
HPC:风冷 Evaluating the Intel MIC Architecture Arndt Bode Leibniz Supercomputing Centre,Germany with input from Iris Christadler,Alexander Heinecke and Volker Weinber June 2011,ISC,Hamburg m TECHNSCHE 人5 MONCHEN
HPC:风冷
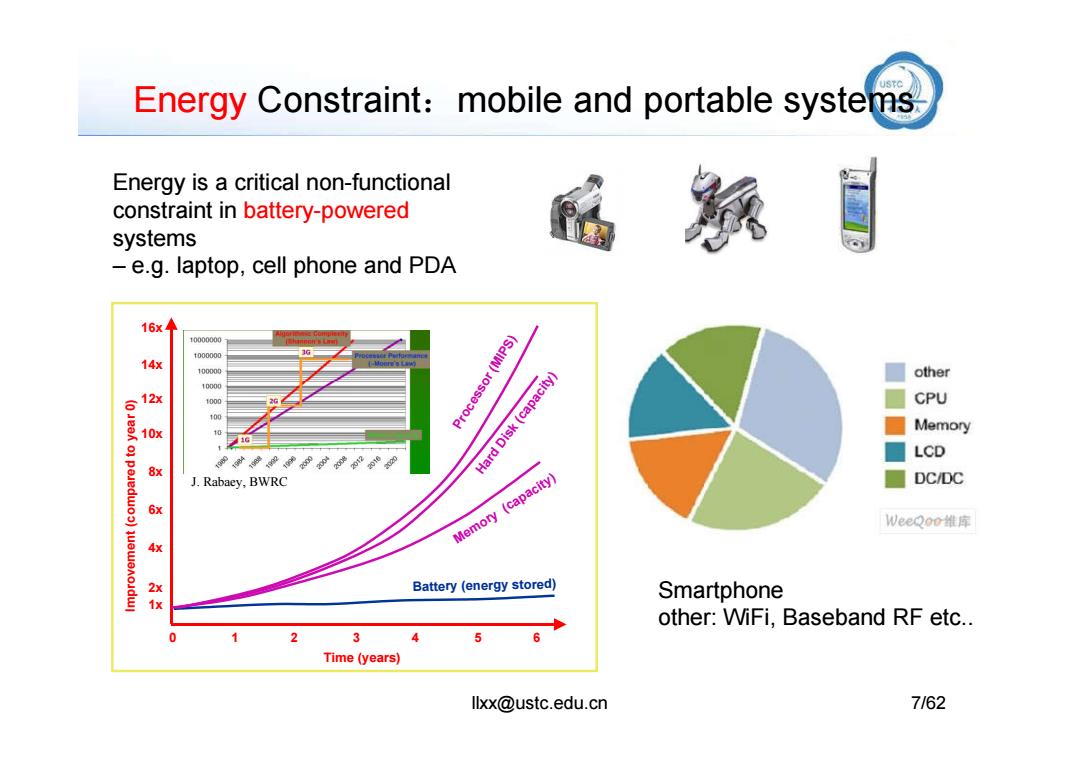
C Energy Constraint:mobile and portable systems Energy is a critical non-functional constraint in battery-powered systems -e.g.laptop,cell phone and PDA 16x◆ 10000000 1000000 14X 10000 other 1000g 6 12x 1000 Processor(MIPS) Hard Disk(capacity) CPU 100 10X Memory LCD o]peiedwo) 8x J.Rabaey.BWRC DC/DC 6x Memory(capacity】 VeeQoo锥库 4x 2x Battery (energy stored) Smartphone other:WiFi,Baseband RF etc.. 2 Time(years) llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7162
Energy Constraint:mobile and portable systems Processor (MIPS) Hard Disk (capacity) 16x 14x Energy is a critical non-functional constraint in battery-powered systems – e.g. laptop, cell phone and PDA llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/62 Processor (MIPS) Hard Disk (capacity) Memory (capacity) Battery (energy stored) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 12x 10x 8x 6x 4x 2x Improvement (compared to year 0) 1x Time (years) J. Rabaey, BWRC Smartphone other: WiFi, Baseband RF etc
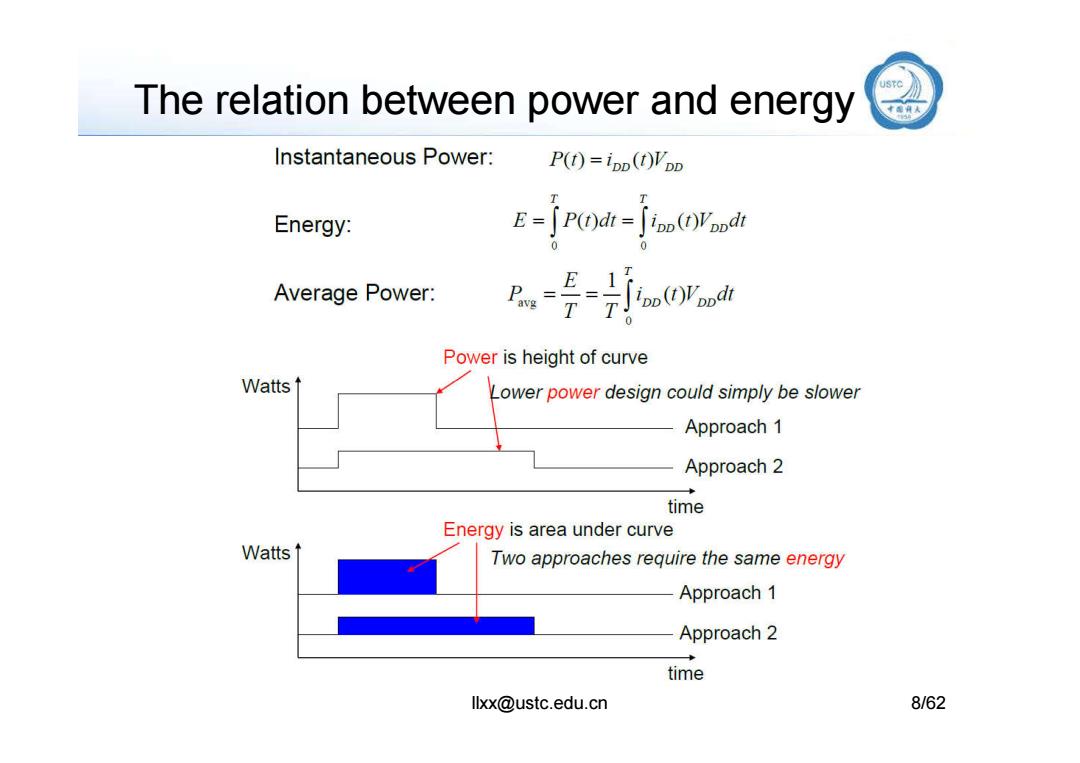
The relation between power and energy Instantaneous Power: P(t)=ipD(t)VDD EP(d (d T Energy: Average Power: Power is height of curve Watts Lower power design could simply be slower Approach 1 Approach 2 time Energy is area under curve Watts Two approaches require the same energy Approach 1 Approach 2 time llxx@ustc.edu.cn 8/62
The relation between power and energy llxx@ustc.edu.cn 8/62

Power and Energy ·Circuit level view -dynamic(transistor switching),short circuit,leakage current P=Pan +Pe+Pu =0.5CLVDD Af +IsV DDA+IRVDD Voo:supply voltage; CL:node capacitance; Capacitive(Dynamic)Power Static (Leakage)Power Vdd f.clock frequency; A:activity factor: n Vout Isc:Short circuit current; lIk:leakage current .Dynamic power is the dominant source now. .Static power is growing faster Higher Architecture level view -Datapath Power,Memory System Power,Bus Power,etc llxx@ustc.edu.cn 9/62
Power and Energy • Circuit level view — dynamic (transistor switching), short circuit, leakage current dyn sc lk L DD sc DD lkVDD P P P P C V Af I V A I 2 0.5 VDD: supply voltage; CL: node capacitance; f: clock frequency; A: activity factor; llxx@ustc.edu.cn 9/62 A: activity factor; Isc:Short circuit current ; Ilk: leakage current • Architecture level view —Datapath Power, Memory System Power, Bus Power,etc •Dynamic power is the dominant source now. •Static power is growing faster Higher
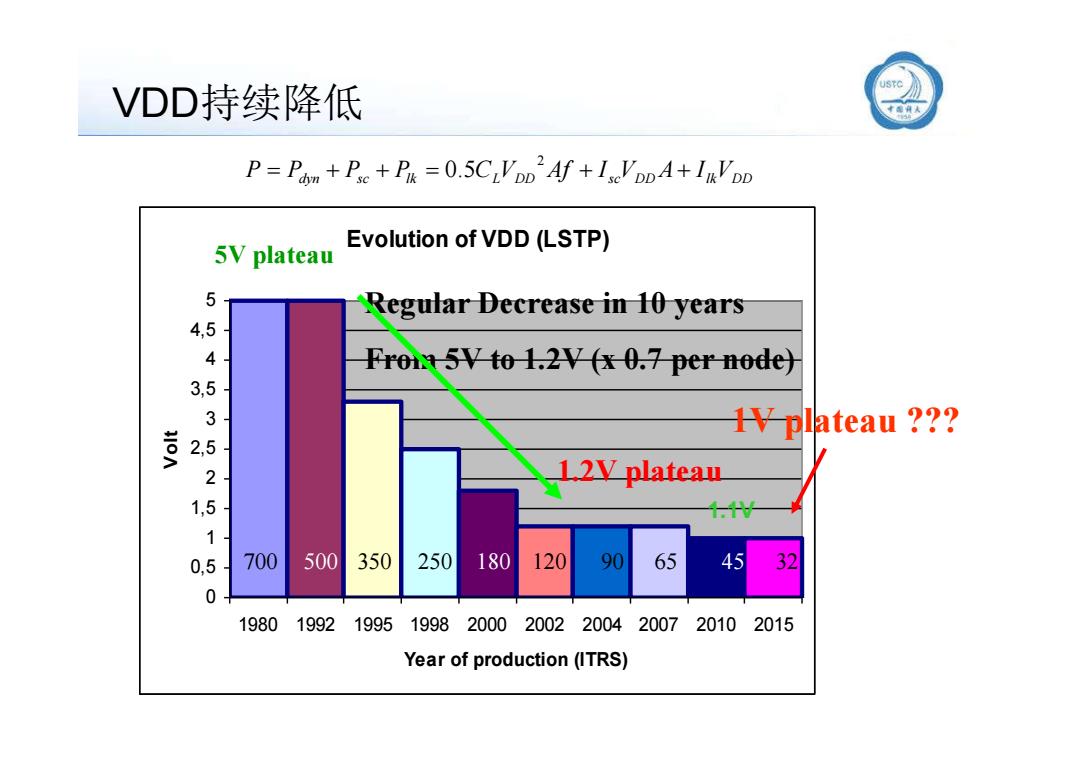
VDD持续降低 P=Pam +Pse+P=0.5CLVDD'Af +IsVDDA+InVDD Evolution of VDD(LSTP) 5V plateau 5 Regular Decrease in 10 years 433525 Froi 5V to 1.2V (x 0.7 per node) HVplateau ?? 12V plateau 0,5 700 500 350 250 180 120 90 65 45 0 1980 1992 1995 1998 20002002 2004 20072010 2015 Year of production(ITRS)
VDD持续降低 Evolution of VDD (LSTP) 3,5 4 4,5 5 5V plateau Regular Decrease in 10 years From 5V to 1.2V (x 0.7 per node) dyn sc lk L DD sc DD lkVDD P P P P C V Af I V A I 2 0.5 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 1980 1992 1995 1998 2000 2002 2004 2007 2010 2015 Year of production (ITRS) Volt 1V plateau ??? 1.2V plateau 700 350 250 120 90 65 45 32 1.1V 500 180