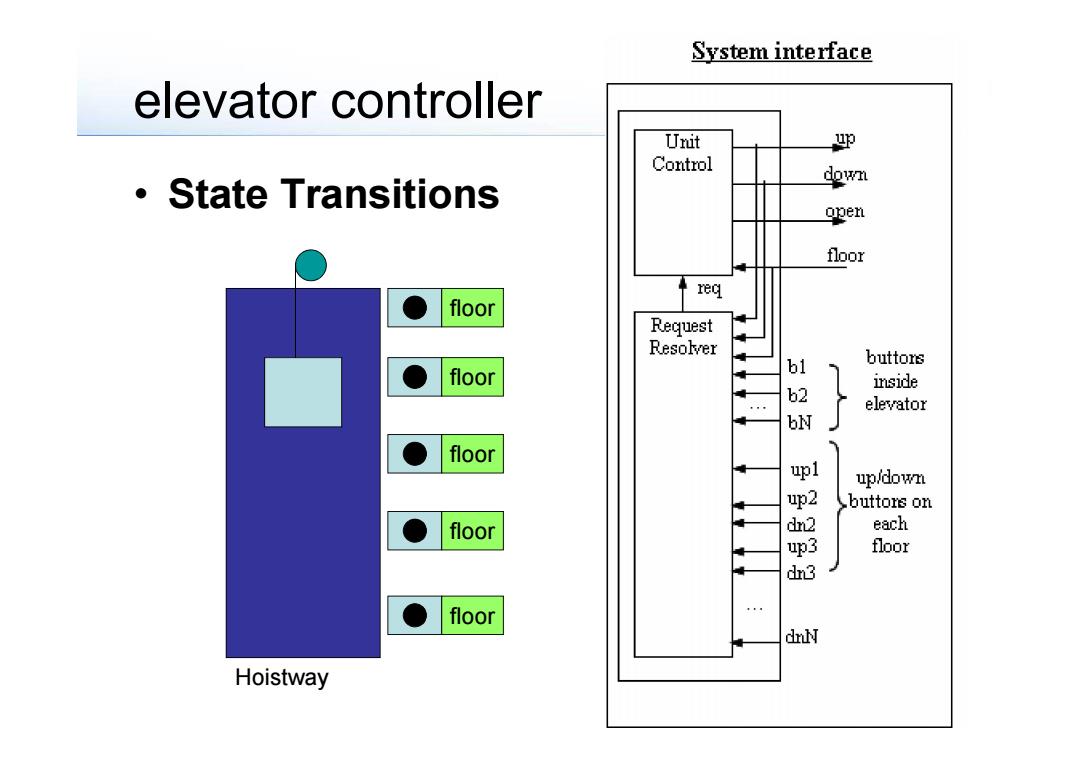
System interface elevator controller Unit 的 Control State Transitions down apen floor req floor Request Resolver floor b1 buttons inside N elevator floor up1 up/down buttors on floor each floor dn3 floor dnN Hoistway
elevator controller • State Transitions floor floor floor floor floor Hoistway

三种描述方法:自然语言、算法、状态图 "If the elevator is stationary and the loop floor requested is equal to the if (req_floor curr_floor)then current floor,then the elevator direction idle; remains idle. elseif(req_floor curr_floor)then If the elevator is stationary and the floor requested is less than the direction :down; current floor,then lower the elseif(req_floor curr_floor)then elevator to the requested floor. direction :up; If the elevator is stationary and the end if; floor requested is greater than end loop; the current floor,then raise the elevator to the requested floor" req_floor<curr_floor req_floor=curr_floor req_floor>curr_floor req_floor<curr_floor req_floor>curr_floor down)reg floor=curr floor idle req_floor=curr_floor up rea floo2 curr floor小 reg floorscurr floor llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/112
llxx@ustc.edu.cn 7/112 三种描述方法:自然语言、算法、状态图

形式化方法(Formal Method) 定义:采用离散数学的方法建立系统的精确的数学模型,并 对模型进行分析。 -运用形式化语言,进行形式化的规格描述、模型推理和验证。 o 目的:保证系统设计的正确性 保证规格说明的无二义性,使得证明和验证系统实现满足用户和系 统需求成为可能。 - 检查模型的一致性,推导模型的逻辑结果,模拟执行模型等 ● 效益 一系统代码规模 ·1979年,哥伦比亚航天飞机4000万行 ·2001年,XP3500万行,目前4000万行;Vista超过5000万行。 -非形式化技术:软件故障率2~20个/千行代码 形式化技术:软件故障率0.75个/千行代码(1992年,英国民航局信 息显示系统) llxx@ustc.edu.cn 8/112
llxx@ustc.edu.cn 8/112 形式化方法(Formal Method) • 定义:采用离散数学的方法建立系统的精确的数学模型,并 对模型进行分析。 – 运用形式化语言,进行形式化的规格描述、模型推理和验证。 • 目的:保证系统设计的正确性 – 保证规格说明的无二义性,使得证明和验证系统实现满足用户和系 统需求成为可能。 – 检查模型的一致性,推导模型的逻辑结果,模拟/执行模型等 • 效益 – 系统代码规模 • 1979年,哥伦比亚航天飞机4000万行 • 2001年, XP 3500万行,目前4000万行;Vista超过5000万行。 – 非形式化技术:软件故障率2~20个/千行代码 – 形式化技术:软件故障率0.75个/千行代码(1992年,英国民航局信 息显示系统)

离散系统(discrete system) STC 定义:系统状态只在有限的时间点或可数的时 间点上由随机事件驱动的系统 一由异步、突发的事件驱动状态演化 一行为:用其演化过程的状态序列和事件序列来刻画 ·状态变迁系统:状态通常只取有限个离散值 一系统状态的变化是在一个时间点上瞬间完成的. - 如排队系统(queue system),状态量的变化只 是在离散的随机时间点上发生. ·离散事件系统、离散事件动态系统 -事件->动作->状态 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 9/112
离散系统(discrete system) • 定义:系统状态只在有限的时间点或可数的时 间点上由随机事件驱动的系统 – 由异步、突发的事件驱动状态演化 – 行为:用其演化过程的状态序列和事件序列来刻画 • 状态变迁系统:状态通常只取有限个离散值 – 系统状态的变化是在一个时间点上瞬间完成的. – 如排队系统(queue system),状态量的变化只 是在离散的随机时间点上发生. • 离散事件系统、离散事件动态系统 – 事件->动作->状态 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 9/112
形式化开发过程 》 ·建立需求与系统模型之间的映射关系 -模型获取 ·从现实世界向模型表示的转化过程 ·形式规约 模型验证 ·判断模型表示是否符合需求 ASIC Analog I/O Processor Memory ·形式证明与验证 -模型变换 ·从模型表示向计算机系统的转化过程 一一对多关系,即一个模型对应多种实现 DSP 》一致性检查 Code ·设计求精 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 10/112
llxx@ustc.edu.cn 10/112 形式化开发过程 • 建立需求与系统模型之间的映射关系 – 模型获取 • 从现实世界向模型表示的转化过程 • 形式规约 – 模型验证 • 判断模型表示是否符合需求 • 形式证明与验证 – 模型变换 • 从模型表示向计算机系统的转化过程 – 一对多关系,即一个模型对应多种实现 » 一致性检查 • 设计求精 Processor Analog I/O Memory ASIC DSP Code