
Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability ■Example of L.L.Bean The selling season for ski jackets is from November to February. L.L.Bean currently purchases the entire season's supply of ski jackets from the manufacturer before the start of the selling season High level of product availability>High inventory> High Cost SEIEE AU406 6
+ - SEIEE AU406 Example of L. L. Bean The selling season for ski jackets is from November to February. L.L.Bean currently purchases the entire season’s supply of ski jackets from the manufacturer before the start of the selling season High level of product availability High inventory High Cost 6 Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability

Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability Cost of overstocking the products Co Cost of understocking the products →Cu Possible scenarios Seasonal items with a single order in a season Demand during stockout is backlogged Demand during stockout is lost The company has to decide the size of the order SEIEE AU406 12-7
+ - SEIEE AU406 12-7 Factors Affecting the Optimal Level of Product Availability Cost of overstocking the products Cost of understocking the products Possible scenarios Seasonal items with a single order in a season Demand during stockout is backlogged Demand during stockout is lost The company has to decide the size of the order
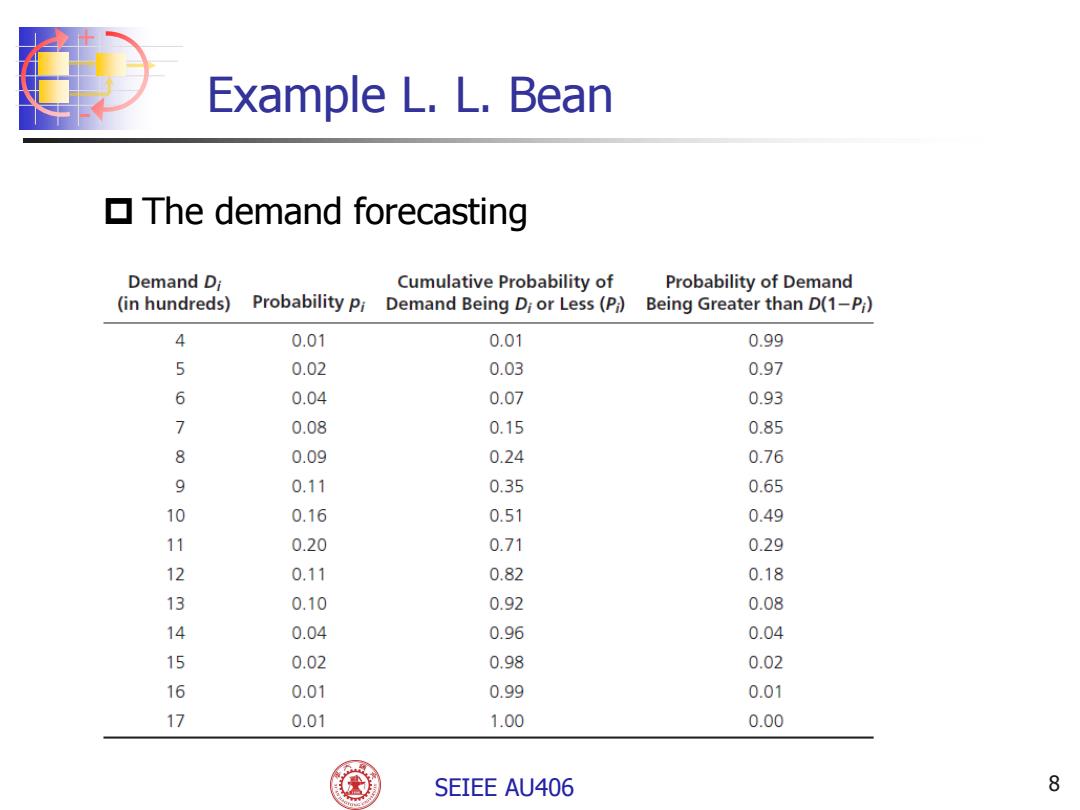
Example L.L.Bean The demand forecasting Demand Di Cumulative Probability of Probability of Demand (in hundreds) Probability pi Demand Being Di or Less(Pi) Being Greater than D(1-Pj) 4 0.01 0.01 0.99 5 0.02 0.03 0.97 6 0.04 0.07 0.93 7 0.08 0.15 0.85 8 0.09 0.24 0.76 9 0.11 0.35 0.65 10 0.16 0.51 0.49 11 0.20 0.71 0.29 12 0.11 0.82 0.18 13 0.10 0.92 0.08 14 0.04 0.96 0.04 15 0.02 0.98 0.02 16 0.01 0.99 0.01 17 0.01 1.00 0.00 SEIEE AU406 8
+ - SEIEE AU406 8 Example L. L. Bean The demand forecasting

Example L.L.Bean Cost of the products c=45 ▣Retail price pa=$1O0 Discounted price =$50 Holding and transportation cost for season =$10 Salvage value s=50-10=$40 The profit of each sold parkas =p-c=$100-45=55 The loss of each discounted parkas c-s=5 Cost of Overstocking: Co=c-s=$5 Cost of Understocking:C=p-c=$55 SEIEE AU406 9
+ - SEIEE AU406 9 Cost of the products c=$45 Retail price p= $100 Discounted price = $50 Holding and transportation cost for season = $10 Salvage value s= 50-10 =$40 The profit of each sold parkas =p-c= $100- $45=$55 The loss of each discounted parkas = c-s =$5 Example L. L. Bean Cost of Overstocking: Cost of Understocking:

Example L.L.Bean The expected profit from ordering 1,000 parkas is given as 10 7 Expeted profit =(p-)-(1.000-D)(cs)1.00(p) =$49.900 To decide whether to order 1,100 parkas,evaluate the extra 100. Expected profit from the extra 100 parkas 5,500 X Prob(demand 1,100) -500×Prob(demand<1,100)=$5,500×0.49-$500×0.51=$2,440 SEIEE AU406 10
+ - SEIEE AU406 The expected profit from ordering 1,000 parkas is given as 10 Example L. L. Bean To decide whether to order 1,100 parkas, evaluate the extra 100