
Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue
Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue
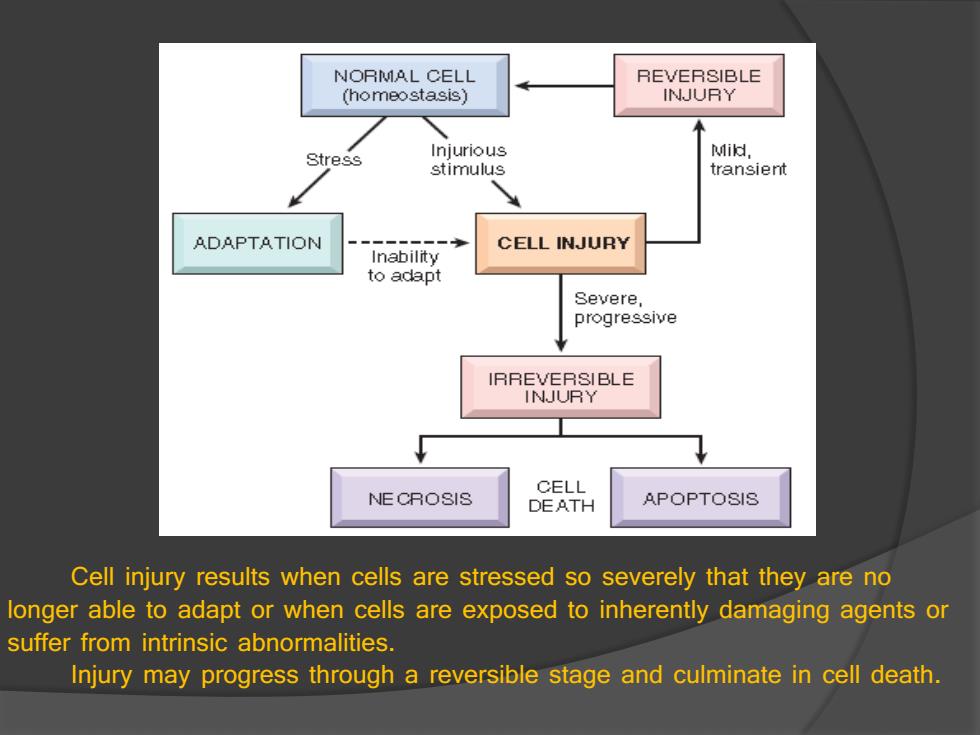
NORMAL CELL REVERSIBLE (homeostasis) INJURY Stress Injurious Mi以, stimulus transient ADAPTATION CELL INJURY Inability to adapt Severe, progressive IRREVERSIBLE INJURY CELL NE CROSIS DEATH APOPTOSIS Cell injury results when cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or when cells are exposed to inherently damaging agents or suffer from intrinsic abnormalities. Injury may progress through a reversible stage and culminate in cell death
Cell injury results when cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or when cells are exposed to inherently damaging agents or suffer from intrinsic abnormalities. Injury may progress through a reversible stage and culminate in cell death

CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia) o Chemical Agents o Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Factors oNutritional Imbalances o Physical Agents o Aging
CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia) Chemical Agents Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Factors Nutritional Imbalances Physical Agents Aging

THE MORPHOLOGY OF CELL AND TISSUE INJURY E.g. myocardial cells Reversible i Irreversible cell injury cell injury Ultrastructural Light changes microscopic √noncontractile changes Cell Cell death after 1 to 2 function minutes of ischemia \Grass morphologic dead after 2 to changes 3 hours by electron microscopy by light DURATION OF INJURY microscopy for 6 to 12 hours The relationship among cellular function,cell death,and the morphologic changes of cell injury
THE MORPHOLOGY OF CELL AND TISSUE INJURY The relationship among cellular function, cell death, and the morphologic changes of cell injury. E.g. myocardial cells noncontractile after 1 to 2 minutes of ischemia dead after 2 to 3 hours by electron microscopy by light microscopy for 6 to 12 hours

>Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue Hydropic degeneration Fatty change Hyaline degeneration Myxoid degeneration Deposition of amyloid Intracellular accumulation of glycogen Deposition of pathological pigments
►Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue Hydropic degeneration Fatty change Hyaline degeneration Myxoid degeneration Deposition of amyloid Intracellular accumulation of glycogen Deposition of pathological pigments