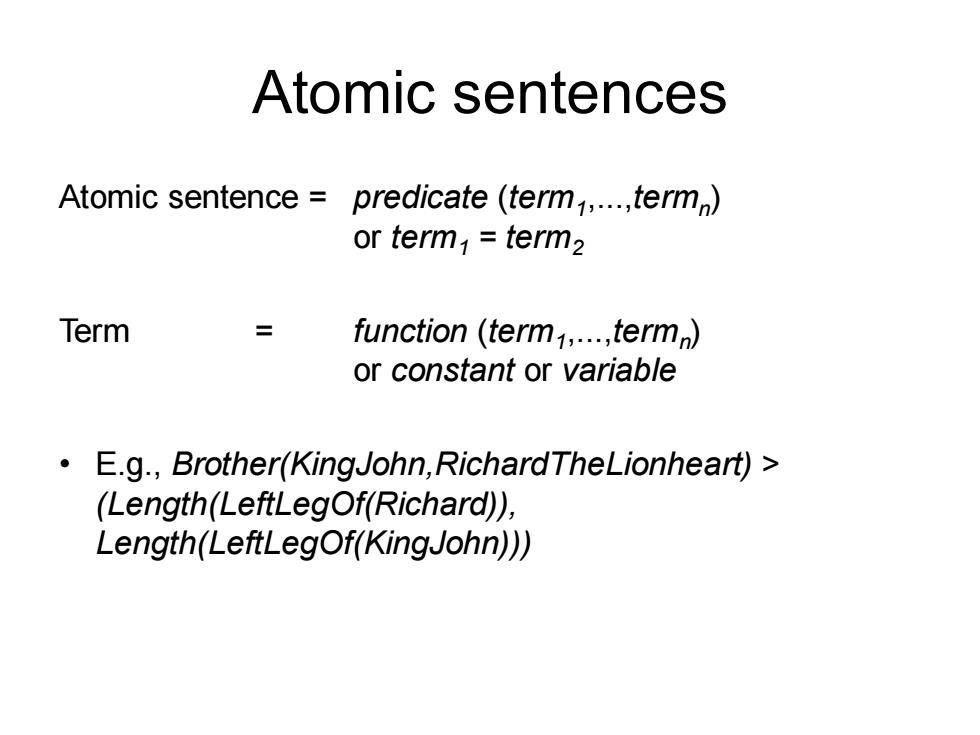
Atomic sentences Atomic sentence predicate (term,...,term) or term=term2 Term function (term,...,term) or constant or variable E.g.,Brother(KingJohn,RichardTheLionheart)> (Length(LeftLegOf(Richard)), Length(LeftLegOf(KingJohn)))
Atomic sentences Atomic sentence = predicate (term1 ,...,termn ) or term1 = term2 Term = function (term1 ,...,termn ) or constant or variable • E.g., Brother(KingJohn,RichardTheLionheart) > (Length(LeftLegOf(Richard)), Length(LeftLegOf(KingJohn)))

Complex sentences Complex sentences are made from atomic sentences using connectives S,S1ΛS2,S1VS2,S1→S2,S1台S2, E.g.Sibling(KingJohn,Richard) Sibling(Richard,KingJohn) >(1,2)V≤(1,2) >(1,2)Λ>(1,2)
Complex sentences • Complex sentences are made from atomic sentences using connectives • S, S1 S2 , S1 S2 , S1 S2 , S1 S2 , E.g. Sibling(KingJohn,Richard) Sibling(Richard,KingJohn) >(1,2) ≤ (1,2) >(1,2) >(1,2)
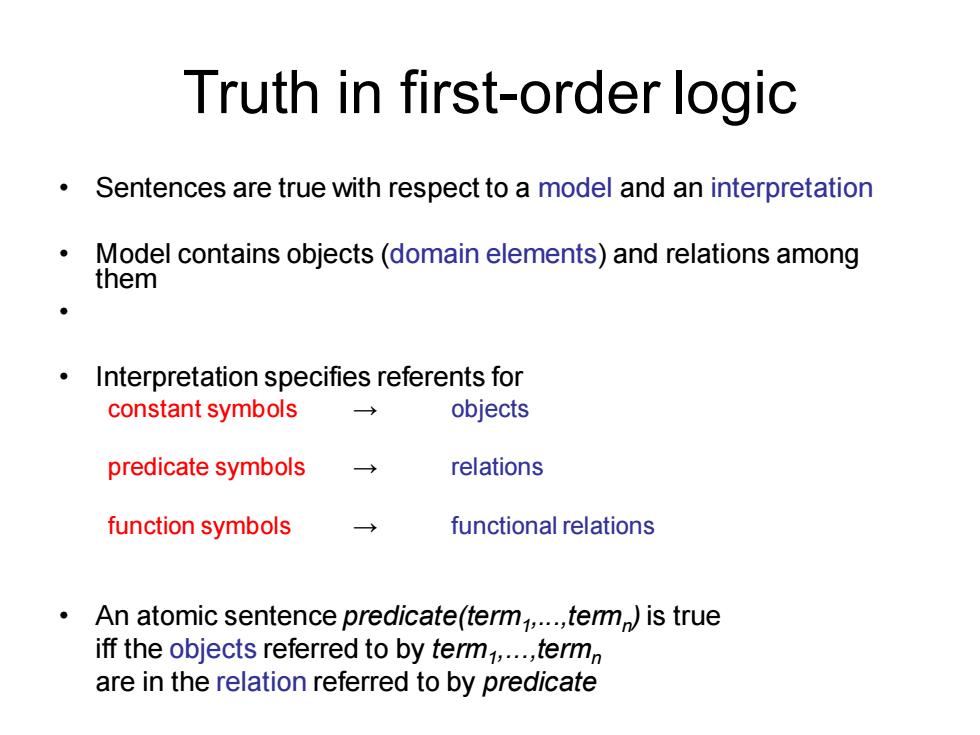
Truth in first-order logic Sentences are true with respect to a model and an interpretation Model contains objects(domain elements)and relations among them Interpretation specifies referents for constant symbols → objects predicate symbols → relations function symbols functional relations An atomic sentence predicate(termj,...,tem)is true iff the objects referred to by term,...,termn are in the relation referred to by predicate
Truth in first-order logic • Sentences are true with respect to a model and an interpretation • Model contains objects (domain elements) and relations among them • • Interpretation specifies referents for constant symbols → objects predicate symbols → relations function symbols → functional relations • An atomic sentence predicate(term1 ,...,termn ) is true iff the objects referred to by term1 ,...,termn are in the relation referred to by predicate
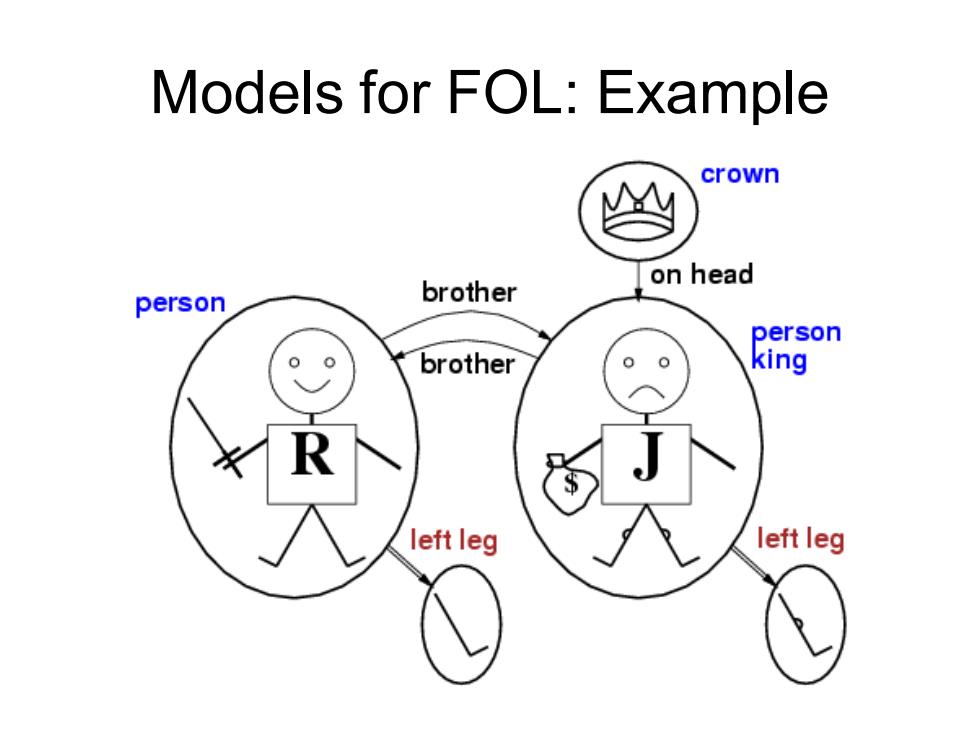
Models for FOL:Example crown on head person brother person brother king left leg left leg
Models for FOL: Example