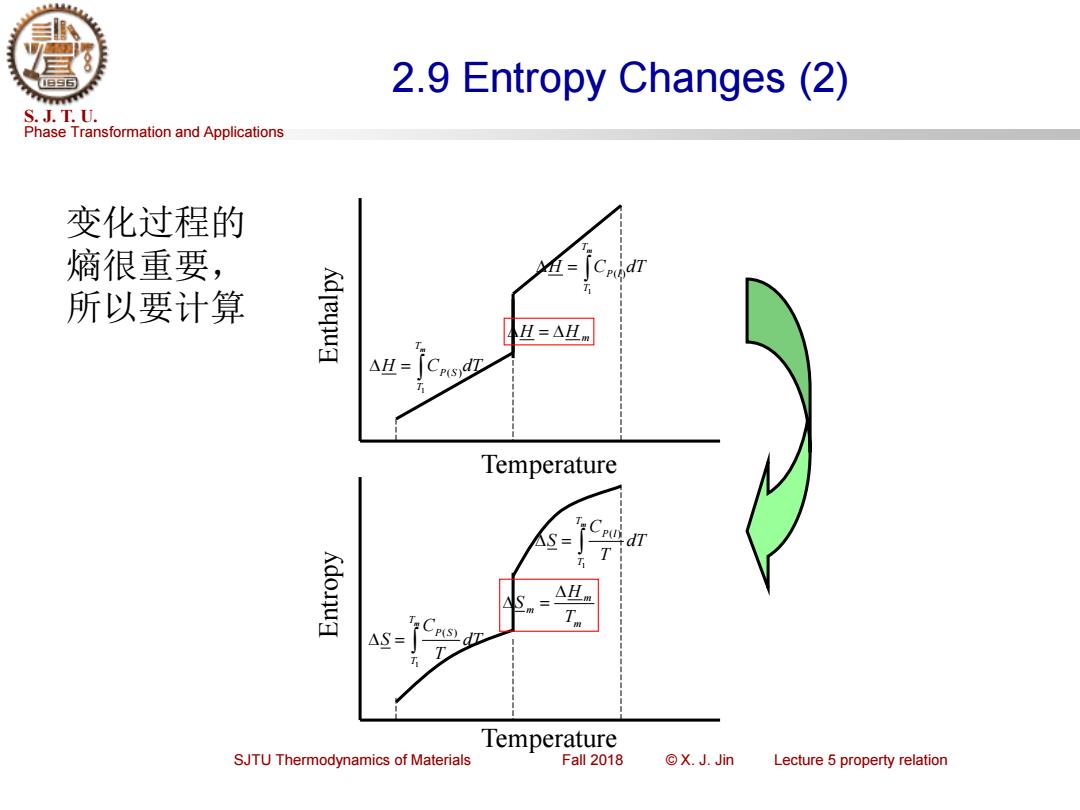
2.9 Entropy Changes(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 变化过程的 熵很重要, 所以要计算 H=△Hm △H= Temperature S= Cpu dT Kdonud △Hm △S= P(S Temperature SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 2.9 Entropy Changes (2) = Tm T P S dT T C S 1 ( ) = Tm T P l dT T C S 1 ( ) m m m T H S = Temperature Entropy = Tm T H CP S dT 1 ( ) = Tm T H CP l dT 1 ( ) H = H m Temperature Enthalpy 变化过程的 熵很重要, 所以要计算
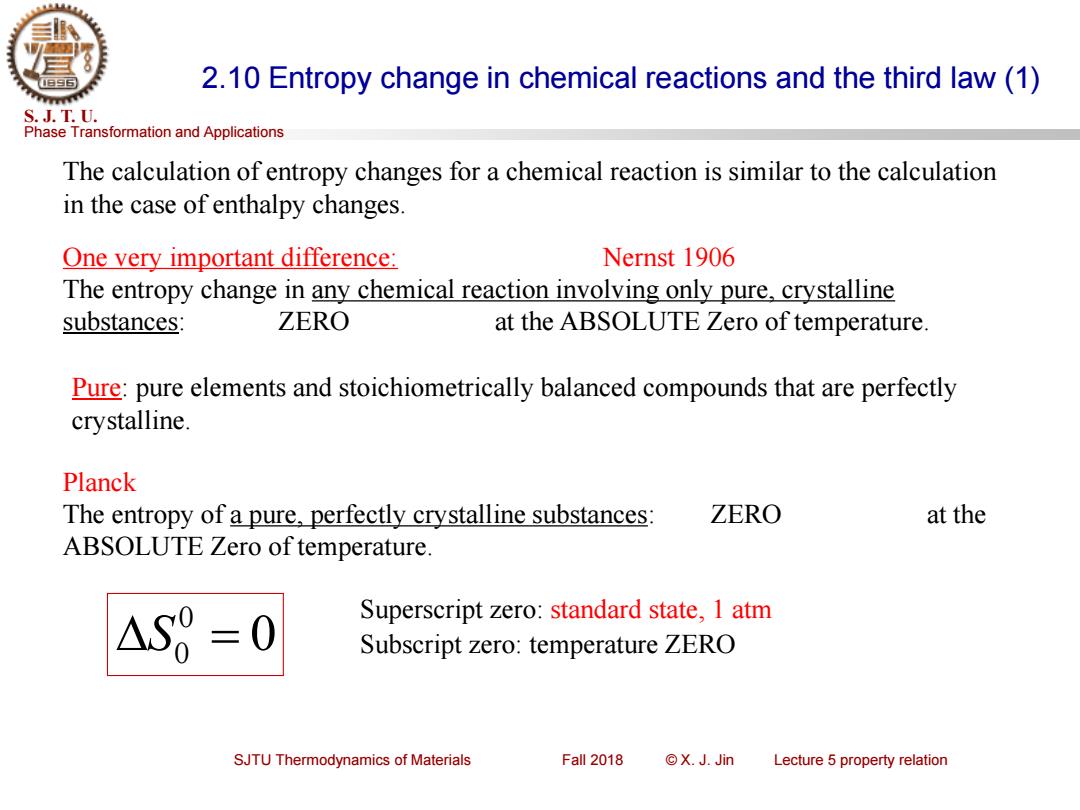
2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law(1) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The calculation of entropy changes for a chemical reaction is similar to the calculation in the case of enthalpy changes. One very important difference: Nernst 1906 The entropy change in any chemical reaction involving only pure,crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. Pure:pure elements and stoichiometrically balanced compounds that are perfectly crystalline. Planck The entropy of a pure,perfectly crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. AS8=0 Superscript zero:standard state,1 atm Subscript zero:temperature ZERO SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law (1) The calculation of entropy changes for a chemical reaction is similar to the calculation in the case of enthalpy changes. One very important difference: Nernst 1906 The entropy change in any chemical reaction involving only pure, crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. Pure: pure elements and stoichiometrically balanced compounds that are perfectly crystalline. Planck The entropy of a pure, perfectly crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. 0 0 S0 = Superscript zero: standard state, 1 atm Subscript zero: temperature ZERO
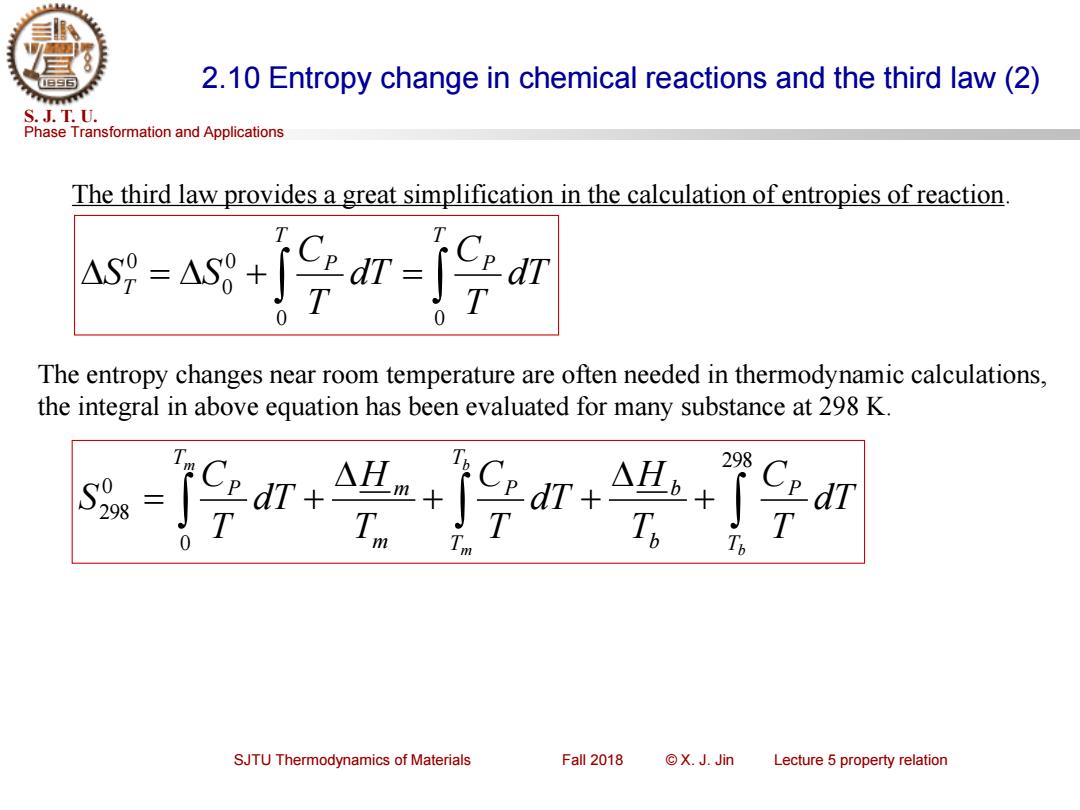
2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The third law provides a great simplification in the calculation of entropies of reaction A=as+fn号m The entropy changes near room temperature are often needed in thermodynamic calculations, the integral in above equation has been evaluated for many substance at 298 K. 298 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law (2) The third law provides a great simplification in the calculation of entropies of reaction. = + = T P T P T dT T C dT T C S S 0 0 0 0 0 The entropy changes near room temperature are often needed in thermodynamic calculations, the integral in above equation has been evaluated for many substance at 298 K. + + + = + 298 0 0 298 b b m m T P T T b P b m m T P dT T C T H dT T C T H dT T C S

Index of nomenclature S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Helmholtz free energy(F):亥姆赫茨自由能 Gibbs free energy(G):吉布斯自由能 Chemical potential:化学位 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation Index of nomenclature Helmholtz free energy (F): 亥姆赫茨自由能 Gibbs free energy (G): 吉布斯自由能 Chemical potential:化学位 Index of nomenclature
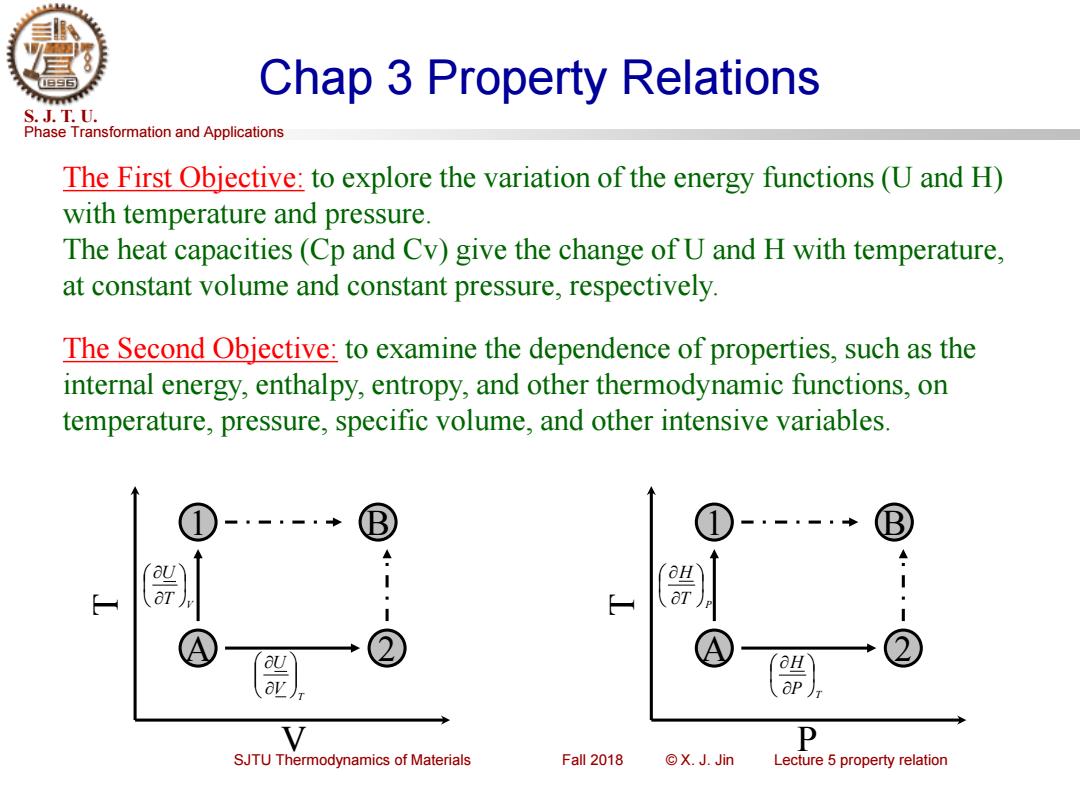
Chap 3 Property Relations S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The First Objective:to explore the variation of the energy functions(U and H) with temperature and pressure. The heat capacities(Cp and Cv)give the change of U and H with temperature, at constant volume and constant pressure,respectively. The Second Objective:to examine the dependence of properties,such as the internal energy,enthalpy,entropy,and other thermodynamic functions,on temperature,pressure,specific volume,and other intensive variables. a av V P SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation Chap 3 Property Relations The First Objective: to explore the variation of the energy functions (U and H) with temperature and pressure. The heat capacities (Cp and Cv) give the change of U and H with temperature, at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. The Second Objective: to examine the dependence of properties, such as the internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, and other thermodynamic functions, on temperature, pressure, specific volume, and other intensive variables. 2 1 B A V T T V U T V U 2 1 B A P T P T H T P H