
2.2.3 the azimuthal,orbital angular momentum,I .Denotes the different energy sublevels within the main level "n" .Also indicates the shape of the orbitals around the nucleus. orbital angular momentum -degeneracy, 1=0,1,2..n-1 degeneracy =21+1 0 1 2 34,5,6.. type p d f g,h,i... degeneracy 1 3 5 7 9,11,13. 500 2 2p () -1000 个 1500
2.2.3 the azimuthal, orbital angular momentum, l •Denotes the different energy sublevels within the main level “n” •Also indicates the shape of the orbitals around the nucleus. l 0 1 2 3 4, 5, 6 … type s p d f g, h, i … degeneracy 1 3 5 7 9, 11, 13 … orbital angular momentum degeneracy, l = 0, 1, 2 …n –l degeneracy = 2 l + 1

The operator of angular momentum P=M+M?+好 M,=-ih(y z M,ih(sin- +cot0cosφ。) e a M,=-ih(z- -x x 02 M,=-i(cos a 1 ae -cotesin a a M.=-ih(x -y- y x M.=-ih- o M2=-10 62 (sin0 sin0 80 +sm00 1 a0
( ) ( ) ˆ ( ) ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ 2 2 2 2 x y y M i x z x x M i z y z z M i y M M M M z y x x y z The operator of angular momentum M i M i M i z y x (cos cot sin ) (sin cot cos ) ] sin1 (sin ) sin1 [ 22 2 2 2 M
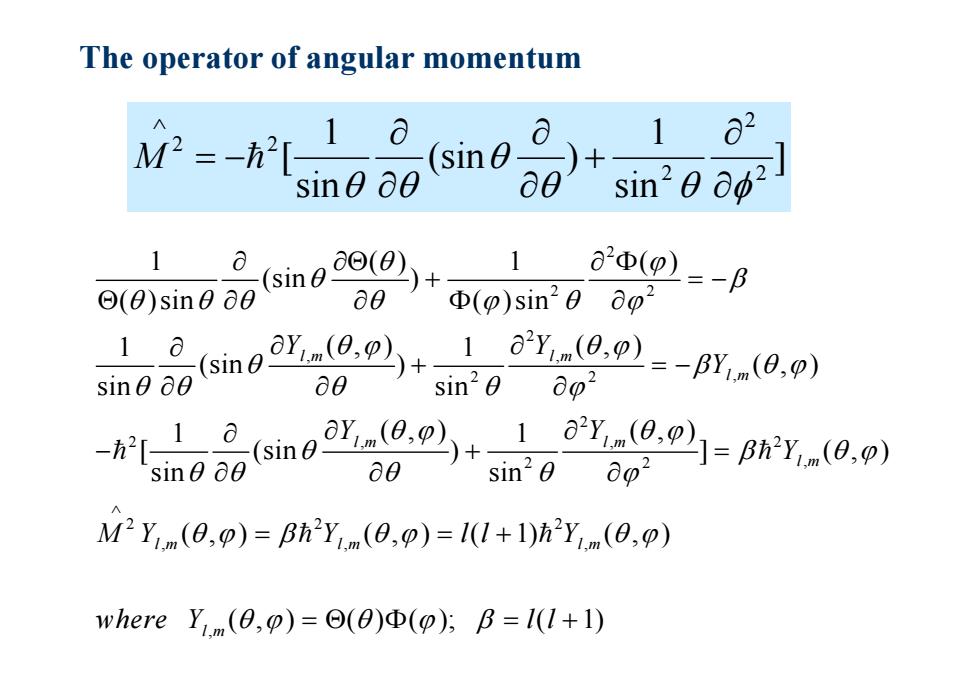
The operator of angular momentum M2-h[-10 a (sin 2 X sin0 60 a0 sin20 00 (sin a20(9)=-p ⊙(0)sin0o0 08s+ Φ(p)sin20ao2 1(simo(.(0.)y0) sin0 00 ∂8 sin20 0p2 -[10 (simoo(0.o.)y0.) sin0 00 a0 sin20 0o2 M2Ym(0,p)=Bh2Ym(0,p)=1(1+1)hY,m(0,p) where Ym(8,p)=©(8)Φ(p);B=l(1+1)
The operator of angular momentum ] sin 1 (sin ) sin 1 [ 2 2 2 2 2 M 2 2 2 2 , , 2 2 , 2 2 , ,2 2 2 , 2 2 , , 1 () 1 () (sin ) ( )sin ( )sin 1 1 (, ) (, ) (sin ) ( , ) sin sin 1 1 (, ) (, ) [ (sin ) ] ( , ) sin sin (, ) (, ) ( lm lm l m lm lm l m lm lm Y Y Y Y Y Y MY Y l 2 , , 1) ( , ) ( , ) ( ) ( ); ( 1) l m l m l Y where Y l l

M2Ψ=2Ψ 2=10+1)h2 =V1l+1)h M=I(1+1)h (1=0,1,23.…) When there exist an angular momentum,there is also a magnetic moment. u=- eM 2me 4=2i0+1h=+g 2m。 。= e h=9.274×1024J.T-1 Bohr magneton 2
( ) ( 1) 0,1,2,3 ( 1) ( 1) 2 2 2 2 M l l l l l l l M When there exist an angular momentum, there is also a magnetic moment. J T Bohr magneton m e l l l l m e M m e e e e e e 24 1 9.274 10 2 ( 1) ( 1) 2 2

2.2.4 Magnetic Quantum Number,m Denotes the direction or orientation of an orbital m,=magnetic→type,“orientation in space”-→ORBITAL m=0,±1,±2..±1 m orbital number of orbitals in a subshell 0 0s =2/+1 0Pz ±1Px ±1Py 2 0 d2z2x2-y2=dz? ±1dz ±1dyz ±2dx2y2 1s orbital ±2dy
ml = magnetic type, “orientation in space” ORBITAL ml = 0, ±1, ±2 …±l number of orbitals in a subshell = 2 l + 1 l ml orbital 0 0s 1 0pz ±1 px ±1 py 2 0d2z2-x2 -y2 = dz2 ±1 dxz ±1 dyz ±2 dx2 –y2 ±2 dxy 1s orbital 2.2.4 Magnetic Quantum Number , m • Denotes the direction or orientation of an orbital