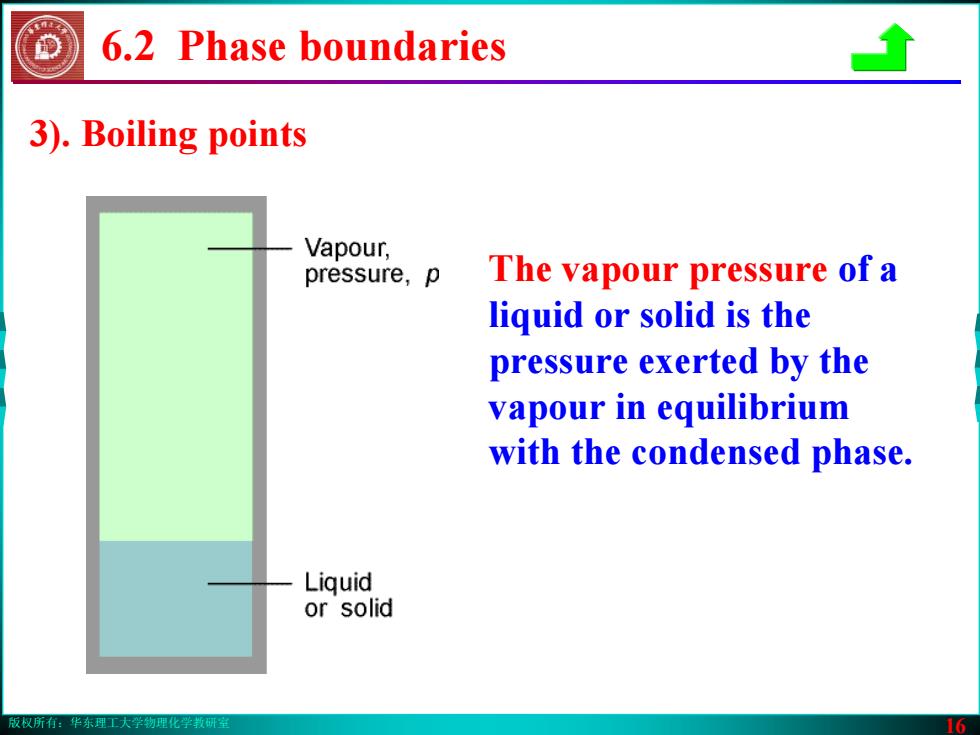
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 16 6.2 Phase boundaries The vapour pressure of a liquid or solid is the pressure exerted by the vapour in equilibrium with the condensed phase. 3). Boiling points
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 16 6.2 Phase boundaries The vapour pressure of a liquid or solid is the pressure exerted by the vapour in equilibrium with the condensed phase. 3). Boiling points
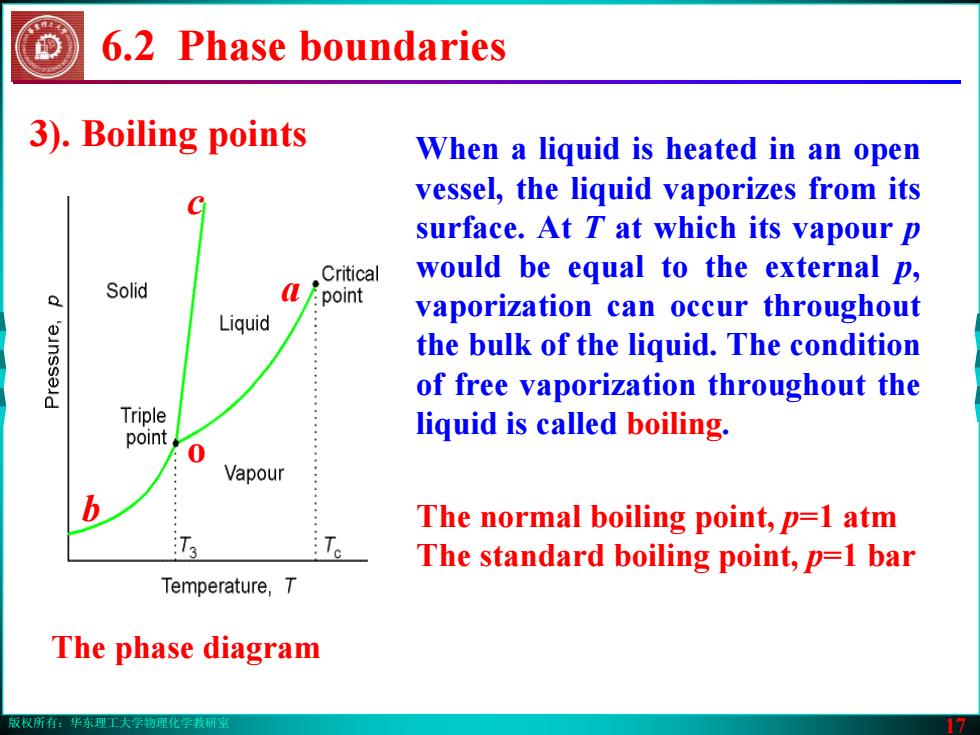
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 17 6.2 Phase boundaries 3). Boiling points The phase diagram b a c o When a liquid is heated in an open vessel, the liquid vaporizes from its surface. At T at which its vapour p would be equal to the external p, vaporization can occur throughout the bulk of the liquid. The condition of free vaporization throughout the liquid is called boiling. The normal boiling point, p=1 atm The standard boiling point, p=1 bar
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 17 6.2 Phase boundaries 3). Boiling points The phase diagram b a c o When a liquid is heated in an open vessel, the liquid vaporizes from its surface. At T at which its vapour p would be equal to the external p, vaporization can occur throughout the bulk of the liquid. The condition of free vaporization throughout the liquid is called boiling. The normal boiling point, p=1 atm The standard boiling point, p=1 bar
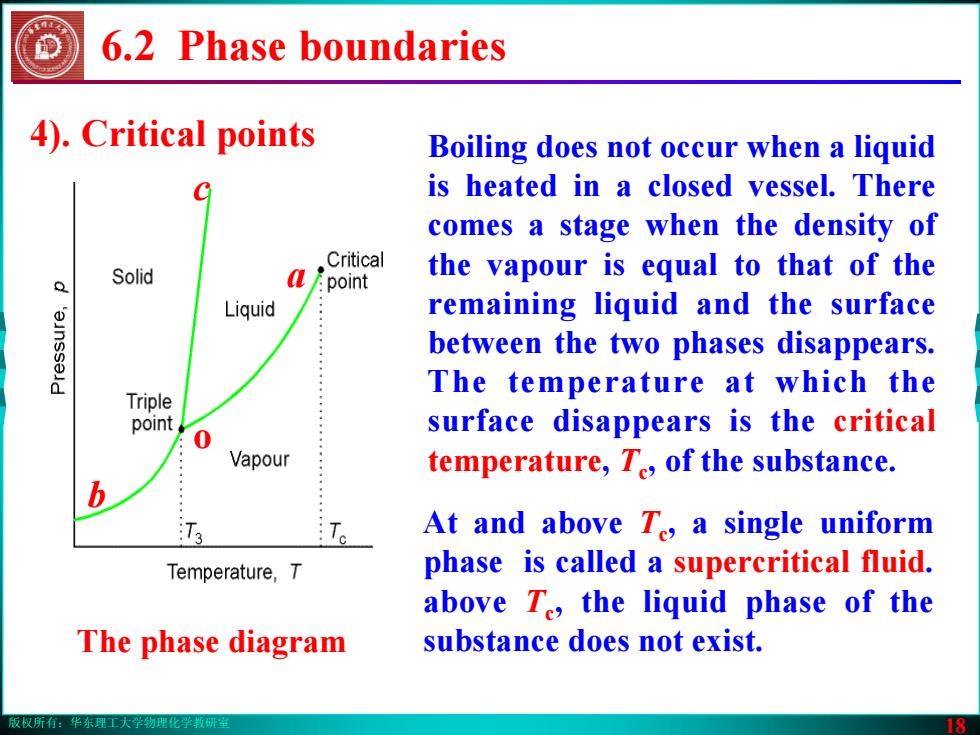
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 18 6.2 Phase boundaries 4). Critical points Boiling does not occur when a liquid is heated in a closed vessel. There comes a stage when the density of the vapour is equal to that of the remaining liquid and the surface between the two phases disappears. The temperature at which the surface disappears is the critical temperature, Tc, of the substance. The phase diagram b a c o At and above Tc, a single uniform phase is called a supercritical fluid. above Tc, the liquid phase of the substance does not exist
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 18 6.2 Phase boundaries 4). Critical points Boiling does not occur when a liquid is heated in a closed vessel. There comes a stage when the density of the vapour is equal to that of the remaining liquid and the surface between the two phases disappears. The temperature at which the surface disappears is the critical temperature, Tc, of the substance. The phase diagram b a c o At and above Tc, a single uniform phase is called a supercritical fluid. above Tc, the liquid phase of the substance does not exist

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 19 6.2 Phase boundaries (a)A liquid in equilibrium with its vapour. (b)When a liquid is heated in a sealed container, the density of the vapour phase increases and that of the liquid decreases slightly. (c)There comes a stage, at which the two densities are equal and the interface between the fluids disappears. 4). Critical points
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 19 6.2 Phase boundaries (a)A liquid in equilibrium with its vapour. (b)When a liquid is heated in a sealed container, the density of the vapour phase increases and that of the liquid decreases slightly. (c)There comes a stage, at which the two densities are equal and the interface between the fluids disappears. 4). Critical points
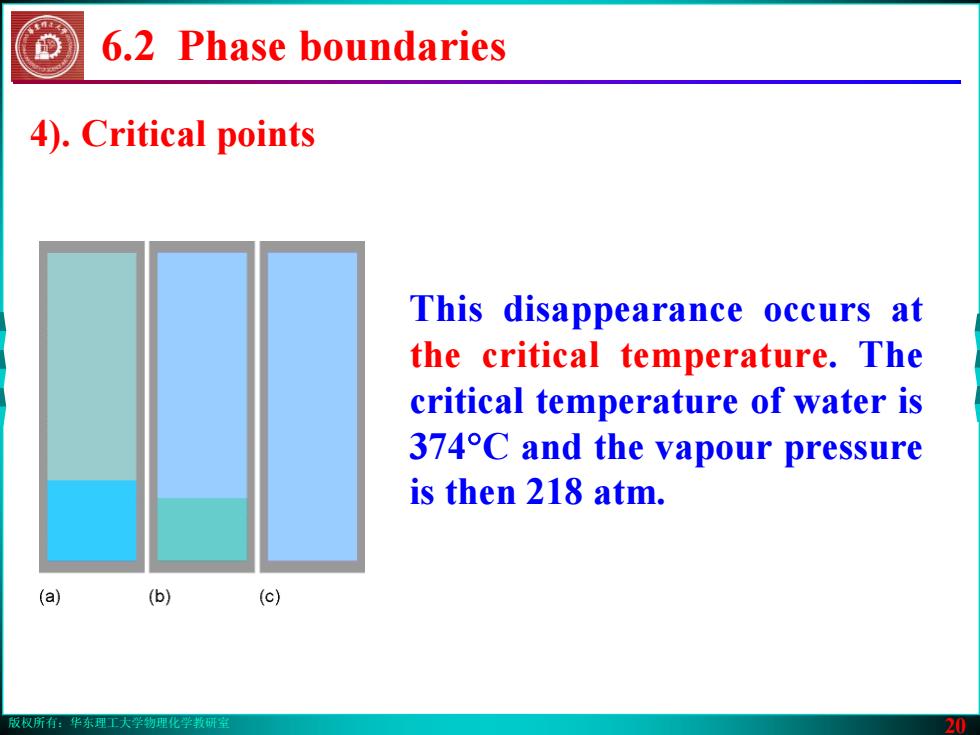
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 20 6.2 Phase boundaries This disappearance occurs at the critical temperature. The critical temperature of water is 374°C and the vapour pressure is then 218 atm. 4). Critical points
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 20 6.2 Phase boundaries This disappearance occurs at the critical temperature. The critical temperature of water is 374°C and the vapour pressure is then 218 atm. 4). Critical points