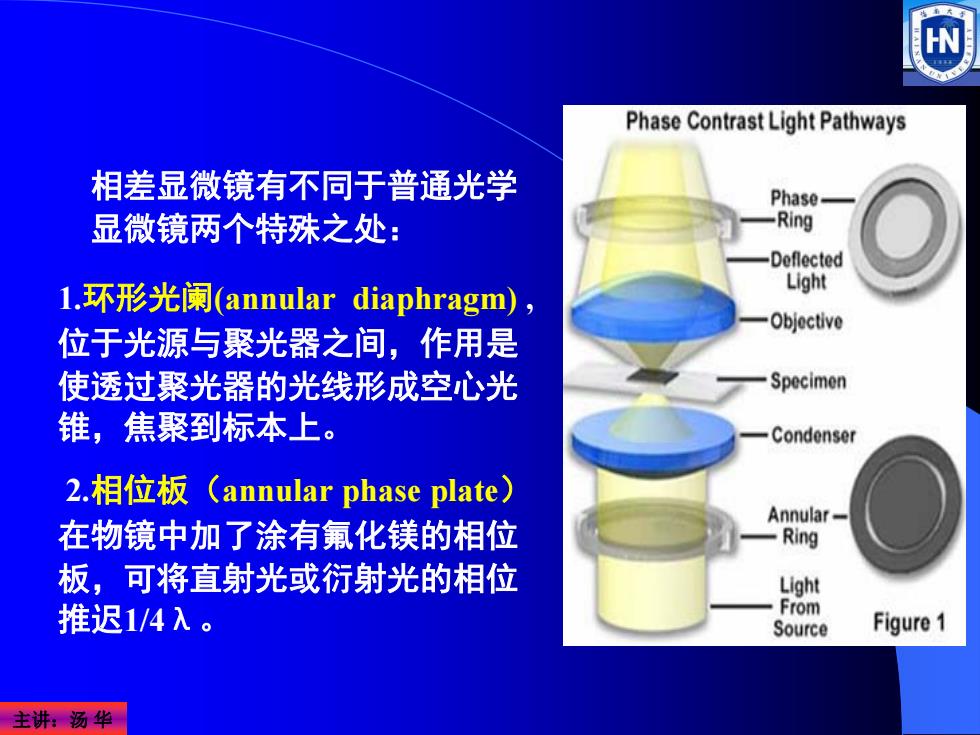
Phase Contrast Light Pathways 相差显微镜有不同于普通光学 Phase 显微镜两个特殊之处: -Ring Deflected 1.环形光阑(annular diaphragm), Light Objective 位于光源与聚光器之间,作用是 使透过聚光器的光线形成空心光 Specimen 锥,焦聚到标本上。 Condenser 2.相位板(annular phase plate) Annular 在物镜中加了涂有氟化镁的相位 -Ring 板,可将直射光或衍射光的相位 Light 推迟1/4入。 From Source Figure1 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 1.环形光阑(annular diaphragm) , 位于光源与聚光器之间,作用是 使透过聚光器的光线形成空心光 锥,焦聚到标本上。 2.相位板(annular phase plate) 在物镜中加了涂有氟化镁的相位 板,可将直射光或衍射光的相位 推迟1/4λ。 相差显微镜有不同于普通光学 显微镜两个特殊之处:
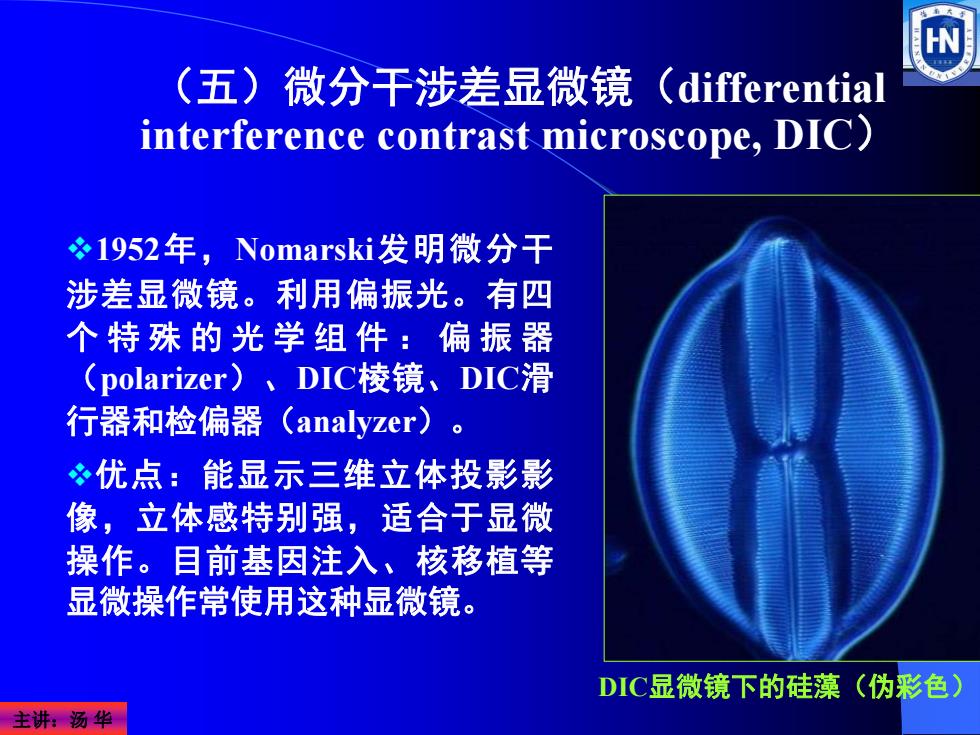
(五)微分干涉差显微镜(differential interference contrast microscope,DIC) 1952年,Nomarski发明微分干 涉差显微镜。利用偏振光。有四 个特殊的光学组件:偏振器 (polarizer)、DIC棱镜、DIC滑 行器和检偏器(analyzer)。 优点:能显示三维立体投影影 像,立体感特别强,适合于显微 操作。目前基因注入、核移植等 显微操作常使用这种显微镜。 DIC显微镜下的硅藻(伪彩色) 主讲汤华
主讲:汤 华 1952年,Nomarski发明微分干 涉差显微镜。利用偏振光。有四 个特殊的光学组件:偏振器 (polarizer)、DIC棱镜、DIC滑 行器和检偏器(analyzer)。 优点:能显示三维立体投影影 像,立体感特别强,适合于显微 操作。目前基因注入、核移植等 显微操作常使用这种显微镜。 (五)微分干涉差显微镜(differential interference contrast microscope, DIC) DIC显微镜下的硅藻(伪彩色)
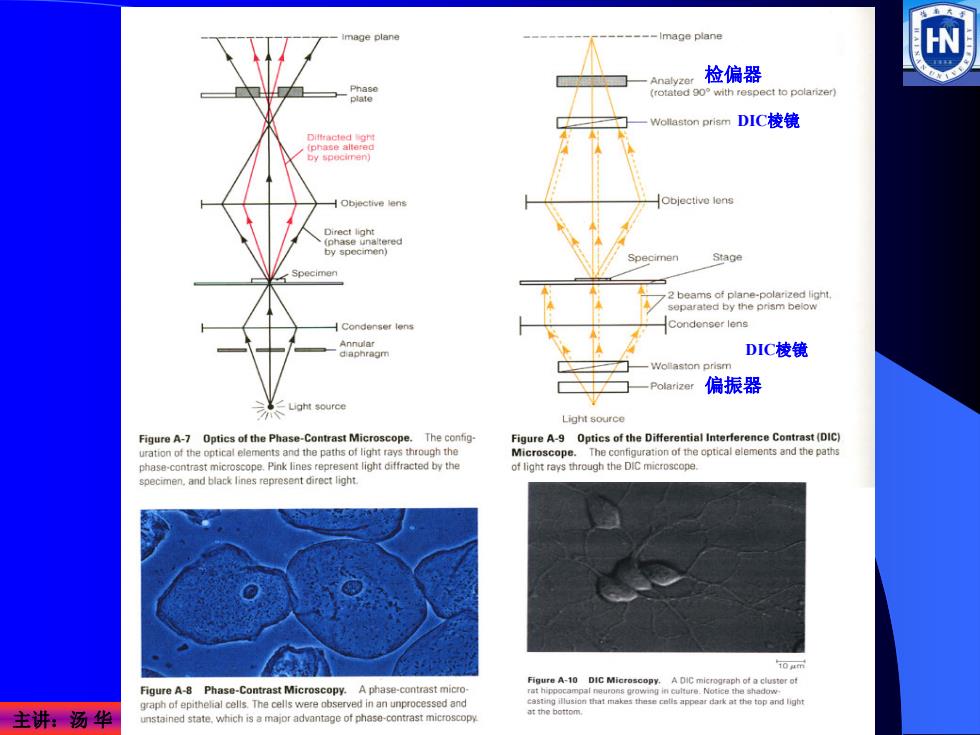
mage plane -Image plane W 检偏器 -8 ct to polarizer -Wollaston prism DIC棱镜 H Objective lens Objective lens by specimen Stage Specimen Condonser lens Annular diaphragm DIC棱镜 -Polarizer 偏振器 Light source Light source Figure A-7 Optics of the Phase-Contrast Microscope.The config- Figure A-9 Optics of the Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) urationof the optical elements and the paths of light rays through the Microscope The configuration of the optical elements and the paths phase-contrast microscope.Pink lines represent light diffracted by the of light rays through the DIC specimen.and black lines represent direct light. 10 e Figure A-8 Phase-Contrast Microscopy.A phase-contrast micro raph of epithelial cells.The cells were observed in an unprocessed and 主讲:汤华 Shetmakeheaosappearhrktetoplga unstained state.which is a major advantage of phase-contrast microscopy
主讲:汤 华 偏振器 检偏器 DIC棱镜 DIC棱镜
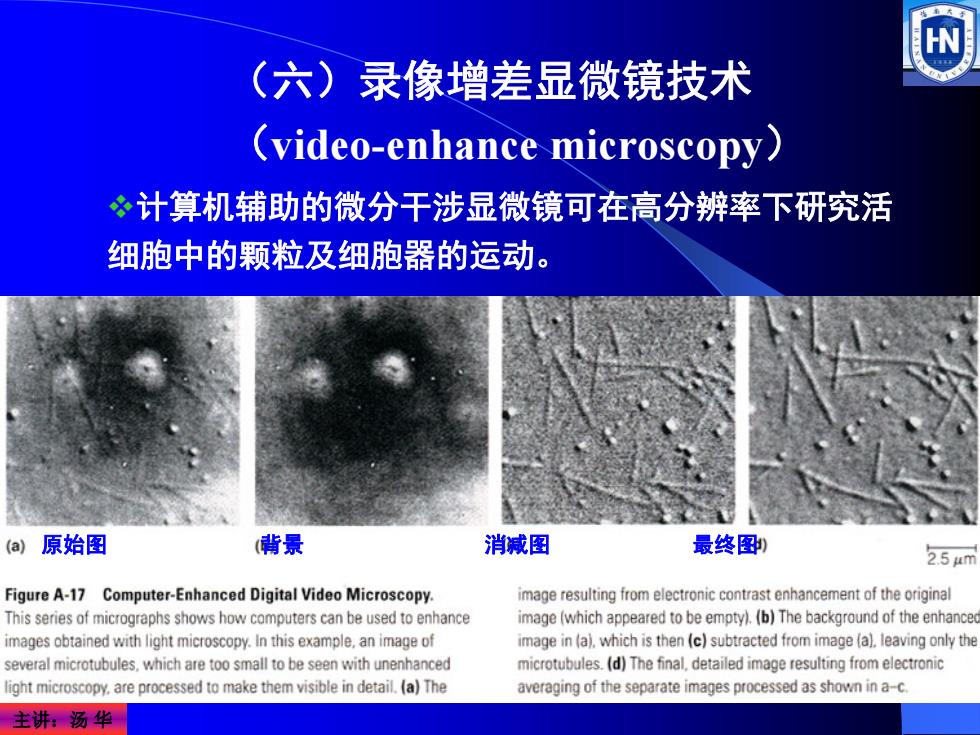
(六)录像增差显微镜技术 (video-enhance microscopy) 计算机辅助的微分干涉显微镜可在高分辨率下研究活 细胞中的颗粒及细胞器的运动。 (a)原始图 (背景 消减图 最终图, 2.54m Figure A-17 Computer-Enhanced Digital Video Microscopy. image resulting from electronic contrast enhancement of the original This series of micrographs shows how computers can be used to enhance image(which appeared to be empty).(b)The background of the enhance images obtained with light microscopy.In this example,an image of image in (a).which is then (c)subtracted from image (a).leaving only the several microtubules,which are too small to be seen with unenhanced microtubules.(d)The final.detailed image resulting from electronic ight microscopy.are processed to make them visible in detail.(a)The averaging of the separate images processed as shown in a-c. 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 (六)录像增差显微镜技术 (video-enhance microscopy) 原始图 背景 消减图 最终图 计算机辅助的微分干涉显微镜可在高分辨率下研究活 细胞中的颗粒及细胞器的运动

二、电子显微镜技术(electron microscopy) 电子显微镜的基本知识: 电镜与光镜的比较 电镜与光镜光路图比较 ?电子显微镜的基本构造 主要电镜制样技术: ?负染色技术 冰冻蚀刻技术 必超薄切片技术 ?电镜三维重构技术 扫描电镜技术(Scanning electron microscope,SEM) 主讲:汤华
主讲:汤 华 二、电子显微镜技术(electron microscopy) 电子显微镜的基本知识: 电镜与光镜的比较 电镜与光镜光路图比较 电子显微镜的基本构造 主要电镜制样技术: 负染色技术 冰冻蚀刻技术 超薄切片技术 电镜三维重构技术 扫描电镜技术(Scanning electron microscope,SEM)