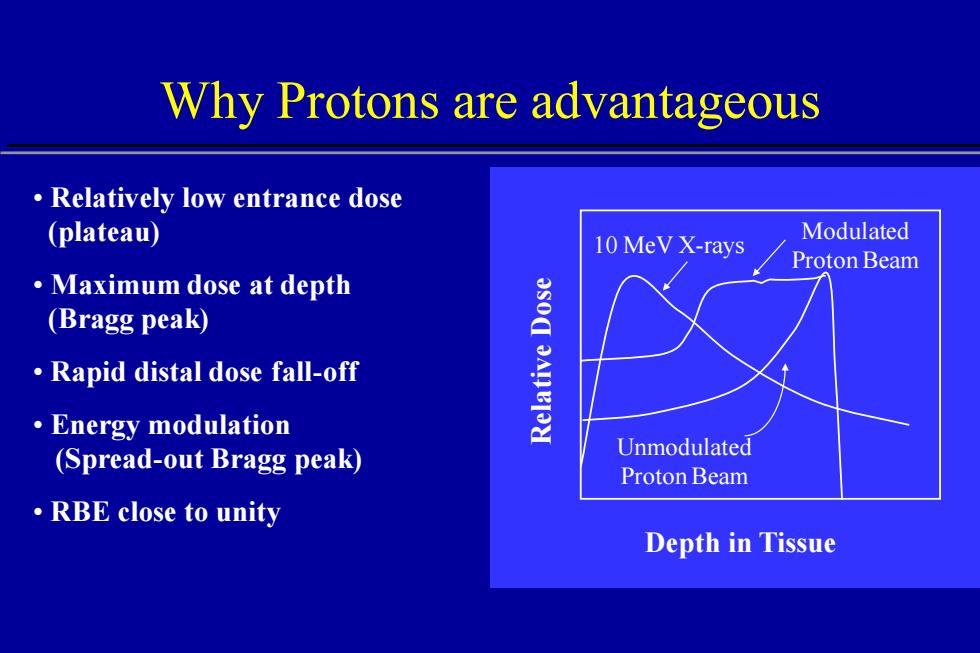
Why Protons are advantageous Relatively low entrance dose (plateau) 10 MeV X-rays Modulated Proton Beam ·Maximum dose at depth (Bragg peak) Rapid distal dose fall-off ·Energy modulation (Spread-out Bragg peak) Unmodulated Proton Beam ·RBE close to unity Depth in Tissue
Why Protons are advantageous • Relatively low entrance dose (plateau) • Maximum dose at depth (Bragg peak) • Rapid distal dose fall-off • Energy modulation (Spread-out Bragg peak) • RBE close to unity Depth in Tissue Relative Dose 10 MeV X-rays Modulated Proton Beam Unmodulated Proton Beam
Uncertainties in Proton Therapy Patient related: Physics related: ·Patient setup ·CT number conversion ·Patient movements ·Dose calculation 。Organ motion ·Body contour Machine related: 。Target definition ·Device tolerances Biology related: ·Beam energy ·Relative biological effectiveness (RBE)
Uncertainties in Proton Therapy • Patient setup • Patient movements • Organ motion • Body contour • Target definition • Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) • Device tolerances ° Biology related: • Beam energy ° Patient related: ° Physics related: • CT number conversion • Dose calculation ° Machine related:

Treatment Planning Acquisition of imaging data(CT,MRI) Conversion of CT values into stopping power Delineation of regions of interest Selection of proton beam directions :cdmNe>
Treatment Planning • Acquisition of imaging data (CT, MRI) • Conversion of CT values into stopping power • Delineation of regions of interest • Selection of proton beam directions • Design of each beam • Optimization of the plan

Treatment Delivery Fabrication of apertures and boluses ·Beam calibration Alignment of patient using DRRs Computer-controlled dose delivery
Treatment Delivery • Fabrication of apertures and boluses • Beam calibration • Alignment of patient using DRRs • Computer-controlled dose delivery
Computed Tomography (CT) Faithful reconstruction of patient's anatomy Stacked 2D maps of linear X-ray attenuation Electron density relative to water can be derived Calibration curve relates XAray tube CT numbers to relative Detector array proton stopping power
Computed Tomography (CT) X-ray tube Detector array • Faithful reconstruction of patient’s anatomy • Stacked 2D maps of linear X-ray attenuation • Electron density relative to water can be derived • Calibration curve relates CT numbers to relative proton stopping power