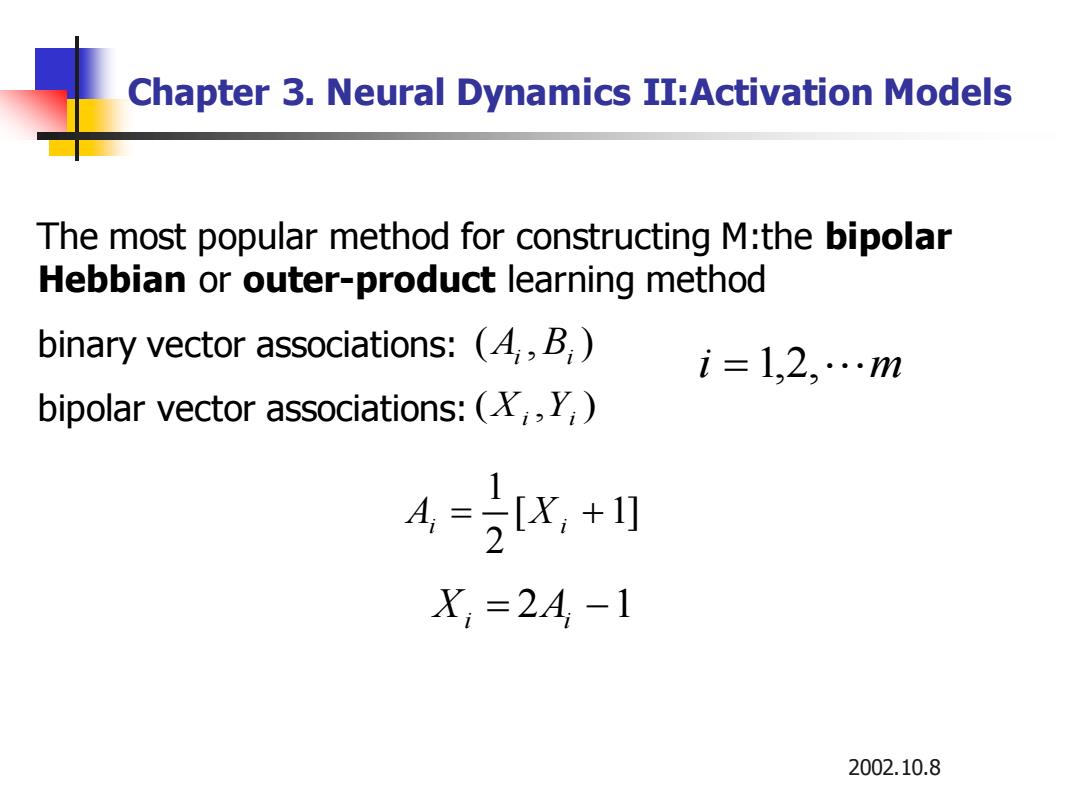
Chapter 3.Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models The most popular method for constructing M:the bipolar Hebbian or outer-product learning method binary vector associations:(4,,B i=1,2,…m bipolar vector associations:(XY 4=K,+ X,=2A-1 2002.10.8
2002.10.8 Chapter 3. Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models The most popular method for constructing M:the bipolar Hebbian or outer-product learning method binary vector associations: bipolar vector associations: ( , ) Ai Bi ( , ) Xi Yi i = 1,2, m [ 1] 2 1 Ai = Xi + Xi = 2Ai −1
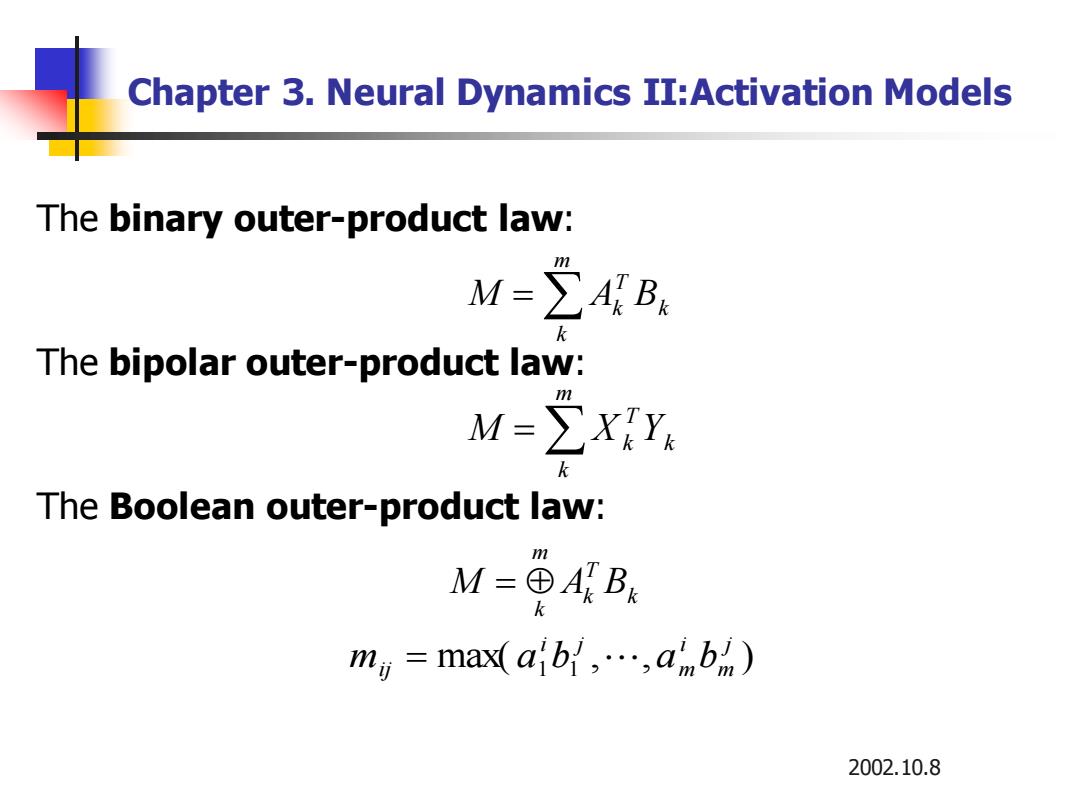
Chapter 3.Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models The binary outer-product law: M=∑AB The bipolar outer-product law: M=∑XY k The Boolean outer-product law: M=田ABE m,=max a'b1,…,anbh) 2002.10.8
2002.10.8 Chapter 3. Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models The bipolar outer-product law: = m k k T M X k Y The binary outer-product law: = m k k T M Ak B The Boolean outer-product law: k T k m k M = A B max( , , ) 1 1 j m i m i j mij = a b a b
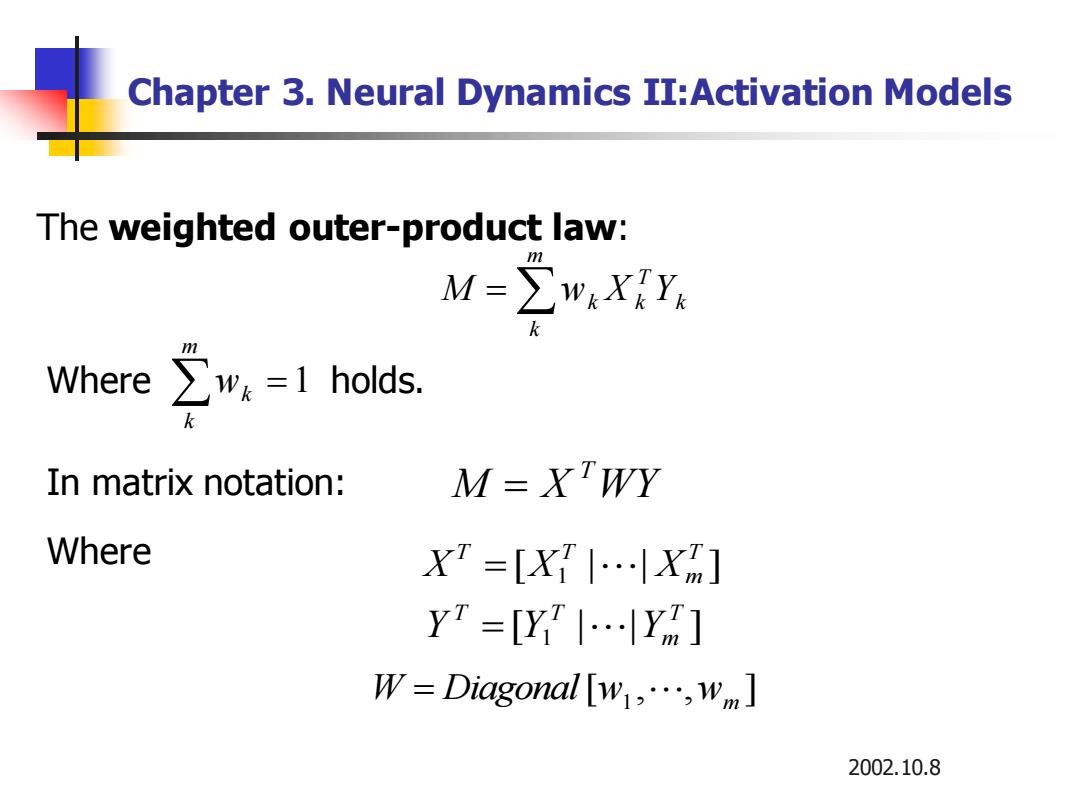
Chapter 3.Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models The weighted outer-product law: m M=∑wXiY Where∑w&=1 holds. In matrix notation: M=XWY Where XT=[X.Xm] Yr=[YI…lYm] W=Diagonal[w1,…,wm] 2002.10.8
2002.10.8 Chapter 3. Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models The weighted outer-product law: In matrix notation: Where holds. = m k k T M wk X k Y = m k wk 1 M X WY T = Where [ | | ] 1 T m T T X = X X [ , , ] W = Diagonal w1 wm [ | | ] 1 T m T T Y = Y Y
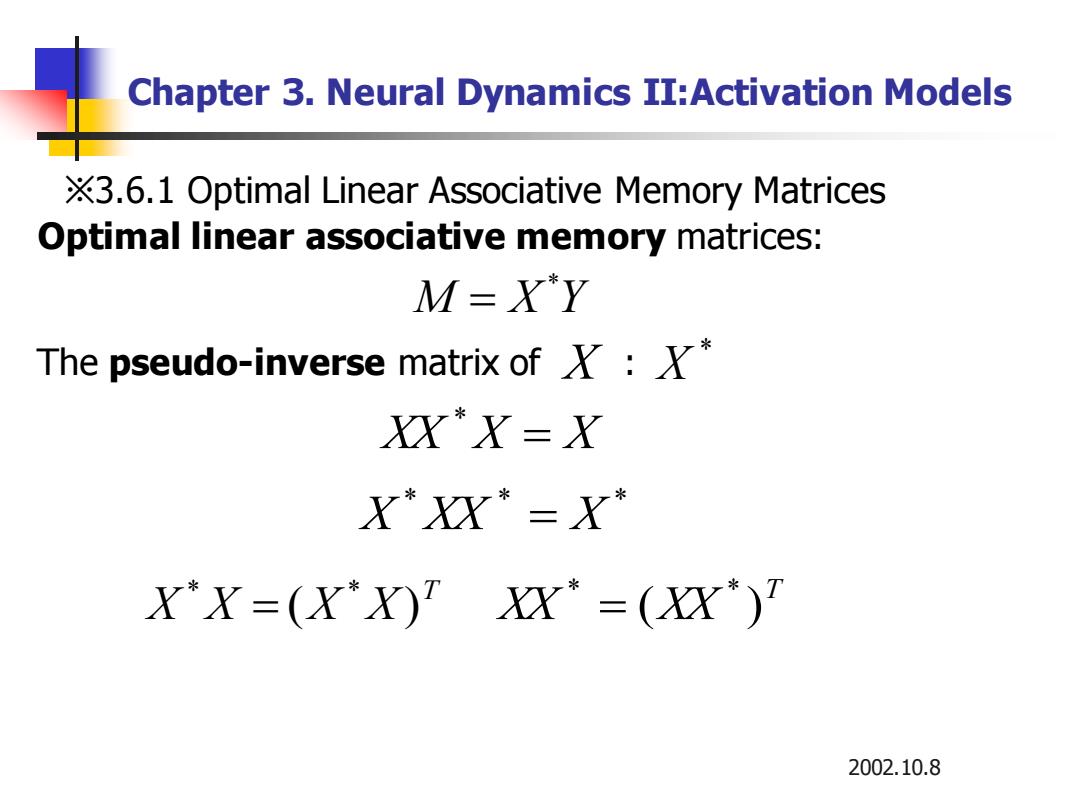
Chapter 3.Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models X3.6.1 Optimal Linear Associative Memory Matrices Optimal linear associative memory matrices: M=XY The pseudo-inverse matrix of: XYY-X X'XX=X X'Y-(XX XX=(XX') 2002.10.8
2002.10.8 Chapter 3. Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models Optimal linear associative memory matrices: M X Y * = XX X = X * * * * X XX = X T X X (X X) * * = T XX (XX ) * * = The pseudo-inverse matrix of X : * X ※3.6.1 Optimal Linear Associative Memory Matrices
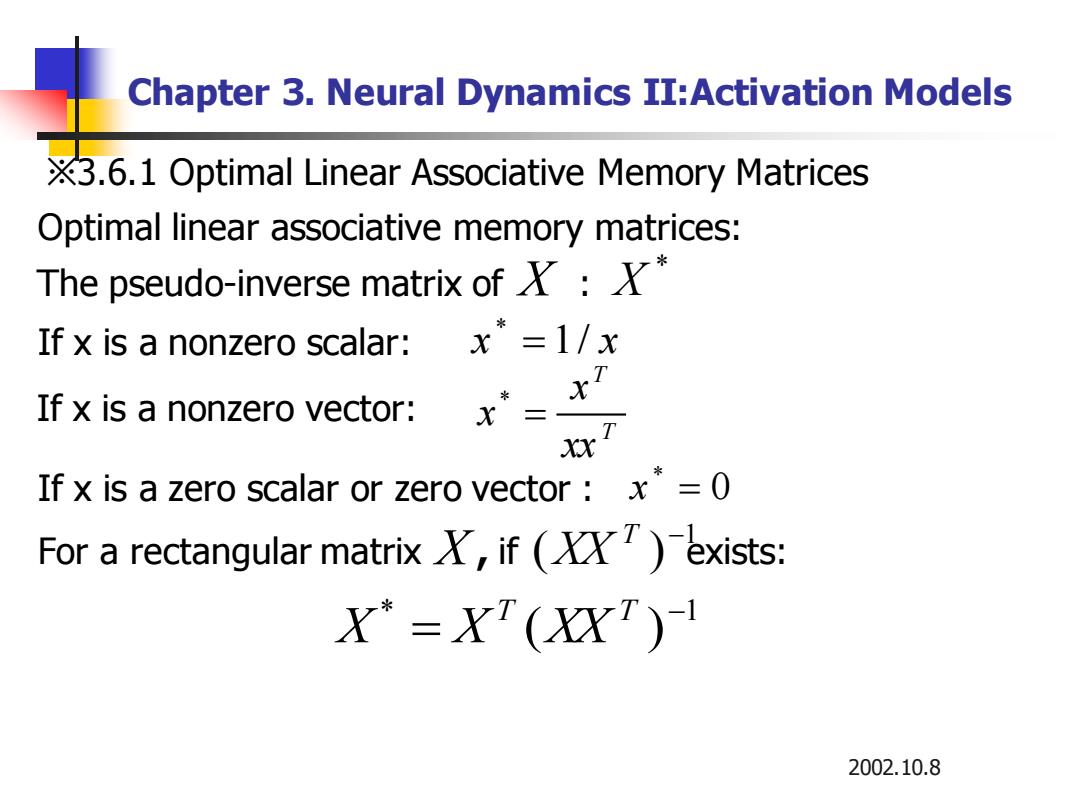
Chapter 3.Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models X3.6.1 Optimal Linear Associative Memory Matrices Optimal linear associative memory matrices: The pseudo-inverse matrix of: If x is a nonzero scalar:x=1/x If x is a nonzero vector: X If x is a zero scalar or zero vector x*=0 For a rectangular matrix X,if ()exists: X"=X(XX) 2002.10.8
2002.10.8 Chapter 3. Neural Dynamics II:Activation Models ※3.6.1 Optimal Linear Associative Memory Matrices Optimal linear associative memory matrices: The pseudo-inverse matrix of X : * X If x is a nonzero scalar: x 1/ x * = If x is a zero scalar or zero vector : For a rectangular matrix , if exists: 0 * x = If x is a nonzero vector: T T xx x x = * 1 ( ) T − XX * 1 ( ) − = T T X X XX X