
Bayesian networks Chapter 14 Section 1 -2
Bayesian networks Chapter 14 Section 1 – 2
Outline 。 Syntax Semantics
Outline • Syntax • Semantics
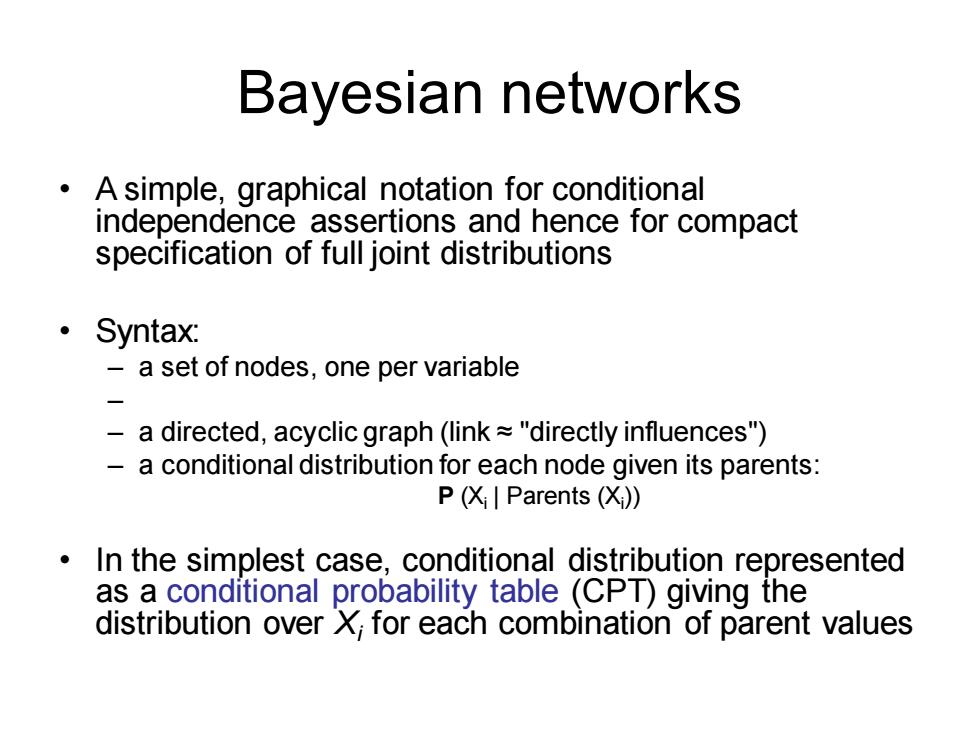
Bayesian networks A simple,graphical notation for conditional independence assertions and hence for compact specification of full joint distributions ·Syntax: -a set of nodes,one per variable a directed,acyclic graph(link~"directly influences") a conditional distribution for each node given its parents: P(X|Parents(Xi)) In the simplest case,conditional distribution represented as a conditional probability table (CPT)giving the distribution over X;for each combination of parent values
Bayesian networks • A simple, graphical notation for conditional independence assertions and hence for compact specification of full joint distributions • Syntax: – a set of nodes, one per variable – – a directed, acyclic graph (link ≈ "directly influences") – a conditional distribution for each node given its parents: P (Xi | Parents (Xi )) • In the simplest case, conditional distribution represented as a conditional probability table (CPT) giving the distribution over Xi for each combination of parent values
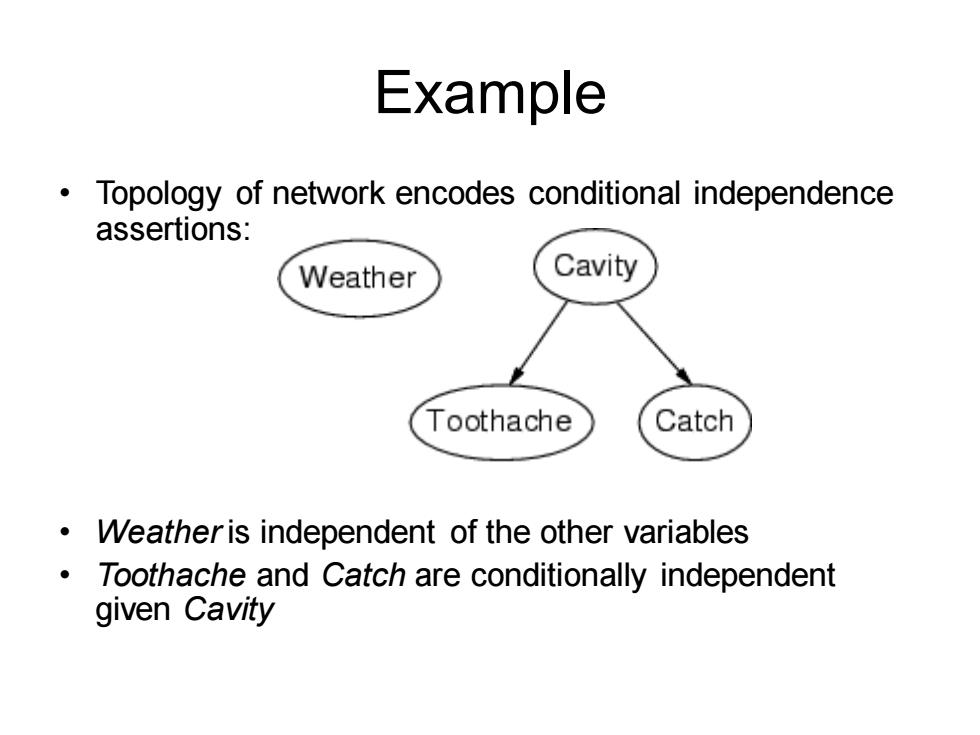
Example Topology of network encodes conditional independence assertions: Weather Cavity Toothache Catch Weatheris independent of the other variables Toothache and Catch are conditionally independent given Cavity
Example • Topology of network encodes conditional independence assertions: • Weather is independent of the other variables • Toothache and Catch are conditionally independent given Cavity

Example I'm at work,neighbor John calls to say my alarm is ringing,but neighbor Mary doesn't call.Sometimes it's set off by minor earthquakes.Is there a burglar? Variables:Burglary,Earthquake,Alarm,JohnCalls,MaryCalls Network topology reflects "causal"knowledge: A burglar can set the alarm off An earthquake can set the alarm off The alarm can cause Mary to call The alarm can cause John to call
Example • I'm at work, neighbor John calls to say my alarm is ringing, but neighbor Mary doesn't call. Sometimes it's set off by minor earthquakes. Is there a burglar? • Variables: Burglary, Earthquake, Alarm, JohnCalls, MaryCalls • Network topology reflects "causal" knowledge: – A burglar can set the alarm off – An earthquake can set the alarm off – The alarm can cause Mary to call – The alarm can cause John to call